Lanthanum trifluoride
Lanthanum trifluoride is a high-melting, ionic compound of lanthanum and fluorine.[2]
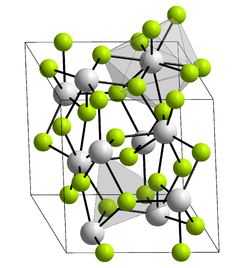
The LaF3 structure
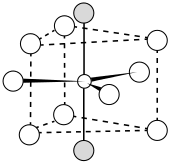
Bonding is ionic with lanthanum highly coordinated. The cation sits at the center of a trigonal prism. Nine fluorides are close: three at the bottom corners of the trigonal prism, three in the faces of the trigonal prism, and three at top corners of the trigonal prism. There are also two fluorides a little further away above and below the prism. The cation can be considered 9-coordinate or 11-coordinate.[2]
The larger sized rare earth elements (lanthanides ), which are those with smaller atomic number, also form trifluorides with the LaF3 structure.[2] Some actinides do as well.
Applications
The material is a component of multimetal fluoride glasses such as ZBLAN.[3] It is also used (with europium trifluoride) in fluoride selective electrodes.
See also
References
- ↑ A. Zalkin and D. H. Templeton: Refinement of the trigonal crystal structure of lanthanum trifluoride with neutron diffraction data. In: Acta Cryst. (1985). B41, 91-93
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Cotton, Simon; Lanthanide and Actinide Chemistry; 2007; pages 25-27
- ↑ Harrington, James A. "Infrared Fiber Optics" (PDF). Rutgers University.
Further reading
- Sobolev, Boris Petrovich; The Rare Earth Trifluorides: The high temperature chemistry of the rare earth trifluorides; Institut d'Estudis Catalans (2000)