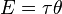Joule
| | |
| Unit system | SI derived unit |
| Unit of | Energy |
| Symbol | J |
| Named after | James Prescott Joule |
| | |
| 1 J in... | is equal to... |
| SI base units | 1 kg·m2/s2 |
| CGS units | 1×107 erg |
| kilowatt hours | 2.78×10−7 kW·h |
| kilocalories | 2.39×10−4 kcal |
| BTUs | 9.48×10−4 BTU |
| electronvolts | 6.24×1018 eV |
The joule (/ˈdʒuːl/ or sometimes /ˈdʒaʊl/), symbol J, is a derived unit of energy, work, or amount of heat in the International System of Units.[1] It is equal to the energy expended (or work done) in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre (1 newton metre or N·m), or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second. It is named after the English physicist James Prescott Joule (1818–1889).[2][3][4]
In terms firstly of base SI units and then in terms of other SI units:
where kg is the kilogram, m is the metre, s is the second, N is the newton, Pa is the pascal, W is the watt, C is the coulomb, and V is the volt.
One joule can also be defined as:
- The work required to move an electric charge of one coulomb through an electrical potential difference of one volt, or one '"coulomb volt" (C·V). This relationship can be used to define the volt.
- The work required to produce one watt of power for one second, or one "watt second" (W·s) (compare kilowatt hour). This relationship can be used to define the watt.
Usage
This SI unit is named after James Prescott Joule. As with every International System of Units (SI) unit whose name is derived from the proper name of a person, the first letter of its symbol is upper case (J). However, when an SI unit is spelled out in English, it should always begin with a lower case letter (joule), except in a situation where any word in that position would be capitalized, such as at the beginning of a sentence or in capitalized material such as a title. Note that "degree Celsius" conforms to this rule because the "d" is lowercase. —Based on The International System of Units, section 5.2.
Confusion with newton-metre
In angular mechanics, torque is analogous to the linear Newtonian mechanics parameter of force, moment of inertia to mass, and angle to distance. Energy is the same in both systems. Thus, although the joule has the same dimensions as the newton-meter (1 J = 1 N·m = 1 kg·m2·s−2), these units are not interchangeable: the CGPM has given the unit of energy the name "joule", but has not given the unit of torque any special name, hence the unit of torque is known as the newton-metre (N·m) - a compound name derived from its constituent parts.[5] Torque and energy are related to each other using the equation
where E is the energy, τ is the torque, and θ is the angle moved (in radians). Since radians are dimensionless, it follows that torque and energy have the same dimensions.
The use of newton-metres for torque and joules for energy is useful in helping avoid misunderstandings and miscommunications.[5] Another solution to this problem is to name the unit of angle, such that the unit of torque is called joule per radian.
Practical examples
One joule in everyday life represents approximately:
- the energy required to lift a small apple (with a mass of approximately 100 g) vertically through one meter.
- the energy released when that same apple falls one meter to the ground.
- the heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of water by 0.24 K.[6]
- the typical energy released as heat by a person at rest, every 1/60th of a second.[7]
- the kinetic energy of a 50 kg human moving very slowly (0.2 m/s).
- the kinetic energy of a tennis ball moving at 23 km/h (6.4 m/s).[8]
- the kinetic energy of 1 kg moving √2 m/s.
Since the joule is also a watt-second and the common unit for electricity sales to homes is the kWh (kilowatt-hour), a kWh is thus 1000 (kilo) x 3600 seconds = 3.6 MJ (megajoules).
Multiples
- For additional examples, see: Orders of magnitude (energy)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nanojoule
The nanojoule (nJ) is equal to one billionth of one joule. One nanojoule is about 1/160 of the kinetic energy of a flying mosquito.[9]
Microjoule
The microjoule (μJ) is equal to one millionth of one joule. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is expected to produce collisions on the order of 1 microjoule (7 TeV) per particle.
Millijoule
The millijoule (mJ) is equal to one thousandth of a joule.
Kilojoule
The kilojoule (kJ) is equal to one thousand (103) joules. Nutritional food labels in certain countries express energy in standard kilojoules (kJ).
One kilojoule per second (1000 watts) is approximately the amount of solar radiation received by one square metre of the Earth in full daylight.[10]
Megajoule
The megajoule (MJ) is equal to one million (106) joules, or approximately the kinetic energy of a one-ton vehicle moving at 160 km/h (100 mph).
Because 1 watt times one second equals one joule, 1 kilowatt-hour is 1000 watts times 3600 seconds, or 3.6 megajoules.
Gigajoule
The gigajoule (GJ) is equal to one billion (109) joules. Six gigajoules is about the amount of potential chemical energy in a barrel of oil, when combusted.[11]
Terajoule
The terajoule (TJ) is equal to one trillion (1012) joules. About 63 terajoules were released by the atomic bomb that exploded over Hiroshima.[12] The International Space Station, with a mass of approximately 450,000 kg and orbital velocity of 7.7 km/s,[13] has a kinetic energy of roughly 13.34 terajoules.
Petajoule
The petajoule (PJ) is equal to one quadrillion (1015) joules. 210 PJ is equivalent to about 50 megatons of TNT. This is the amount of energy released by the Tsar Bomba, the largest man-made nuclear explosion ever.
Exajoule
The exajoule (EJ) is equal to one quintillion (1018) joules. The 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami in Japan had 1.41 EJ of energy according to its 9.0 on the moment magnitude scale. Energy in the United States used per year is roughly 94 EJ.
Zettajoule
The zettajoule (ZJ) is equal to one sextillion (1021) joules. Annual global energy consumption is approximately 0.5 ZJ.
Yottajoule
The yottajoule (YJ) is equal to one septillion (1024) joules. This is approximately the amount of energy required to heat the entire volume of water on Earth by 1 °Celsius.
Conversions
1 joule is equal to:
- 1×107 ergs (exactly)
- 6.24150974×1018 eV (electronvolts)
- 0.2390 cal (thermochemical gram calories or small calories)
- 2.3901×10−4 kcal (thermochemical kilocalories, kilogram calories, large calories or food calories)
- 9.4782×10−4 BTU (British thermal unit)
- 0.7376 ft·lb (foot-pounds)
- 23.7 ft·pdl (foot-poundals)
- 2.7778×10−7 kilowatt-hour
- 2.7778×10−4 watt-hour
- 9.8692×10−3 litre-atmosphere
- 11.1265 femtograms (mass-energy equivalence)
- 1×10−44 foe (exactly)
Units defined exactly in terms of the joule include:
- 1 thermochemical calorie = 4.184 J[14]
- 1 International Table calorie = 4.1868 J[14]
- 1 watt hour = 3600 J
- 1 kilowatt hour = 3.6×106 J (or 3.6 MJ)
- 1 watt second = 1 J
- 1 ton TNT = 4.184 GJ
See also
- Conversion of units of energy
- Orders of magnitude (energy)
- Fluence
- International System of Units
Notes and references
- ↑ International Bureau of Weights and Measures (2006), The International System of Units (SI) (8th ed.), p. 120, ISBN 92-822-2213-6
- ↑ American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Online Edition (2009). Houghton Mifflin Co., hosted by Yahoo! Education.
- ↑ The American Heritage Dictionary, Second College Edition (1985). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Co., p. 691.
- ↑ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Physics, Fifth Edition (1997). McGraw-Hill, Inc., p. 224.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 From the official SI website: "A derived unit can often be expressed in different ways by combining base units with derived units having special names. Joule, for example, may formally be written newton metre, or kilogram metre squared per second squared. This, however, is an algebraic freedom to be governed by common sense physical considerations; in a given situation some forms may be more helpful than others. In practice, with certain quantities, preference is given to the use of certain special unit names, or combinations of unit names, to facilitate the distinction between different quantities having the same dimension."
- ↑ "Units of Heat - BTU, Calorie and Joule". Engineeringtoolbox.com. Retrieved 2013-09-16.
- ↑ This is called the basal metabolic rate. It corresponds to about 1200 kilocalories (also called dietary calories) per day. "At rest" means awake but inactive.
- ↑ Ristinen, Robert A.; Kraushaar, Jack J. (2006). Energy and the Environment (2nd ed.). Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-73989-8.
- ↑ CERN - Glossary
- ↑ "Construction of a Composite Total Solar Irradiance (TSI) Time Series from 1978 to present". Retrieved 2005-10-05.
- ↑ IRS publication
- ↑ Los Alamos National Laboratory report LA-8819, The yields of the Hiroshima and Nagasaki nuclear explosions by John Malik, September 1985. Available online at http://www.mbe.doe.gov/me70/manhattan/publications/LANLHiroshimaNagasakiYields.pdf
- ↑ International Space Station Fact Sheet
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 The adoption of joules as units of energy, FAO/WHO Ad Hoc Committee of Experts on Energy and Protein, 1971. A report on the changeover from calories to joules in nutrition.
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||