Kadamba dynasty
| Kadambas of Banavasi ಬನವಾಸಿ ಕದಂಬರು | |||||
| Empire (Subordinate to Pallava until 345) | |||||
| |||||
 Extent of Kadamba Empire, 500 CE | |||||
| Capital | Banavasi | ||||
| Languages | Sanskrit Kannada | ||||
| Religion | Hinduism | ||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||
| Maharaja | |||||
| - | 345–365 | Mayurasharma | |||
| Krishna Varma II | |||||
| History | |||||
| - | Earliest Kadamba records | 450 | |||
| - | Established | 345 | |||
| - | Disestablished | 525 | |||
| Kadamba Kings (345–525) | |
| (Banavasi Kings) | |
| Mayurasharma | (345–365) |
| Kangavarma | (365–390) |
| Bagitarha | (390–415) |
| Raghu | (415–435) |
| Kakusthavarma | (435–455) |
| Santivarma | (455 -460) |
| Mrigeshavarma | (460–480) |
| Shivamandhativarma | (480–485) |
| Ravivarma | (485–519) |
| Harivarma | (519–525) |
| (Triparvatha Branch) | |
| Krishna Varma I | (455) |
| Vishnuvarma | |
| Simhavarma | |
| Krishna Varma II | |
| Pulakesi I (Chalukya) |
(543–566) |
 |
Kadamba (Kannada: ಕದಂಬರು) (345 – 525 CE) was an ancient royal dynasty of Karnataka, India that ruled northern Karnataka and the Konkan from Banavasi in present day Uttara Kannada district. At the peak of their power under King Kakushtavarma, Kadambas of Banavasi they ruled large parts of Karnataka state.
The dynasty was founded by Mayurasharman in 345 CE which at times showed the potential of developing into imperial proportions, an indication to which is provided by the titles and epithets assumed by its rulers. King Mayurasharma defeated the armies of Pallavas of Kanchi possibly with help of some native tribes. The Kadamba fame reached its peak during the rule of Kakusthavarma, a powerful ruler with whom even the kings of Gupta Dynasty of northern India cultivated marital alliances. Tiring of the endless battles and bloodshed, one of the later descendants, King Shivakoti adopted Jainism. The Kadambas were contemporaries of the Western Ganga Dynasty and together they formed the earliest native kingdoms to rule the land with absolute autonomy. The dynasty later continued to rule as a feudatory of larger Kannada empires, the Chalukya and the Rashtrakuta empires for over five hundred years during which time they branched into Goa and Hanagal.
During the pre-Kadamba era the ruling families that controlled Karnataka, the Mauryas, Satavahanas and Chutus were not natives of the region and the nucleus of power resided outside present day Karnataka. The Kadambas were the first indigenous dynasty to use Kannada, the language of the soil at an administrative level. In the history of Karnataka, this era serves as a broad based historical starting point in the study of the development of region as an enduring geo-political entity and Kannada as an important regional language. Their legacy is so impressive that even the Vijayanagars who fought Islamic kings and raiders, hired Kadamba descendants to manage their Goa military naval fleet.[1]
History
There is no shortage of myths about the origin of the Kadambas. According to one account the dynasty was founded by one Trilochana Kadamba also known from the Halsi and Degamve records as Jayanta who had three eyes and four arms.[2] He was born out of the sweat of Shiva, which had fallen under a Kadamba tree and hence his name Kadamba. According to another myth, Mayurasharma himself was born to Lord Shiva and mother earth and had three eyes.[3] According to Grama Paddhati, a Kannada work dealing with the history of the Tulu Brahmanas, Mayurasharma was born to Lord Shiva and goddess Parvathi under a Kadamba tree in the Sahyadri mountains and hence the name Kadamba. An inscription of the Nagarakhanda Kadambas, a later descendent dynasty, gives a legendary account and traces their lineage back to the Nandas. According to the inscription, King Nanda who had no heir prayed to Lord Shiva in the Kailash mountains when a heavenly voice advised him that two sons would be born to him, would bear the name of Kadamba Kula (family) and they should be instructed in the use of weapons.[2]
There are two theories to the origin of the Kadamba dynasty, a native Kannadiga origin and the other a north Indian origin. Mention of the north Indian origin of the Kadambas are only found in their later records of their offshoot descendent dynasty and is considered legendary. The earliest record making this claim is the 1053 and 1055 inscriptions of Harikesari Deva which are copied in inscriptions thereafter, describing Mayurasharma as the progenitor of the kingdom who established his might on the summit of Mount Himavat. But this theory has not found popularity as there is no indication of this account in any of their early records.[4] On the contrary, the family derives its name from the Kadamba tree that is common only to the South India region.[5]
Historians are divided on the issue of the caste of the Kadamba family, whether the founders of the kingdom belonged to the Brahmin caste as claimed by the Talagunda inscription, or were of tribal origin. A claim has been made that the Kadambas were none other than a tribe called the Kadambu, who were in conflict with the Chera kingdom (of modern Tamil Nadu – Kerala region). The 'Kadambus' find mention in the Tamil Sangam literature as totemic worshippers of the Kadambu tree and the Hindu god Subramanya.[6] While some historians have argued that they being of Brahmin descent made Mayurasharma's ancestors natives of northern India, the counter argument is that it was common for Dravidian peoples to be received into the Brahmanic caste during early and later medieval times. Being native Kannadigas, the Kadambas promptly gave administrative and political importance to their language, Kannada, after coming to power.[7] Its is thus claimed that the family of the Kadambas were undoubtedly of Kanarese descent and may have been admitted into the Brahminical caste.[8][9] The Naga descent of the Kadambas has been stated in early inscriptions of King Krishna Varma I too, which confirms the family was from present day Karnataka.[5]

Inscriptions in Sanskrit and Kannada are the main sources of the Kadamba history. The Talagunda, Gundanur, Chandravalli, Halasi and Halmidi inscription are some of the important inscriptions that throw light on this ancient ruling family of Karnataka.[10] They belonged to the Manavya Gotra and were Haritiputras (lineage), which connects them to the native Chutus of Banavasi, a feudatory of the Satavahana empire.[11] Inscriptions of the Kadambas in Kannada and Sanskrit ascribed to the main dynasty and branch kingdoms have been published by historians.[12][13] The Kadambas minted coins with Nagari, Kannada and Grantha legends which provide additional numismatic evidence of their history.[14][15]
Kadambas were the first rulers to use Kannada as an additional official administrative language, as evidenced by the Halmidi inscription of 450.[16][17][18] Three Kannada inscriptions from their early rule from Banavasi have been discovered.[19] Several early Kadamba dynasty coins bearing the Kannada inscription Vira and Skandha was found in Satara collectorate.[20] A gold coin of King Bhagiratha (390–415 CE) bearing the old Kannada legend Sri and Bhagi also exists.[21] Recent discovery of 5th century Kadamba copper coin in Banavasi with Kannada script inscription Srimanaragi on it proves the usage of Kannada at the administrative level further.[22]
One of their earliest inscriptions, the Talagunda inscription of Santivarma (450) gives what may be the most possible cause for the emergence of the Kadamba kingdom. It states that Mayura sharma was a native of Talagunda, (in present day Shimoga district) and his family got its name from the Kadamba tree that grew near his home.[23][24][25] The inscription narrates how Mayurasharma proceeded to Kanchi in 345 along with his guru and grandfather Veerasarma to pursue his Vedic studies at a Ghatika (school). There, owing to some misunderstanding between him and a Pallava guard or at an Ashvasanstha (a place of horse sacrifice), a quarrel arose in which Mayurasharma was humiliated. In high rage, the Brahmana discontinued his studies, left Kanchi, swearing vengeance on the impudent Pallavas, and took to arms. He collected a faithful group of followers and routed the Pallava armies near Srisilam region. After a prolonged period of low intensity warfare against the Pallavas and other smaller kings such as the Brihad-Banas of Kolar region, he proclaimed independence. Unable to contain him, the Pallavas had to accept his sovereignty.[26][27] Thus in an act of righteous indignation was born the first native kingdom of Karnataka, the Pallava King Skandavarman condescending to recognise the growing might of the Kadambas south of the Malaprabha river as a sovereign power.[28] Though pallavas were mightier than Kadambas yet they taste the defeat." Scholars like Dr.Moraes, Prof.K.A.Nilakanta sastry and others have felt that Mayurasharma availed himself of the confusion that was created by the invasion of Samudragupta who,in his Allahabad Inscription,claims to have defeated, among others,Vishnugopa of Kanchi. Taking advantage of the weakening of the Pallava power, Mayura appears to have succeeded in establishing a new kingdom."[29] The fact that Mayurasharma had to travel to distant Kanchi for Vedic studies gives an indication that Vedic lore was quite rudimentary in the region at that time. The recently discovered Gudnapur inscription states that Mauryasharma's grandfather and preceptor was Virasarma and his father Bandhushena developed the character of a Kshatriya.[30]
Mayurasharma's successor was his son Kangavarma in 365 who had to fight the Vakataka might to protect Kuntala. He was defeated by Vakataka Prithvisena but managed to maintain his freedom.[31] His son Bhagiratha is said to have retrieved his fathers losses but Vakataka inscriptions do not attest to this.[32] His son Raghu died fighting the Pallavas. He was succeeded by his brother Kakusthavarma who was the most ferocious and powerful ruler of the kingdom.[33] He maintained marital relations with even the imperial Guptas of the north, according to the Talagunda inscription. One of his daughters was married to Kumara Gupta's son Skanda Gupta. His other daughter was married to a Vakataka king Narendrasena.[34] He maintained similar relations with the Bhatari, the Alupas of South Canara and the Western Ganga Dynasty of Gangavadi according to the Talagunda inscription. The great poet Kalidasa had visited his court.[35]
After Kakusthavarma only Ravivarma who came to the throne in 485 was able to build upon the kingdom. His rule was marked by a series of clashes within the family, and also against the Pallavas and the Gangas. He is also credited with a victory against the Vakatakas, which extended his Kingdom as far north as the river Narmada. The crux of their kingdom essentially consisted of most of Karnataka, Goa and southern areas of present day Maharashtra. After his death, the kingdom went into decline due to family feuds. The Birur plates of Kadamba Vishnuvarman call Shantivarman "The master of the entire Karnataka region". The Triparvatha branch that broke away in 455 ruled from Murod in Belgavi for some time and merged with the main Banavasi kingdom during rule of Harivarma. Finally the kingdom fell to the prowess of the Badami Chalukyas. The Kadambas thereafter became feudatories of the Badami Chalukyas and later the Rashtrakutas and Kalyani Chalukyas. The successors of Mayurasharma took to the name "varma" to indicate their Kshatriya status.


Coins
Although the Kadamba dynasty has been known from over 50 inscriptions, no coins had been firmly attributed to them until recently. However, coins of these kings came to light for the first time in 2006, when a hoard of coins was discovered, mostly coins of a lesser branch of the Satavahanas, who had ruled in the Banavasi area, a few coins of the Chutus, and Kadamba coins. They have been definitively attributed to the Kadambas because they not only have various Kadamba symbols, such as conches and chakras, but one of the epithets on the coins, sri dosharashi, is known from inscriptions to have been used by the Kadamba king Krishnavarma II (ruled 516–540).[36] Other coins with the legend sri manarashi were also found, along with anepigraphic coins (that is, coins without any legends) featuring flowers, chakras, and conches. The lotus, chakra (discus), and conch are all symbols of the god Vishnu. Kadamba inscriptions frequently invoke Vishnu, indicating they must have been devotees of this deity. The identity of the king named sri manarashi has still not been determined.
The coins are perhaps the earliest ones to use Kannada letters, a confirmation that the Kadambas were the first ruling dynasty indigenous to Karnataka.
Kadamba Coins and the earliest Kannada inscription
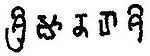

The Halmidi inscription was the earliest known epigraph that showed the early usage of Kannada script (Kadamba script). The stone inscription found at Halmidi has been assigned to C. 450 CE. and belongs to Kadamba ruler Kakusthavarma, whose reign is estimated to be between 435 CE to 455 CE.
In the year 2006, the Jalagars, the sand sievers family, from Tamil Nadu, yielded around 6 Kannada inscribed potin coins from the riverbed of Varada in Sirsi Taluk, which is in Uttara Kannada district. The legends could not be satisfactorily deciphered by Sri MM Prabhu of Mangalore due to the poor chipped condition of coins, and was read Sri Manaragi. Later, when more coins came to limelight, the next year, he managed to attribute it to the Kadambas of Banavasi. The Banavasi village, which is 22 miles (35 km) away from the Sirsi town was the ancient capital of the Kadambas of Banavasi. Banavasi was also known as "Jaldurga" in the Aihole inscription of Pulakeshi II. The Varada river encompassed the Banavasi town in all the four directions to form a natural water port and hence the name Jal (water) durga (port).
For the next two years (2007–2008), the Jalagars made a headway and yielded Satavahana Potin coins bearing Elephant/quadri-directional symbol in quantity above 5000 pieecs along with few hundreds of Kura Potin coins bearing Bull/Bow-and-Arrow symbols. Most of the elephant Satavahana coins were of rulers Siri, Satakarni and Pudumavi. The Satavahaha fractions of up to 50 mg weight, with similar elephant motiff and illegible legend were also obtained. The Bull/Discus Potin coins were issued mainly by Rajno Vishnurudra though other rulers name such as Vishnurudra Putra, Vasithi Putra, Satakarni etc. exist. Third of the series, the inscribed Kadamba Potin coins were found too, but in small quantities, estimated to be around 100 pieces with four unique legend types. Only the coins bearing the legend Sri-Manarashi and Sr-Dhosharashi have been published yet. There exist around 10 die variations of the same. Other coins such as Bull/Trident-Goad coins in bell metal of tetradrachm standard bearing legend Vinukhata Brahmananda were found in 5 to 6 numbers, Copper and Lead coins of Chutukulananda, Mulananda and Sivalananda etc. are seen seldom in those river beds but in too lesser numbers. Copper coins of Chutus were not known hitherto. Since Banavasi was an important religious site of sanctity, the site attracted old-age piigrims from distant places who spent their last days in the holy site. They offered coins such as Guptas, Kushan, Roman, Western Kshatrapas, Vijayanagaras and Hoysalas etc., which stands evidence to this.
As far as the chronology of these Banavasi Kadamba coins concerned, Sri-Dhosharashi coins follow Sri-Manarashi coins as evidenced by the script style. Since Dhosharashi epithet was adorned by Ravivarma, the Manarashi coins are either issued by the predecessors Shanthivarma or Mrigeshavarma. This is understood by the script style of Manarashi coins that resembled more that of Halmidi inscription. Moreover, Halmidi inscription is assigned to Kakkushthavarman. These potin coins are observed in varied weights such as 200 mg to 400 mg stanadard. The fractional coins weighed around 100 mg and contained religious symbols such as Discus, Conch and Lotus, which are the icons of Lord Vishnu.
Their Talagunda inscription had an invocation of Lord Shiva while the Halmidi and Banavasi inscriptions started with an invocation of Lord Vishnu. Moreover, their temple, the Madukeshwara, also seem to have undergone several changes over a period. The initial statue is believed to be of Lord Vishnu while Siva Linga is currently worshipped. Another tale about this place involves the slaying of demon Madhu by Lord Vishnu at the behest of Lord Shiva. This tale is mentioned in the Puranas. So, the religious symbol such as Conch, Discuss and Lotus only signifies the fractional value of coin, which is seen evenin the Hanas and Hagas of the Alupas and Gangas, who were the contemporaries and also in time, the feudatories of the Kadambas of Banavasi.
It is impressive to see the shift of script usage to Kannada, from the Satavahana Brahmi. Satavahana Brahmi was used by the Chutus, Satavahanas and the Kuras respectively as the official script. It is quite possible that Kannada was in use prior to the rule of the Chutus but Brahmi was the script. The usage of Kannada script in coins and inscriptions is the gift of the Kadambas and trend continued in the whole of then Karnataka. The stone tablets recently found in Parkala, Udupi taluk, attests the usage of Kannada around the same period (5th century CE).
Administration
The Kadamba kings called themselves Dharmamaharajas like the Satavahana kings. Dr. Mores has identified various cabinet and other positions in the kingdom from inscriptions. The prime minister (Pradhana), Steward (Manevergade), secretary of council (Tantrapala or Sabhakarya Sachiva), scholarly elders (Vidyavriddhas), physician (Deshamatya), private secretary (Rahasyadhikritha), chief secretary (Sarvakaryakarta), chief justice (Dharmadhyaksha) and other officials (Bhojaka and Ayukta). The army consisted of officers like Jagadala, Dandanayaka and Senapathi.
A crown prince from the royal family helped the king in administration. Princesses of the royal family were appointed as governors of various provinces. King Kakusthavarma had appointed his son Krishna as viceroy of Thriparvatha region. This later proved detrimental to the kingdom as it gave opportunity for break away factions in the kingdom.
The kingdom was divided into Mandalas (provinces) or Desha. Under a Mandala was Vishayas (districts). A total of nine Vishaya have been identified.[37] Under a Vishaya were Mahagramas (Taluk) and Dashagramas (Hobli). Mahagrama had more villages than Dashagramas. One sixth of land produce was collected as tax. Taxes were collected as Perjunka (levy on load), Vaddaravula (social security tax for royal family), Bilkoda (salex tax), Kirukula (land tax), Pannaya (betel tax) and other professional taxes on traders etc.
recently Dr.s.g.samak of shimoga has discovered a hoard of 6 kadamba copper plates from a place called aratalegadde is in shimoha district. in that hoard two new kings so far unknown in the geniology of the kadambas have been identified. they are priyavruta varma and pulinda varma
Culture
Religious condition
The Kadambas were followers of Vedic Hinduism. The founder, Mayurasharma was a Brahmin by birth but later his successors changed their surname to Varma to indicate their Kshatriya status. Some Kadamba kings like Krishna Varma performed the horse sacrifice (Ashwamedha). Their Talagunda inscription starts with an invocation of Lord Shiva while the Halmidi and Banavasi inscriptions start with an invocation of Lord Vishnu. They built the Madhukesvara temple which is considered their family deity. Many records like the Kudalur, Sirsi records speak of grants made by them to scholarly Brahmins. Grants were also made to Buddhist viharas.
The Kadambas also patronised Jainism; several of the latter kings adopted the religion, and built numerous Jain Basadis (temples) that are scattered around Banavasi, Belgavi, Mangaluru and Goa. Kings and Queens of the dynasty were renowned for their support of literature, arts and liberal grants to temples and educational institutions.
Several descendants are scattered around present day Goa, Belgavi, Mangaluru and Bengaluru. Adikavi Pampa highly spoke of this kingdom in his writings. Following are his famous quotes on Banavasi: Aaramkushamittodam nenevudenna manam banavasi deshamam (I shall cherish the sweet memories of Banavasi even when tortured), Maridumbiyagi mEN Kogileyagi puttuvudu nandanadol Banavasi deshadol (As a bee or as nightingale should one born here in this beautiful country of Banavasi).[38]
Architecture

The contribution of the Kadambas to the architectural heritage of Karnataka is certainly worthy of recognition.[39] The Kadamba style can be identified and that it has a few things in common with the Chalukya and the Pallava styles. The most prominent feature of their architecture, basic as it was is their Shikara called Kadamba Shikara. The Shikara is pyramid shaped and rises in steps without any decoration with a Stupika or Kalasha at the top. This style of Shikara are used several centuries later in the Doddagaddavalli Hoysala temple and the Mahakuta temples in Hampi. Some of their temples also use perforated screen windows. It has also been pointed out that in architecture and sculpture, the Kadambas contributed to the foundation of the later Chalukya-Hoysala style.[40]
The Madhukeshwara (Lord Shiva) temple built by them still exists in Banavasi. Built in 10th century and renovated many times, the temple is a very good piece of art. The stone cot with wonderful carvings is one of the main tourist attractions in the temple.
Impact
Kadambotsava ("The festival of Kadamba") a festival is celebrated every year by Government of Karnataka in honour of this kingdom.[41] A popular Kannada film, Mayura starring Dr. Raj Kumar celebrates the creation of the first Kannada kingdom.
On 31 May 2005 Defence minister Pranab Mukherjee commissioned India's most advanced and first dedicated military naval base named INS Kadamba after the Kadamba dynasty, in Karwar.[42]
Lineage
"Kadam's" of Kale a small place at Karad Taluka in Maharashtra State, where it was also known for fine arts and literature is believed to be the last lineage of the same Dynasty as they have hidden sources which are also lost due to lack of preservation and a some of the traces can be found in the Shaivite religious texts and old folk songs also.
See also
- Kadambas of Goa
- History of India
- History of South India
- History of Goa
- Talagunda
- Kadamba architecture
Notes
- ↑ P. 48 Goa Today, Volume 17 By Goa Publications, 1982 - Goa, Daman and Diu (India)
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p8
- ↑ Yet another legend is that Mayurasarma was born to a sister of Jain Thirtankara Ananda Jinavritindra under a Kadamba tree. All these legends are from the records of the later Hangal Kadambas and Kadambas of Goa, George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p7
- ↑ Royal families of the Deccan in the 11th century period often concocted northern origin theories according to George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p.9
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p.10
- ↑ Chopra et al. (2003),p.161
- ↑ Sahitya Akademi (1988), p.1717
- ↑ George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p.11
- ↑ Kadambas were essentially Mysoreans (Rice 1897, pp.296, 335)
- ↑ Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), pp 30–39
- ↑ Both the Talagunda and Gundanur inscriptions attest to this-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p30
- ↑ 21 Kannada and 2 Sanskrit inscriptions have been deciphered and published by George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, New Delhi, Madras, 1990, pp 387–474
- ↑ Dr. D.C. Sircar, Dr. P.B.Desai, Dr. G.S. Gai, N. Lakshminarayana Rao. "Indian Inscriptions-South Indian Inscriptions, vol 15,18". What Is India News Service, Friday, April 28, 2006. Archaeological Survey of India. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ =Govindaraya S. Prabhu (1 November 2001). "Prabhu's web page on Indian Coins-Dynasties of South-Kadambas". Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ Coins with Kannada legends have been discovered from the rule of the Kadambas, according to Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p12
- ↑ A report on Halmidi inscription, Muralidhara Khajane (3 November 2003). "Halmidi village finally on the road to recognition". The Hindu, Monday, November 3, 2003 (Chennai, India: The Hindu). Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ The Kadamba-Western Ganga Dynasty era is a momentous importance to Kannada language for it was with these rulers that Kannada language first gained official language status-K.V. Ramesh, Chalukyas of Vatapi, 1984, Agam Kala Prakashan, Delhi, p10
- ↑ Dr. S.U. Kamath opines that Kannada may have been a local language at this time-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p37
- ↑ Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p37
- ↑ The coins are preserved at the Archaaeological Section, Prince of Wales Museum of Western India, Mumbai – Moraes (1931), p382
- ↑ The coin is preserved at the Indian Historical Research Institute, St. Xavier's College, Mumbai – Moraes (1931), p382
- ↑ According to Dr. B. L. Rice-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p30
- ↑ George M. Moares (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, 1990, p10
- ↑ Dr. Jyotsna Kamat. "Kadambas of Banavasi". 1996–2006 Kamat's Potpourri. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ The Talagunda inscription of 450 states that Mayurasharma was the progenitor of the kingdom. The inscription gives a graphic description of the happenings at Kanchi, "That the hand dextrous in grasping the Kusha (grass), fuel and stones, ladle, melted butter and the oblation vessel, unsheathed a flaming sword, eager to conquer the earth"-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), pp 30–31
- ↑ K.V. Ramesh, Chalukyas of Vatapi, 1984, Agam Kala Prakashan, p6
- ↑ K.V. Ramesh, Chalukyas of Vatapi, 1984, Agam Kala Prakashan, p3
- ↑ A CONCISE HISTORY OF KARNATAKA By Dr.SURYANATH U.KAMATH, page 31.
- ↑ The inscription was discovered by Dr. B.R. Gopal, Arthikaje, Mangalore. "History of Karnataka-Kadambas of Banavasi". 1998-00 OurKarnataka.Com, Inc. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ According to Prof. Jouveau-Dubreuil-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p32
- ↑ The Talagunda inscription describes Bhagiratha as the sole lord of the Kadamba land and the great Sagara himself, indicating he may have retrieved their losses against the Vakatakas-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p32
- ↑ According to Dr. G. M. Moraes who wrote Kadamba Kula: A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, under the rule Kakusthavarma, the kingdom reached its acme of success and the Talagunda record calls him the ornament of the family, the Halsi and Halmidi inscriptions also hold him in high esteem-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p32
- ↑ According to Dr. P.B. Desai and the Balaghat inscription of Vakataka Pritvisena-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p33
- ↑ The Sanskrit work Auchitya Vichara by Kshemendra quotes certain portions of a work by great Poet Kalidasa called Kunthalesvara Dautya which discusses his visit to the Kadamba court. Apparently, the Kadamba did not offer the poet a seat to sit on and Kalidasa had to sit on the ground, indicating the Kadambas treated the ambassador from the Gupta kingdom with scant respect. This is also verified from a Sanskrit work by Bhoja called Shringara Prakasika which mentions a Gupta ambassador being sent to the court of Kuntala. While Dr. Moraes opines the ambassador went during the time of Kadamba king Bhagiratha, Dr. P.B. Desai, R.S. Panchamukhi feel it was during the rule of king Kakusthavarma-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p33
- ↑ K. Ganesh: Coins of Banavasi, Bangalore, March 2008.
- ↑ Prof. R.S. Panchamukhi has identified nine such Vishaya like the Sendraka Vishaya, Tagare Vishaya etc-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), p35
- ↑ Arthikaje, Mangalore. "History of Karnataka-Kadambas of Banavasi". 1998-00 OurKarnataka.Com, Inc. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ Dr. Jyotsna Kamat. "Ancient City of Banavasi". 1996–2006 Kamat's Potpourri. Kamat's Potpourri. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ Dr. G. M. Moraes opines that apart from using some unique features, the Kadambas used many mixed styles in their architecutre derived from their predecessors and overlords. The Kadambas were the originators of the Karnataka architecture-Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002), pp 37–38
- ↑ Kadambotsava is held at Banavasi as it is here that the Kadamba kings organised the spring festival every year. Staff Correspondent (20 January 2006). "Kadambotsava in Banavasi from today". The Hindu, Friday, January 20, 2006 (Chennai, India: The Hindu). Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- ↑ Defense Minister Pranab Mukherjee opened the first phase of India's giant western naval base INS Kadamba in Karwar, Karnataka state, on 31 May. "India Opens Major Naval Base at Karwar". Defence Industry Daily. 21 May 2012. Retrieved 2013-01-30.
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kadamba dynasty. |
- George M. Moraes (1931), The Kadamba Kula, A History of Ancient and Medieval Karnataka, Asian Educational Services, New Delhi, Madras, 1990 ISBN 81-206-0595-0
- Encyclopaedia of Indian literature vol. 2, (1988) Sahitya Akademi, ISBN 81-260-1194-7
- Dr. Suryanath U. Kamath, A Concise history of Karnataka from pre-historic times to the present, Jupiter books, 2001, MCC, Bangalore (Reprint 2002) LCCN 809-5179, OCLC 7796041
- K.V. Ramesh, Chalukyas of Vatapi, 1984, Agam Kala Prakashan, Delhi ISBN 3987-10333
- Chopra P.N., Ravindran T.K., Subrahmanian N. (2003), History of South India (Ancient, Medieval and Modern), Part 1, Chand publications, New Delhi ISBN 81-219-0153-7
- Rice, B.L. (2001) [1897]. Mysore Gazatteer Compiled for Government-vol 1. New Delhi, Madras: Asian Educational Services. ISBN 81-206-0977-8.
- "Kadambas of Banavasi, Dr. Jyotsna Kamat". Kamat's Potpourri. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- "History of Karnataka – Kadambas of Banavasi, Arthikaje". OurKarnataka.Com. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- "Indian Inscriptions". Archeological Survey of India. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- "5th century copper coin discovered at Banavasi". Deccan Herald. February 7, 2006. Archived from the original on 6 October 2006. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- "Halmidi village finally on the road to recognition". The Hindu (Chennai, India). 3 November 2003. Retrieved 2006-11-28.
- Heche karnataka One of the village falling under kadamba empire.
- "Indian Coins, Dynasties of South India, Govindayara Prabhu". G.S Prabhu. 1 November 2001. Retrieved 2006-11-13.
External links
| Classical India | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline and cultural period |
Northwestern India (Punjab-Sapta Sindhu) |
Indo-Gangetic Plain | Central India | Southern India | ||||
| Western Gangetic Plain | Northern India (Central Gangetic Plain) |
Northeastern India | ||||||
| IRON AGE | ||||||||
| Culture | Late Vedic Period | Late Vedic Period (Brahmin ideology)[lower-alpha 1] |
Late Vedic Period (Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[lower-alpha 2] |
Pre-history | ||||
| 6th century BCE | Gandhara | Kuru-Panchala | Magadha | Adivasi (tribes) | ||||
| Culture | Persian-Greek influences | "Second Urbanisation" Rise of Shramana movements |
Pre-history | |||||
| 5th century BCE | (Persian rule) | Shishunaga dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | |||||
| 4th century BCE | (Greek conquests) |
Nanda empire |
||||||
| HISTORICAL AGE | ||||||||
| Culture | Spread of Buddhism | Pre-history | Sangam period (300 BCE – 200 CE) | |||||
| 3rd century BCE | Maurya Empire | Early Cholas Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||||
| Culture | Preclassical Hinduism[lower-alpha 3] - "Hindu Synthesis"[lower-alpha 4] (ca. 200 BCE-300 CE)[lower-alpha 5][lower-alpha 6] Epics - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition Mahayana Buddhism |
Sangam period (continued) | ||||||
| 2nd century BCE | Indo-Greek Kingdom | Sunga Empire | Adivasi (tribes) | Early Cholas Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
| 1st century BCE | Yona | Maha-Meghavahana Dynasty | ||||||
| 1st century CE | Kuninda Kingdom | |||||||
| 2nd century | Pahlava | Varman dynasty | ||||||
| 3rd century | Kushan Empire | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | ||||
| Culture | "Golden Age of Hinduism"(ca. 320-650 CE)[lower-alpha 7] Puranas Co-existence of Hinduism and Buddhism | |||||||
| 4th century | Gupta Empire | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Kadamba Dynasty Western Ganga Dynasty | ||||||
| 5th century | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |||||
| 6th century | Kalabhras dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |||||||
| Culture | Late-Classical Hinduism (ca. 650-1100 CE)[lower-alpha 8] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra Decline of Buddhism in India | |||||||
| 7th century | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty, Harsha | Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) | |||
| 8th century | Kidarite Kingdom | Pandyan Kingdom Kalachuri | ||||||
| 9th century | Indo-Hephthalites (Huna) | Gurjara-Pratihara | Pandyan Kingdom Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai | |||||
| 10th century | Pala dynasty Kamboja-Pala dynasty |
Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Rashtrakuta | ||||||
| Culture | Islamic rule and "Sects of Hinduism" (ca. 1100-1850 CE)[lower-alpha 9] - Medieval and Late Puranic Period (500–1500 CE)[lower-alpha 10] | |||||||
| 11th century | (Islamic conquests) Kabul Shahi (Islamic Empire) |
Pala Empire |
Adivasi (tribes) | Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Later Cholas Chera Perumals of Makkotai Yadava dynasty | ||||
| 12th century | Later Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Alupa Dynasty Chera-Ai Dynasty Venadu Cheras | |||||||
| 13th century | Later Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) Venadu Cheras | |||||||
| 14th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Ruled from Madurai) Khilji Dynasty Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar(Ruled from Thenkaasi after conquest)) | |||||||
| 15th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| 16th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| 17th century | Pandyan Kingdom(Thenkaasi Pandiyar) | |||||||
| ||||||||