Loganin
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Loganin | ||
|---|---|---|
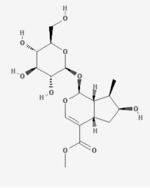 | ||
| IUPAC name (1S,4aS,6S,7R,7aS)-6-Hydroxy-7-methyl-1-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-1,4a,5,6,7,7a-hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyran-4-carboxylate | ||
| Other names Loganoside | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 18524-94-2 | |
| PubChem | 87691 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@H]1[C@H](C[C@H]2[C@@H]1[C@@H](OC=C2C(=O)OC)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O)O)O)O|Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C17H26O10 | |
| Molar mass | 390.38 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
Loganin is a iridoid glycoside isolated from Alstonia boonei,[1] a medicinal tree of West Africa.
References
- ↑ Adotey, John Prosper Kwaku; Adukpo, Genevieve Etornam; Opoku Boahen, Yaw; Armah, Frederick Ato (2012). "A Review of the Ethnobotany and Pharmacological Importance of Alstonia boonei De Wild (Apocynaceae)". ISRN Pharmacology 2012: 1. doi:10.5402/2012/587160.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.