Lift (mathematics)
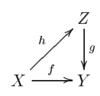
 h = f.
h = f.
A basic example in topology is lifting a path in one space to a path in a covering space. Consider, for instance, mapping opposite points on a sphere to the same point, a continuous map from the sphere covering the projective plane. A path in the projective plane is a continuous map from the unit interval, [0,1]. We can lift such a path to the sphere by choosing one of the two sphere points mapping to the first point on the path, then maintain continuity. In this case, each of the two starting points forces a unique path on the sphere, the lift of the path in the projective plane. Thus in the category of topological spaces with continuous maps as morphisms, we have
Lifts are ubiquitous; for example, the definition of fibrations (see homotopy lifting property) and the valuative criteria of separated and proper maps of schemes are formulated in terms of existence and (in the last case) unicity of certain lifts.
![{\begin{aligned}f\colon &[0,1]\to {\mathbb {RP}}^{2},&\qquad &{\text{(projective plane path)}}\\g\colon &S^{2}\to {\mathbb {RP}}^{2},&\qquad &{\text{(covering map)}}\\h\colon &[0,1]\to S^{2}.&\qquad &{\text{(sphere path)}}\end{aligned}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/b/2/c/e/b2cea3ca30c8665d50c9f14305c616da.png)