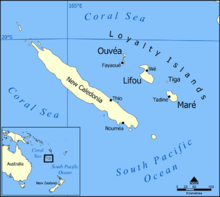
Lifou Island
 map of Lifou, central islands of loyalty islands, New Caledonia dependency, oceania | |
 | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Pacific Ocean |
| Coordinates | 20°54′S 167°12′E / 20.9°S 167.2°ECoordinates: 20°54′S 167°12′E / 20.9°S 167.2°E |
| Archipelago | Loyalty Islands |
| Area | 1,197.1 km2 (462.2 sq mi) |
| Length | 81 km (50.3 mi) |
| Width | 16–24 km (9.9–14.9 mi) |
| Country | |
|
France | |
| Overseas departments and territories of France |
|
| Commune | Lifou |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 10151 (as of 2004) |
| Density | 8.48 /km2 (21.96 /sq mi) |
| Ethnic groups | Kanaks 96.9%, Europeans 2.6%, Polynesians 0.1%, Other 0.4% |
Lifou Island or Drehu in the local language is the largest, most populous and most important island of the Loyalty Islands, in the archipelago of New Caledonia, an overseas territory of France in the Pacific Ocean. With a total area of 1,207 square kilometers Lifou is located east of Australia at 20°54′S 167°12′E / 20.9°S 167.2°E.
Background
First discovered by the Frenchman Dumont d’Urville in 1857,
[1] it was soon visited by whalers and traders Lifou and became a destination for Protestant and Catholic Missionaries out to save the local populations souls. In 1864 the islands were annexed by France who in turn established it as an Aboriginal Reserve[2] as it was not believed suitable for extensive colonialization.
Administration
The island is part of the commune (municipality) of Lifou, in the Islands Province of New Caledonia. The administrative center of the commune is located at Wé, on the east side of Lifou Island at Chateaubriand Bay. The local currency is the CFP Franc (French Pacific Franc).[3]
Geography

Irregular in shape, Lifou Island is 81 km (50 mi) long and 16 to 24 km (10 to 15 miles) wide. The island is flat with no hills or rivers, but has abundant vegetation, dense interior jungles, fertile soils, terraced cliffs and breath taking reefs and corals.
Lifou Island is a former coral atoll that was part of a submerged volcano. Nearly 2 million years ago, the island was uplifted to its present shape and elevation, today it sits at a mere 60m above sea level at its highest point. Since there are no rivers on Lifou, the water comes from rain that seeps through the calcareous soil and forms freshwater ponds.
Food
With its rich Pacific waters fish including crab, lobster, turtle are in abundance, along with typical raised animals such as goat, pig and chicken. Crops include coconut, banana, taro, sweet potato, yam and vanilla. While the French introduction of coffee stayed on.
Economy
Tourism is a major industry on the island. Chief exports include copra, rubber, vanilla and sugarcane.
Culture
The term Kanak[4] is used for natives of the islands and their native language of the island is Drehu, with people descending from Melanesians and Polynesians.[3] With a total of 19 different tribes inhabiting the three Loyalty Islands, six of which are on Lifou.
The current traditional high chief of the island is Evanes Boula, who is chief of 13 of the three islands tribes,[5] succeeding Henri Boula on the 13th June 1999.
References
- ↑ "Lifou, an island of many faces". www.iles-loyaute.com. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ↑ "Discover Lifou". en.newcaledonia-tv.com. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Lifou, Loyalty Island". www.royalcaribbean.com. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ↑ "New Caledonia". www.everyculture.com/. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
- ↑ "LÖSSI (High Chiefdom)". members.iinet.net.au. Retrieved 25 September 2012.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Lifou. |