Le Portel
| Le Portel | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Le Portel | |
|
Location within Nord-Pas-de-Calais region 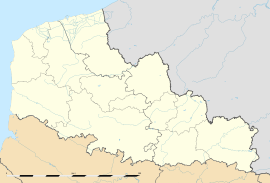 Le Portel | |
| Coordinates: 50°42′27″N 1°34′28″E / 50.7075°N 1.5744°ECoordinates: 50°42′27″N 1°34′28″E / 50.7075°N 1.5744°E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nord-Pas-de-Calais |
| Department | Pas-de-Calais |
| Arrondissement | Boulogne-sur-Mer |
| Canton | Le Portel |
| Intercommunality | Communauté d'agglomération du Boulonnais |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2008–2014) | Laurent Feutry |
| Area | |
| • Land1 | 3.85 km2 (1.49 sq mi) |
| Population (2006) | |
| • Population2 | 10,253 |
| • Population2 Density | 2,700/km2 (6,900/sq mi) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 62667 / 62480 |
| Elevation |
0–59 m (0–194 ft) (avg. 27 m or 89 ft) |
|
1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km² (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. 2 Population without double counting: residents of multiple communes (e.g., students and military personnel) only counted once. | |
Le Portel is a commune in the Pas-de-Calais department in the Nord-Pas-de-Calais region of France.
Geography
Le Portel is a tourist, fishing and light industrial town situated about 2 miles (3.2 km) southwest of Boulogne town centre, at the junction of the D236 and D119 roads. It has a beach and the white cliffs of the English coast can be seen across the sea on clear days.
History
Le Portel translates as "the little port." The original Le Portel was a hamlet east of the town of Outreau. It became an independent municipality on June 13, 1856 by an imperial decree of Napoleon III.
In the 19th century, flint tools were discovered in the centre of the village, by the river near the Hamel Bridge, evidence of the long occupation of the site. A Gallo-Roman cemetery has been excavated in the hamlet of Châtillon.
Of agricultural origin, it grew rapidly during the 19th century because of fishing, along with the nearby port of Boulogne-sur-Mer. Sailors of Portel were as numerous as those of Boulogne before World War I. In 1841, two Le Portel sailors were on the ship Belle Poule, that brought back the remains of Napoleon.
During the Second World War, on 8 and 9 September 1943, Le Portel suffered as part of Operation Fortitude, a diversionary manoeuvre by the Allies to fool the Germans into believing the possibility of a landing on the English Channel. The bombings, which destroyed nearly 90% of homes, also killed more than 500 people. On 12 August 1944, Charles de Gaulle was at Le Portel for its liberation. The town received the Croix de guerre with silver star for its sacrifice.
Population
| Year | 1962 | 1968 | 1975 | 1982 | 1990 | 1999 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population | 11,198 | 11,379 | 11,112 | 10,984 | 10,615 | 10,720 | 10,253 |
| From the year 1962 on: No double counting—residents of multiple communes (e.g. students and military personnel) are counted only once. | |||||||
Places of interest
- Two twentieth century churches.
- Fort de l'Heurt, built from 1803/1805 by order of Napoleon Bonaparte.
- Fort d'Alprech, built in 1883.
- The lighthouse.
- The Fort de Couppes 1883 .
- The Atlantic Wall German fortress.
Notable people
- Alfred Desenclos, composer, was born here.
- Lucien Leduc, football player, was born here.
Twin towns
-
 Portel-des-Corbières, France
Portel-des-Corbières, France -
 Stockelsdorf, Germany
Stockelsdorf, Germany -
 Kawara, Burkina Faso
Kawara, Burkina Faso
See also
References
External links
- Official town website (French)
- Official Tourist website of Le Portel Plage (French)
- Official website: Tourism in Boulogne and in the Boulonnais region
- Association de Sauvegarde du Fort de l'Heurt et du Patrimoine Portelois (French)
- Web site on the history of Le Portel Plage (French)
-

Le Portel Plage
-
Statue of the Madonna
-
The beach and in the distance, Fort de l'Heurt
-

Town hall
-
The fort de Couppes
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Le Portel. |


