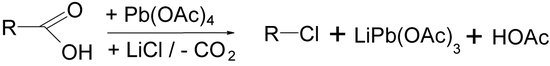Kochi reaction
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Kochi reaction is an organic reaction for the decarboxylation of carboxylic acids to alkyl halides with lead tetraacetate and a lithium chloride or other lithium salts.[1]
The reaction is a variation of the Hunsdiecker reaction.
References
- ↑ A New Method for Halodecarboxylation of Acids Using Lead(IV) Acetate Jay K. Kochi J. Am. Chem. Soc.; 1965; 87(11); 2500–02. doi:10.1021/ja01089a041
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.