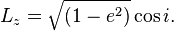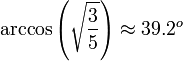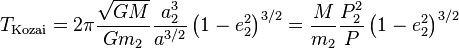Kozai mechanism
In celestial mechanics, the Kozai mechanism, or the Lidov–Kozai mechanism, refers to the orbit of a satellite that is perturbed by another body orbiting farther out. Due to the perturbation, the orbit of the satellite experiences libration (oscillation about a constant value) of its argument of pericenter. As the orbit librates, there is a periodic exchange between its inclination and its eccentricity.
The effect was described in 1961 by the Soviet specialist in space dynamics Michael Lidov (Russian: ru:Михаил Львович Лидов) while analyzing the orbits of artificial and natural satellites of planets,[1] and in 1962 by the Japanese astronomer Yoshihide Kozai while analyzing the orbits of the asteroids.[2] Since then this effect has been found to be an important factor shaping the orbits of irregular satellites of the planets, trans-Neptunian objects, and a few extrasolar planets and multiple star systems.
Kozai mechanism
In the hierarchical, restricted three-body problem, it is assumed that the satellite has negligible mass compared with the other two bodies (the "primary" and the "perturber"), and that the distance between the primary and perturber is much greater than the distance from the primary to the satellite. These assumptions would be valid, for instance, in the case of an artificial satellite in a low-Earth orbit that is perturbed by the moon, or a short-period comet that is perturbed by Jupiter.
Under these approximations, the orbit-averaged equations of motion for the satellite have a conserved quantity: the component of the satellite's orbital angular momentum parallel to the angular momentum of the primary/perturber angular momentum. This conserved quantity can be expressed in terms of the satellite's eccentricity e and inclination i relative to the plane of the outer binary:
Conservation of Lz means that orbital eccentricity can be "traded for" inclination. Thus, near-circular, highly-inclined orbits can become very eccentric. Since increasing eccentricity while keeping the semimajor axis constant reduces the distance between the objects at periapsis, this mechanism can cause comets (perturbed by Jupiter) to become sungrazing.
Kozai oscillations will be present if Lz is lower than a certain value. At the critical value of Lz, a "fixed-point" orbit appears, with constant inclination given by
For values of Lz less than this critical value, there is a one-parameter family of orbital solutions having the same Lz but different amounts of variation in e or i. Remarkably, the degree of possible variation in i is independent of the masses involved, which only set the timescale of the oscillations.[3]
Consequences
The Kozai mechanism causes the argument of pericenter to librate about either 90° or 270°, which is to say that its periapse occurs when the body is farthest from the equatorial plane. This effect is part of the reason that Pluto is dynamically protected from close encounters with Neptune.
The Kozai mechanism places restrictions on the orbits possible within a system, for example
- for a regular moon: if the orbit of a planet's moon is highly inclined to the planet's orbit, the eccentricity of the moon's orbit will increase until, at closest approach, the moon is destroyed by tidal forces
- for irregular satellites: the growing eccentricity will result in a collision with a regular moon, the planet, or alternatively, the growing apocenter may push the satellite outside the Hill sphere
Timescale
The basic timescale associated with Kozai oscillations is[3]
where a indicates semimajor axis, P is orbital period, e is eccentricity and m is mass; variables with subscript "2" refer to the outer (perturber) orbit and variables lacking subscripts refer to the inner (satellite) orbit; M is the mass of the primary. The period of oscillation of all three variables (e, i, ω) is the same, but depends on how "far" the orbit is from the fixed-point orbit, becoming very long for the separatrix orbit that separates librating (Kozai) orbits from oscillating orbits.
See also
- Jacobi integral
- Tisserand's relation
References
- ↑ Lidov, M. L. (1962). "The evolution of orbits of artificial satellites of planets under the action of gravitational perturbations of external bodies". Planetary and Space Science 9: 719–759. Bibcode:1962P&SS....9..719L. doi:10.1016/0032-0633(62)90129-0.
- ↑ Kozai, Y. (1962). "Secular perturbations of asteroids with high inclination and eccentricity". The Astronomical Journal 67: 591. Bibcode:1962AJ.....67..591K. doi:10.1086/108790. Retrieved 4 April 2013.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Merritt, David (2013). Dynamics and Evolution of Galactic Nuclei. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press. p. 575.