L-selectride
| L-selectride | ||
|---|---|---|
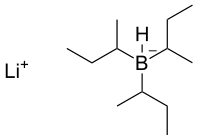 | ||
| IUPAC name lithium tri-sec-butyl(hydrido)borate(1-) | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 38721-52-7 | |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Li+].CCC(C)[BH-](C(C)CC)C(C)CC|Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C12H28BLi | |
| Molar mass | 190.10 g/mol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
L-selectride is an organoborane. It is used in organic chemistry as a reducing agent, for example in the reduction of a ketone, as part of Overman's synthesis of strychnine.[1]

Under certain conditions, L-selectride can selectively reduce enones by conjugate addition of hydride, owing to the greater steric hindrance the bulky hydride reagent experiences at the carbonyl carbon relative to the (also-electrophilic) β-position.[2] L-Selectride can also stereoselectively reduce carbonyl groups in a 1,2-fashion, again due to the steric nature of the hydride reagent.[3]
N-selectride and K-selectride are related compounds, but instead of lithium as cation they have sodium and potassium cations respectively.
References
- ↑ S. D. Knight, L. E. Overman and G. Pairaudeau (1993). "Synthesis applications of cationic aza-Cope rearrangements. 26. Enantioselective total synthesis of (-)-strychnine". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115 (20): 9293–9294. doi:10.1021/ja00073a057.
- ↑ Clayden, Jonathan; Greeves, Nick; Warren, Stuart; Wothers, Peter (2001). Organic Chemistry (1st ed.). Oxford University Press. p. 685. ISBN 978-0-19-850346-0.
- ↑ Scott A. Miller and A. Richard Chamberlin (1989). "Highly selective formation of cis-substituted hydroxylactams via auxiliary-controlled reduction of imides". J. Org. Chem. 54 (11): 2502–2504. doi:10.1021/jo00272a004.