KV50
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| KV50 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Burial site of Animals | ||
| Location | East Valley of the Kings | |
| Discovery Date | January 1906 | |
| Excavated by | Edward R. Ayrton | |
| Previous : KV49 |
Next : KV51 | |
Tomb KV50 is located in the Valley of the Kings, in Egypt. It contained the burial of a dog mummey and a mummified monkey,[1] and is probably associated with the nearby tomb of Amenhotep II (KV35).
Recent (winter 2009/10) excavations in this area[2] by an SCA team attempting to relocate tombs KV50, KV51, KV52 and KV 53 revealed 18th Dyn blue painted pottery, tools and hieratic and figured ostraca which included :
- a sketch of a seated queen presenting an offering
- depictions of sexual scenes with woman and animals
- cartouches of Rameses II.
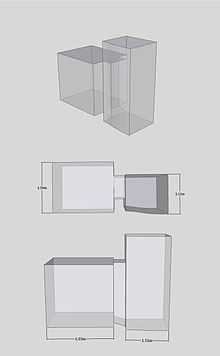
Isometric, plan and elevation images of KV50 taken from a 3d model
References
- ↑ http://www.thebanmappingproject.com/atlas/index_kv.asp?tombID=867
- ↑ Egyptian Archeology (Egypt Exploration Society publication) No.37 p.26
- Reeves, N & Wilkinson, R.H. The Complete Valley of the Kings, 1996, Thames and Hudson, London
- Siliotti, A. Guide to the Valley of the Kings and to the Theban Necropolises and Temples, 1996, A.A. Gaddis, Cairo
External links
- Theban Mapping Project:KV50 – Includes detailed maps of most of the tombs.
Coordinates: 25°44′27″N 32°36′8″E / 25.74083°N 32.60222°E
| |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.