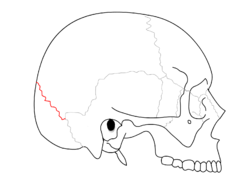
| Lambdoid suture |
| |
| Lambdoid suture. (shown in red line.) |
| |
| Side view of the skull. ('Lambdoidal suture' visible at right.) |
|
| Latin |
sutura lambdoidea |
| Gray's |
p.132 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The lambdoid suture (or lambdoidal suture) is a dense, fibrous connective tissue joint on the posterior aspect of the skull that connects the parietal bones with the occipital bone. It is continuous with the occipitomastoid suture.
Its name comes from its lambda-like shape.
Clinical significance
At birth, the bones of the skull do not meet. If certain bones of the skull grow too fast, then craniosynostosis (premature closure of the sutures) may occur. This can result in skull deformities. If the lambdoid suture closes too soon on one side, the skull will appear twisted and asymmetrical, a condition called "plagiocephaly." Plagiocephaly refers to the shape and not the condition. The condition is craniosynostosis.
The lambdoidal suture articulates with the occipital bone and parietal bones.
Additional images
| Lambdoid suture, seen from behind. (there are wormian bones in this skull.) |
|
References
- "Sagittal suture." Stedman's Medical Dictionary, 27th ed. (2000).
- Moore, Keith L., and T.V.N. Persaud. The Developing Human: Clinically Oriented Embryology, 7th ed. (2003).
External links