Levoamphetamine
| Levoamphetamine | |
|---|---|
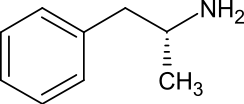 | |
| Systematic name (2R)-1-Phenylpropan-2-amine[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 156-34-3 |
| PubChem | 32893 |
| ChemSpider | 30477 |
| EC number | 205-850-8 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:42724 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL19393 |
| Beilstein Reference | 2432739 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1125855 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:C[C@@H](N)Cc1ccccc1C[C@@H](N)CC1=CC=CC=C1|Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C9H13N |
| Molar mass | 135.21 g mol−1 |
| log P | 1.789 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Routes of administration |
Oral |
| Legal status |
|
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Levoamphetamine (also levamfetamine, (R)-amphetamine or (−)-amphethamine) is a psychostimulant known to increase wakefulness and concentration in association with decreased appetite and fatigue. Levoamphetamine is the levorotatory stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule.
Chemistry
Levoamphetamine is the levorotary stereoisomer of the amphetamine molecule. The amphetamine racemate contains two stereoisomers, dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine, both exhibiting amphetaminergic (amphetamine-like) effects.
Formulations
Adderall
The drug Adderall contains 25% levoamphetamine and 75% dextroamphetamine.[2]
Benzedrine
Benzedrine was a racemic (1:1 racemate) mixture of dextroamphetamine and levoamphetamine introduced in the United States delivered by an inhaler in 1933[3] for decongestant uses. Benzedrine was converted into tablet form in 1938 after it was discovered that amphetamine could treat narcolepsy and behavioral disorders.
See also
References
- ↑ "Amphetamine - PubChem Public Chemical Project". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 8 August 2005. Descriptors Computed from Structure. Retrieved 26 September 2011.
- ↑ Physicians' Desk Reference, 2009, pg 3012
- ↑ http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/benzedrine
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||