Josephson phase
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In superconductivity, the Josephson phase is the difference of the phases of the quantum mechanical wave function in two superconducting electrodes forming a Josephson junction.
For example, if the macroscopic wave functions 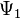 and
and  in superconductors 1 and 2 are given by
in superconductors 1 and 2 are given by
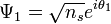

then the Josephson phase is 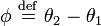 .
.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.