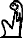Kawit (queen)
| |||||
| Kawit in hieroglyphs |
|---|
Kawit was an ancient Egyptian queen consort, a lower ranking wife of Pharaoh Mentuhotep II of the 11th dynasty. Her tomb (DBXI.9) and small decorated chapel were found in her husband's Deir el-Bahari temple complex,[1] behind the main building, along with the tombs of five other ladies, Ashayet, Henhenet, Kemsit, Sadeh and Mayet. She and three other women of the six bore queenly titles, and most of them were priestesses of Hathor, so it is possible that they were buried there as part of the goddess's cult, but it is also possible that they were the daughters of nobles the king wanted to keep an eye upon.
Her stone sarcophagus is now in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo.[1] The queen is depicted with short hair, she is sitting on a chair, a servant girl is arranging her hair, while a servant is poring her a drink.[2] On her sarcophagus her only titles are priestess and King's Ornament (a title for noble ladies at court), her queenly title appears only in her chapel. Also in her tomb were six miniature wax figurines depicting Kawit, in small wooden coffins, these may be early versions of ushabti.[3]
Her titles were: King's Beloved Wife (ḥmt-nỉswt mrỉỉ.t=f ), King's Ornament (ẖkr.t-nỉswt), King's Sole Ornament (ẖkr.t-nỉswt wˁtỉ.t), Priestess of Hathor (ḥm.t-nṯr ḥwt-ḥrw).[4]
Sources
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Dodson, Aidan, Hilton, Dyan. The Complete Royal Families of Ancient Egypt. Thames & Hudson. ISBN 0-500-05128-3 (2004), p.88
- ↑ Dodson & Hilton, op.cit., p.89
- ↑ Grajetzki, Wolfram. Ancient Egyptian Queens: A Hieroglyphic Dictionary. London: Golden House Publications. ISBN 0-9547218-9-6 (2005), p.29
- ↑ Grajetzki, op.cit., p.29
![V31 [k] k](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/h/i/e/r/hiero_V31.png)
![G1 [A] A](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/h/i/e/r/hiero_G1.png)
![G43 [w] w](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/h/i/e/r/hiero_G43.png)
![M17 [i] i](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/h/i/e/r/hiero_M17.png)
![X1 [t] t](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/h/i/e/r/hiero_X1.png)