Liebenburg is a municipality in the district of Goslar, in Lower Saxony, Germany.
Geography
The municipal area is situated north of the Harz mountain range, within the eastern Salzgitter Hills of the Innerste Uplands. It borders on the district capital Goslar, approx. 12 km (7.5 mi) in the south; the adjacent municipalities in the north are Salzgitter-Bad and Schladen in Wolfenbüttel District.
Subdivisions
The municipality comprises Liebenburg proper (with 2,729 inhabitants) and the following nine villages, which were incorporated on 1 July 1972:
- Dörnten (1,475 inhabitants)
- Groß Döhren (1,134)
- Heißum (384)
- Klein Döhren (499)
- Klein Mahner (372)
- Neuenkirchen (268)
- Ostharingen (314)
- Othfresen (2,302) with Heimerode and Posthof
- Upen (448)
History

Preserved walls of Liebenburg Castle
From 1292 to 1302, Liebenburg Castle was erected by the Hildesheim bishop Siegfried II of Querfurt where his bishopric bordered on the lands of the Dukes of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel.
Pawned to the citizens of Braunschweig from 1366, it was seized by Duke Henry V the Younger of Brunswick-Wolfebüttel during the Hildesheim Diocesan Feud in 1523. The duke in turn lost it to the Protestant Schmalkaldic League, whose troops campaigned the Brunswick lands from 1542 until 1547. During the Thirty Years' War, the stronghold was used as headquarters by Albrecht von Wallenstein in 1625, it was occupied by Swedish troops in 1633 and reconquered by Imperial forces in 1641.
The heavily damaged castle was restored to Hildesheim, while day laborers and craftsmen lived within the walls. The Hildesheim prince-bishops promoted the settlement of Catholic families. The castle itself was partly rebuilt in a Baroque style by the order of Bishop Clemens August of Bavaria until the outbreak of the Seven Years' War in 1756. After the bishopric was finally secularised in 1802, Liebenburg fell to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814.
Demographics
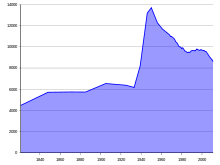
Population statistics
| Year |
Inhabitants |
|---|
| 1821 |
4,464 |
| 1848 |
5,710 |
| 1871 |
5,737 |
| 1885 |
5,727 |
| 1905 |
6,535 |
| 1925 |
6,375 |
|
| Year |
Inhabitants |
|---|
| 1933 |
6,167 |
| 1939 |
8,206 |
| 1946 |
13,208 |
| 1950 |
13,700 |
| 1956 |
12,279 |
|
| Year |
Inhabitants |
|---|
| 1961 |
11,687 |
| 1968 |
11,143 |
| 1970 |
10,982 |
| 1975 |
10,405 |
| 1980 |
9,851 |
|
| Year |
Inhabitants |
|---|
| 1985 |
9,502 |
| 1990 |
9,655 |
| 1995 |
9,803 |
| 2000 |
9,693 |
| 2005 |
9,431 |
|
Politics
Seats in the municipal assembly (Gemeinderat) as of 2011 council elections:
External links
References