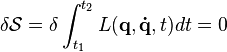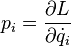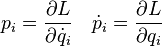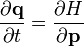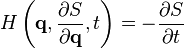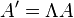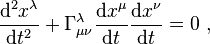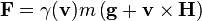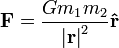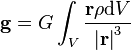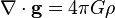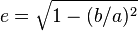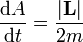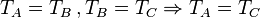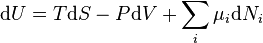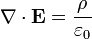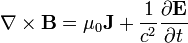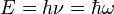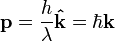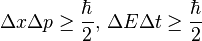Laws of science
The laws of science or scientific laws are statements that describe, predict, and perhaps explain why, a range of phenomena behave as they appear to in nature.[1] The term "law" has diverse usage in many cases: approximate, accurate, broad or narrow theories, in all natural scientific disciplines (physics, chemistry, biology, geology, astronomy etc.). An analogous term for a scientific law is a principle.
Scientific laws:
- summarize a large collection of facts determined by experiment into a single statement,
- can usually be formulated mathematically as one or several statements or equation, or at least stated in a single sentence, so that it can be used to predict the outcome of an experiment, given the initial, boundary, and other physical conditions of the processes which take place,
- are strongly supported by empirical evidence - they are scientific knowledge that experiments have repeatedly verified (and never falsified). Their accuracy does not change when new theories are worked out, but rather the scope of application, since the equation (if any) representing the law does not change. As with other scientific knowledge, they do not have absolute certainty like mathematical theorems or identities, and it is always possible for a law to be overturned by future observations.
- are often quoted as a fundamental controlling influence rather than a description of observed facts, e.g. "the laws of motion require that..."
Laws differ from hypotheses and postulates, which are proposed during the scientific process before and during validation by experiment and observation. These are not laws since they have not been verified to the same degree and may not be sufficiently general, although they may lead to the formulation of laws. A law is a more solidified and formal statement, distilled from repeated experiment.
Although the nature of a scientific law is a question in philosophy and although scientific laws describe nature mathematically, scientific laws are practical conclusions reached by the scientific method; they are intended to be neither laden with ontological commitments nor statements of logical absolution.
Fundamentally, all scientific laws follow from physics, laws which occur in other sciences ultimately follow from physical laws. Often, from mathematically fundamental viewpoints, universal constants emerge from scientific laws.
Conservation laws
Conservation and symmetry
Most significant laws in science are conservation laws. These fundamental laws follow from homogeneity of space, time and phase, in other words symmetry.
- Noether's theorem: Any quantity which has a continuous differentiable symmetry in the action has an associated conservation law.
- Conservation of mass was the first law of this type to be understood, since most macroscopic physical processes involving masses, for example collisions of massive particles or fluid flow, provide the apparent belief that mass is conserved. Mass conservation was observed to be true for all chemical reactions. In general this is only approximative, because with the advent of relativity and experiments in nuclear and particle physics: mass can be transformed into energy and vice versa, so mass is not always conserved, but part of the more general conservation of mass-energy.
- Conservation of energy, momentum and angular momentum for isolated systems can be found to be symmetries in time, translation, and rotation.
- Conservation of charge was also realized since charge has never been observed to be created or destroyed, and only found to move from place to place.
Continuity and transfer
Conservation laws can be expressed using the general continuity equation (for a conserved quantity) can be written in differential form as:
where ρ is some quantity per unit volume, J is the flux of that quantity (change in quantity per unit time per unit area). Intuitively, the divergence (denoted ∇•) of a vector field is a measure of flux diverging radially outwards from a point, so the negative is the amount piling up at a point, hence the rate of change of density in a region of space must be the amount of flux leaving or collecting in some region (see main article for details). In the table below, the fluxes, flows for various physical quantities in transport, and their associated continuity equations, are collected for comparison.
Physics, conserved quantity Conserved quantity q Volume density ρ (of q) Flux J (of q) Equation Hydrodynamics, fluids m = mass (kg) ρ = volume mass density (kg m−3) ρ u, where<br/ > u = velocity field of fluid (m s−1)
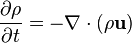
Electromagnetism, electric charge q = electric charge (C) ρ = volume electric charge density (C m−3) J = electric current density (A m−2) 
Thermodynamics, energy E = energy (J) u = volume energy density (J m−3) q = heat flux (W m−2) 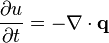
Quantum mechanics, probability P = (r, t) = ∫|Ψ|2d3r = probability distribution ρ = ρ(r, t) = |Ψ|2 = probability density function (m−3),
Ψ = wavefunction of quantum system
j = probability current/flux 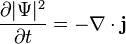
More general equations are the convection–diffusion equation and Boltzmann transport equation, which have their roots in the continuity equation.
Laws of classical mechanics
Principle of least action
All of classical mechanics, including Newton's laws, Lagrange's equations, Hamilton's equations, etc., can be derived from this very simple principle:
where 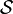 is the action; the integral of the Lagrangian
is the action; the integral of the Lagrangian
of the physical system between two times t1 and t2. The kinetic energy of the system is T (a function of the rate of change of the configuration of the system), and potential energy is V (a function of the configuration and its rate of change). The configuration of a system which has N degrees of freedom is defined by generalized coordinates q = (q1, q2, ... qN).
There are generalized momenta conjugate to these coordinates, p = (p1, p2, ..., pN), where:
The action and Lagrangian both contain the dynamics of the system for all times. The term "path" simply refers to a curve traced out by the system in terms of the generalized coordinates in the configuration space, i.e. the curve q(t), parameterized by time (see also parametric equation for this concept).
The action is a functional rather than a function, since it depends on the Lagrangian, and the Lagrangian depends on the path q(t), so the action depends on the entire "shape" of the path for all times (in the time interval from t1 to t2). Between two instants of time, there are infinitely many paths, but one for which the action is stationary (to first order) is the true path. The stationary value for the entire continuum of Lagrangian values corresponding to some path, not just one value of the Lagrangian, is required (in other words its not as simple as "differentiating a function and setting it to zero, then solving the equations to find the points of maxima and minima etc", rather this idea is applied to the entire "shape" of the function, see calculus of variations for more details on this procedure).[2]
Notice L is not the total energy E of the system due to the difference, rather than the sum:
The following[3][4] general approaches to classical mechanics are summarized below in the order of establishment. They are equivalent formulations, Newton's is very commonly used due to simplicity, but Hamilton's and Lagrange's equations are more general, and their range can extend into other branches of physics with suitable modifications.
Laws of motion Principle of least action: 
The Euler-Lagrange equations are: Using the definition of generalized momentum, there is the symmetry:
Hamilton's equations The Hamiltonian as a function of generalized coordinates and momenta has the general form:
Hamilton-Jacobi equation Newton's laws They are low-limit solutions to relativity. Alternative formulations of Newtonian mechanics are Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics.
The laws can be summarized by two equations (since the 1st is a special case of the 2nd, zero resultant acceleration):
where p = momentum of body, Fij = force on body i by body j, Fij = force on body j by body i.
For a dynamical system the two equations (effectively) combine into one:
in which FE = resultant external force (due to any agent not part of system). Body i does not exert a force on itself.
From the above, any equation of motion in classical mechanics can be derived.
- Corollaries in mechanics
- Corollaries in fluid mechanics
Equations describing fluid flow in various situations can be derived, using the above classical equations of motion and often conservation of mass, energy and momentum. Some elementary examples follow.
- Archimedes' principle
- Bernoulli's principle
- Poiseuille's law
- Stoke's law
- Navier–Stokes equations
- Faxén's law
Laws of gravitation and relativity
Modern laws
Postulates of special relativity are not "laws" in themselves, but assumptions of their nature in terms of relative motion.
Often two are stated as "the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames" and "the speed of light is constant". However the second is redundant, since the speed of light is predicted by Maxwell's equations. Essentially there is only one.
The said posulate leads to the Lorentz transformations – the transformation law between two frame of references moving relative to each other. For any 4-vector
this replaces the Galilean transformation law from classical mechanics. The Lorentz transformations reduce to the Galilean transformations for low velocities much less than the speed of light c.
The magnitudes of 4-vectors are invariants - not "conserved", but the same for all inertial frames (i.e. every observer in an inertial frame will agree on the same value), in particular if A is the four-momentum, the magnitude can derive the famous invariant equation for mass-energy and momentum conservation (see invariant mass):
in which the (more famous) mass-energy equivalence E = mc2 is a special case.
General relativity is governed by the Einstein field equations, which describe the curvature of space-time due to mass-energy equivalent to the gravitational field. Solving the equation for the geometry of space warped due to the mass distribution gives the metric tensor. Using the geodesic equation, the motion of masses falling along the geodesics can be calculated.
- Gravitomagnetism
In a relatively flat spacetime due to weak gravitational fields, gravitational analogues of Maxwell's equations can be found; the GEM equations, to describe an analogous gravitomagnetic field. They are well established by the theory, and experimental tests form ongoing research.[5]
Einstein field equations (EFE): where Λ = cosmological constant, Rμν = Ricci curvature tensor, Tμν = Stress-energy tensor, gμν = metric tensor
Geodesic equation: where Γ is a Christoffel symbol of the second kind, containing the metric.
GEM Equations If g the gravitational field and H the gravitomagnetic field, the solutions in these limits are:
where ρ is the mass density and J is the mass current density or mass flux.
In addition there is the gravitomagnetic Lorentz force: where m is the rest mass of the particlce and γ is the Lorentz factor.
Classical laws
Kepler's Laws, though originally discovered from planetary observations (also due to Tycho Brahe), are true for any central forces.[6]
Newton's law of universal gravitation: For two point masses:
For a non uniform mass distribution of local mass density ρ (r) of body of Volume V, this becomes:
Gauss' law for gravity: An equivalent statement to Newton's law is:
Kepler's 1st Law: Planets move in an ellipse, with the star at a focus where
is the eccentricity of the elliptic orbit, of semi-major axes a (planet aphelion) and semi-minor axes b (planet perihelion). This equation in itself is nothing physically fundamental; simply the polar equation of an ellipse in vector form, in which the pole (origin of polar coordinate system) is positioned at a focus of the ellipse, centred on the central star.
Kepler's 2nd Law: equal areas are swept out in equal times (area bounded by two radial distances and the orbital circumference): where L is the orbital angular momentum of the particle (i.e. planet) of mass m about the focus of orbit,
Kepler's 3rd Law: The square of the orbital time period T is proportional to the mean radius a: where M is the mass of the central body (i.e. star).
Thermodynamics
Laws of thermodynamics First law of thermodynamics: The change in internal energy dU in a closed system is accounted for entirely by the heat δQ absorbed by the system and the work δW done by the system: Second law of thermodynamics: There are many statements of this law, perhaps the simplest is "the entropy of isolated systems never decreases",
meaning reversible changes have zero entropy change, irreversible process are positive, and impossible process are negative.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics: If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they are in thermal equilibrium with one another. - As the temperature T of a system approaches absolute zero, the entropy S approaches a minimum value C: as T → 0, S → C.
For homogeneous systems the first and second law can be combined into the Fundamental thermodynamic relation: Onsager reciprocal relations: sometimes called the Fourth Law of Thermodynamics 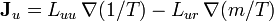 ;
;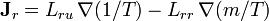 .
.
- Newton's law of cooling
- Fourier's law
- Ideal gas law, combines a number of separately developed gas laws;
- Boyle's law
- Charles's law
- Gay-Lussac's law
- Avogadro's law, into one)
- now improved by other equations of state
- Dalton's law (of partial pressures)
- Boltzmann equation
- Carnot's theorem
- Kopp's law
Electromagnetism
Maxwell's equations give the time-evolution of the electric and magnetic fields due to electric charge and current distributions. Given the fields, the Lorentz force law is the equation of motion for charges in the fields.
Maxwell's equations Gauss's law for electricity
Faraday's law
Ampère's circuital law (with Maxwell's correction)
Lorentz force law: Quantum electrodynamics (QED): Maxwell's equations are generally true and consistent with relativity - but they do not predict some observed quantum phenomena (e.g. light propagation as EM waves, rather than photons, see Maxwell's equations for details). They are modified in QED theory.
These equations can be modified to include magnetic monopoles, and are consistent with our observations of monopoles either existing or not existing; if they do not exist, the generalized equations reduce to the ones above, if they do, the equations become fully symmetric in electric and magnetic charges and currents. Indeed there is a duality transformation where electric and magnetic charges can be "rotated into one another", and still satisfy Maxwell's equations.
- Pre-Maxwell laws
These laws were found before the formulation of Maxwell's equations. They are not fundamental, since they can be derived from Maxwell's Equations. Coulomb's Law can be found from Gauss' Law (electrostatic form) and the Biot-Savart Law can be deduced from Ampere's Law (magnetostatic form). Lenz' Law and Faraday's Law can be incorporated into the Maxwell-Faraday equation. Nonetheless they are still very effective for simple calculations.
- Lenz's law
- Coulomb's Law
- Biot-Savart law
- Other laws
- Ohm's law
- Kirchhoff's laws
- Joule's law
Photonics
Classically, optics is based on a variational principle: light travels from one point in space to another in the shortest time.
In geometric optics laws are based on approximations in Euclidean geometry (such as the paraxial approximation).
- Law of reflection
- Law of refraction, Snell's law
In physical optics, laws are based on physical properties of materials.
- Brewster's angle
- Malus's law
- Beer–Lambert law
In actuality, optical properties of matter are significantly more complex and require quantum mechanics.
Laws of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics has its roots in postulates. This leads to results which are not usually called "laws", but hold the same status, in that all of quantum mechanics follows from them.
One postulate that a particle (or a system of many particles) is described by a wavefunction, and this satisfies a quantum wave equation: namely the Schrödinger equation (which can be written as a non-relativistic wave equation, or a relativistic wave equation). Solving this wave equation predicts the time-evolution of the system's behaviour, analogous to solving Newton's laws in classical mechanics.
Other postulates change the idea of physical observables; using quantum operators; some measurements can't be made at the same instant of time (Uncertainty principles), particles are fundamentally indistinguishable. Another postulate; the wavefunction collapse postulate, counters the usual idea of a measurement in science.
Quantum mechanics, Quantum field theory Schrödinger equation (general form): Describes the time dependence of a quantum mechanical system.
The Hamiltonian (in quantum mechanics) H is a self-adjoint operator acting on the state space,
 (see Dirac notation) is the instantaneous quantum state vector at time t, position r, i is the unit imaginary number, ħ = h/2π is the reduced Planck's constant.
(see Dirac notation) is the instantaneous quantum state vector at time t, position r, i is the unit imaginary number, ħ = h/2π is the reduced Planck's constant.Wave-particle duality Planck–Einstein law: the energy of photons is proportional to the frequency of the light (the constant is Planck's constant, h).
De Broglie wavelength: this laid the foundations of wave-particle duality, and was the key concept in the Schrödinger equation,
Heisenberg uncertainty principle: Uncertainty in position multiplied by uncertainty in momentum is at least half of the reduced Planck constant, similarly for time and energy;
The uncertainty principle can be generalized to any pair of observables - see main article.
Wave mechanics Schrödinger equation (original form):
Pauli exclusion principle: No two identical fermions can occupy the same quantum state (bosons can). Mathematically, if two particles are interchanged, fermionic wavefunctions are anti-symmetric, while bosonic wavefunctions are symmetric: 
where ri is the position of particle i, and s is the spin of the particle. There is no way to keep track of particles physically, labels are only used mathematically to prevent confusion.
Radiation laws
Applying electromagnetism, thermodynamics, and quantum mechanics, to atoms and molecules, some laws of electromagnetic radiation and light are as follows.
- Stefan-Boltzmann law
- Planck's law of black body radiation
- Wien's displacement law
- Radioactive decay law
Laws of chemistry
Chemical laws are those laws of nature relevant to chemistry. Historically, observations lead to many empirical laws, though now it is known that chemistry has its foundations in quantum mechanics.
The most fundamental concept in chemistry is the law of conservation of mass, which states that there is no detectable change in the quantity of matter during an ordinary chemical reaction. Modern physics shows that it is actually energy that is conserved, and that energy and mass are related; a concept which becomes important in nuclear chemistry. Conservation of energy leads to the important concepts of equilibrium, thermodynamics, and kinetics.
Additional laws of chemistry elaborate on the law of conservation of mass. Joseph Proust's law of definite composition says that pure chemicals are composed of elements in a definite formulation; we now know that the structural arrangement of these elements is also important.
Dalton's law of multiple proportions says that these chemicals will present themselves in proportions that are small whole numbers (i.e. 1:2 for Oxygen:Hydrogen ratio in water); although in many systems (notably biomacromolecules and minerals) the ratios tend to require large numbers, and are frequently represented as a fraction.
More modern laws of chemistry define the relationship between energy and its transformations.
- Reaction kinetics and Equilibria
- In equilibrium, molecules exist in mixture defined by the transformations possible on the timescale of the equilibrium, and are in a ratio defined by the intrinsic energy of the molecules—the lower the intrinsic energy, the more abundant the molecule. Le Chatelier's principle states that the system opposes changes in conditions from equilibrium states, i.e. there is an opposition to change the state of an equilibrium reaction.
- Transforming one structure to another requires the input of energy to cross an energy barrier; this can come from the intrinsic energy of the molecules themselves, or from an external source which will generally accelerate transformations. The higher the energy barrier, the slower the transformation occurs.
- There is a hypothetical intermediate, or transition structure, that corresponds to the structure at the top of the energy barrier. The Hammond–Leffler postulate states that this structure looks most similar to the product or starting material which has intrinsic energy closest to that of the energy barrier. Stabilizing this hypothetical intermediate through chemical interaction is one way to achieve catalysis.
- All chemical processes are reversible (law of microscopic reversibility) although some processes have such an energy bias, they are essentially irreversible.
- The reaction rate has the mathematical parameter known as the rate constant. The Arrhenius equation gives the temperature and activation energy dependence of the rate constant, an empirical law.
- Gas laws
- Chemical transport
Geophysical laws
- Archie's law
- Buys-Ballot's law
- Birch's law
- Byerlee's law
Biological laws
- Life is based on cells.[7]
- All life has genes.[7]
- All life occurs through biochemistry.[7]
- Mendelian inheritance
See also
Notes
- ↑ "law of nature". Oxford English Dictionary (3rd ed.). Oxford University Press. September 2005.
- ↑ Feynman Lectures on Physics: Volume 2, R.P. Feynman, R.B. Leighton, M. Sands, Addison-Wesley, 1964, ISBN 0-201-02117-X
- ↑ Encyclopaedia of Physics (2nd Edition), R.G. Lerner, G.L. Trigg, VHC Publishers, 1991, ISBN (Verlagsgesellschaft) 3-527-26954-1 (VHC Inc.) 0-89573-752-3
- ↑ Classical Mechanics, T.W.B. Kibble, European Physics Series, McGraw-Hill (UK), 1973, ISBN 07-084018-0
- ↑ Gravitation and Inertia, I. Ciufolini and J.A. Wheeler, Princeton Physics Series, 1995, ISBN 0-691-03323-4
- ↑ 2.^ Classical Mechanics, T.W.B. Kibble, European Physics Series, McGraw-Hill (UK), 1973, ISBN 07-084018-0
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Paul Nurse (2010-10-12). Sir Paul Nurse: Organisms are information networks. Newton via The Guardian. Event occurs at 15:20. Retrieved 2012-06-15.
External links
- Physics Formulary, a useful book in different formats containing many or the physical laws and formulae.
- Eformulae.com, website containing most of the formulae in different disciplines.