Left upper quadrant
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
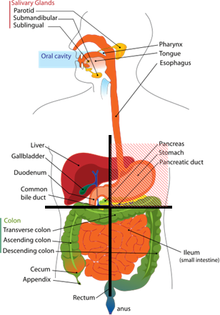
A Graphic showing Contents of Left upper quadrant
The Left upper quadrant of the human abdomen, often abbreviated as LUQ, is used to refer to a portion of the abdomen that allows doctors to localise pain and tenderness, scars, lumps and other items of interest. The LUQ extends from the median plane to the left of the patient, and from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage.
The term is not used in comparative anatomy, since most other animals do not stand erect. The equivalent term for animals is 'left anterior quadrant'.
Important organs
- Stomach
- Spleen
- Left lobe of liver
- Body of pancreas
- Left kidney and adrenal gland
- Splenic flexure of colon
- Parts of transverse and descending colon
Clinical significance
The LUQ may be painful and/or tender in such conditions as appendicitis, in case of intestinal malrotation
External links
| |||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
