Labia minora
| Labia minora | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Labia minora (inner labia) | |
| Latin | labium minus pudendi |
| Gray's | subject #270 1265 |
| Precursor | Urogenital folds |
| Dorlands/Elsevier | Labia minora pudendi |
The labia minora (singular: labium minus), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, vaginal lips, or nymphae,[1] are two flaps of skin on either side of the human vaginal opening, situated between the labia majora (outer labia, or outer lips). Inner lips vary widely in size, colour, and shape from woman to woman. They are homologous to male urethra and penile skin.[2]
Structure
The inner lips extend from the clitoris obliquely downward, laterally, and backward on either side of the vulval vestibule, ending between the bottom of the vulval vestibule and the outer lips. The posterior ends (bottom) of the inner lips are usually joined across the middle line by a fold of skin, named the frenulum labiorum pudendi or fourchette.
On the front, each lip divides into two portions. The upper part of each lip passes above the clitoris to meet the upper part of the other lip—which will often be a little larger or smaller—forming a fold which overhangs the glans clitoridis; this fold is named the preputium clitoridis. The lower part passes beneath the glans clitoridis and becomes united to its under surface, forming, with the inner lip of the opposite side, the frenulum clitoridis.
Histology
On the opposed surfaces of the labia minora are numerous sebaceous glands not associated with hair follicles. They are lined by stratified squamous epithelium on those surfaces.[2]
Variation
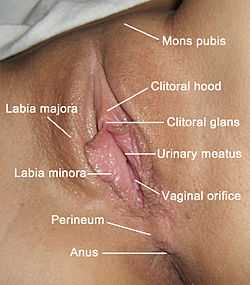
In or around 2004, researchers from the Department of Gynaecology, Elizabeth Garret Anderson Hospital in London, measured the labia and other genital structures of 50 women from the age of 18 to 50, with a mean age of 35.6. The results were:[3]
| Measuring | Range | Mean [SD] |
|---|---|---|
| Clitoral length (mm) | 5–35 | 19.1 [8.7] |
| Clitoral glans width (mm) | 3–10 | 5.5 [1.7] |
| Clitoris to urethra (mm) | 16–45 | 28.5 [7.1] |
| Labia majora length (cm) | 7.0–12.0 | 9.3 [1.3] |
| Labia minora length (mm) | 20–100 | 60.6 [17.2] |
| Labia minora width (mm) | 7–50 | 21.8 [9.4] |
| Perineum length (mm) | 15–55 | 31.3 [8.5] |
| Vaginal length (cm) | 6.5–12.5 | 9.6 [1.5] |
| Tanner stage (n) | IV | 4 |
| Tanner stage (n) | V | 46 |
| Colour of genital area compared with surrounding skin (n) |
Same | 9 |
| Colour of genital area compared with surrounding skin (n) |
Darker | 41 |
| Rugosity of labia (n) | Smooth | 14 |
| Rugosity of labia (n) | Moderate | 34 |
| Rugosity of labia (n) | Marked | 2 |
In female anatomy macronymphia is the term used for an abnormally large labia minora commonly found as a racial characteristic in certain ethnic groups such as Khoisans[4]
Additional images
-

Organs of the female reproductive system.
-

Outer anatomy of clitoris.
See also
References
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
- ↑ nymphae. Dictionary.com. Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary. Merriam-Webster, Inc. (accessed: November 24, 2007).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Manual of Obstetrics. (3rd ed.). Elsevier. pp. 1-16. ISBN 9788131225561.
- ↑ Lloyd, Jillian et al. "Female genital appearance: 'normality' unfolds", British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, May 2005, Vol. 112, pp. 643–646. PMID 15842291
- ↑ Cruciani, F; Santolamazza, P; Shen, P; Macaulay, V; Moral, P; Olckers, A; Modiano, D; Holmes, S; Destro-Bisol, G; Coia, V; Wallace, DC; Oefner, PJ; Torroni, A; Cavalli-Sforza, LL; Scozzari, R; Underhill, PA (May 2002). "A back migration from Asia to sub-Saharan Africa is supported by high-resolution analysis of human Y-chromosome haplotypes.". American Journal of Human Genetics 70 (5): 1197–214. doi:10.1086/340257. PMC 447595. PMID 11910562.
External links
- labium+minus at eMedicine Dictionary
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||