Lifting scheme

The lifting scheme is a technique for both designing wavelets and performing the discrete wavelet transform. Actually it is worthwhile to merge these steps and design the wavelet filters while performing the wavelet transform. This is then called the second generation wavelet transform. The technique was introduced by Wim Sweldens.
The discrete wavelet transform applies several filters separately to the same signal. In contrast to that, for the lifting scheme the signal is divided like a zipper. Then a series of convolution-accumulate operations across the divided signals is applied.
Basics
The basic idea of lifting is the following:
If a pair of filters  is complementary,
that is it allows for perfect reconstruction,
then for every filter
is complementary,
that is it allows for perfect reconstruction,
then for every filter  the pair
the pair 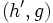 with
with 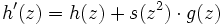 allows for perfect reconstruction, too.
Of course, this is also true for every pair
allows for perfect reconstruction, too.
Of course, this is also true for every pair 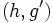 of the form
of the form  .
The converse is also true:
If the filterbanks
.
The converse is also true:
If the filterbanks  and
and 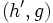 allow for perfect reconstruction,
then there is a unique filter
allow for perfect reconstruction,
then there is a unique filter  with
with 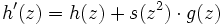 .
.
Each such transform of the filterbank (or the respective operation in a wavelet transform) is called a lifting step. A sequence of lifting steps consists of alternating lifts, that is, once the lowpass is fixed and the highpass is changed and in the next step the highpass is fixed and the lowpass is changed. Successive steps of the same direction can be merged.
Properties
- Perfect reconstruction
- Every transform by the lifting scheme can be inverted.
- Every perfect reconstruction filter bank can be decomposed into lifting steps by the Euclidean algorithm.
- That is, "lifting decomposable filter bank" and "perfect reconstruction filter bank" denotes the same.
- Every two perfect reconstructable filter banks can be transformed into each other by a sequence of lifting steps. (If
 and
and  are polyphase matrices with the same determinant, the lifting sequence from
are polyphase matrices with the same determinant, the lifting sequence from  to
to  , is the same as the one from the lazy polyphase matrix
, is the same as the one from the lazy polyphase matrix  to
to 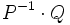 .)
.) - Speedup by a factor of two. This is only possible because lifting is restricted to perfect reconstruction filterbanks. That is, lifting somehow squeezes out redundancies caused by perfect reconstructability.
- In place: The transformation can be performed immediately in the memory of the input data with only constant memory overhead.
- Non-linearities: The convolution operations can be replaced by any other operation. For perfect reconstruction only the invertibility of the addition operation is relevant. This way rounding errors in convolution can be tolerated and bit-exact reconstruction is possible. However the numeric stability may be reduced by the non-linearities. This must be respected if the transformed signal is processed like in lossy compression.
Although every reconstructable filter bank can be expressed in terms of lifting steps, a general description of the lifting steps is not obvious from a description of a wavelet family. However, for instance for simple cases of the Cohen-Daubechies-Feauveau wavelet, there is an explicit formula for their lifting steps. (See the respective article)
Generalized Lifting
The Generalized Lifting Scheme is a derivative of the Lifting Scheme, in which the addition and subtraction operations are absorbed into the update and prediction steps, respectively. These steps can be any (invertible) mapping, leading to a more general lifting scheme.
Applications
- Wavelet transform with integer values: WAILI
- Fourier transform with bit-exact reconstruction: Soontorn Oraintara, Ying-Jui Chen, Truong Q. Nguyen: Integer Fast Fourier Transform
- Construction of wavelets with a required number of smoothness factors and vanishing moments
- Construction of wavelets matched to a given pattern: Henning Thielemann: Optimally matched wavelets
- Implementation of the Discrete Wavelet Transform in JPEG 2000
See also
- The Feistel scheme in cryptology uses much the same idea of dividing data and alternating function application with addition. Both in the Feistel scheme and the Lifting scheme this is used for symmetric en- and decoding.
External links
- A comprehensive introduction to the Fast Lifting Wavelet Transform
- Ingrid Daubechies, Wim Sweldens: Factoring Wavelet Transforms into Lifting Steps
- Lifting wavelet Transform steps :
- The Lifting Scheme: A Construction of Second Generation Wavelets
- Introduction to Wavelets (with detailed coverage of lifting scheme) by René Puchinger