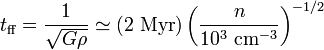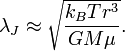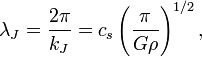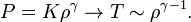Jeans instability
| Star formation |
|---|
 |
| Object classes |
|
Interstellar medium Molecular cloud Bok globule Dark nebula Young stellar object Protostar T Tauri star Herbig Ae/Be star Herbig–Haro object |
| Theoretical concepts |
|
Initial mass function Jeans instability Kelvin–Helmholtz mechanism Nebular hypothesis Planetary migration |
|
|
In physics, the Jeans instability causes the collapse of interstellar gas clouds and subsequent star formation. It occurs when the internal gas pressure is not strong enough to prevent gravitational collapse of a region filled with matter. For stability, the cloud must be in hydrostatic equilibrium, which in case of a spherical cloud translates to:
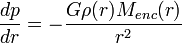 ,
,
where 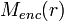 is the enclosed mass,
is the enclosed mass,  is the pressure,
is the pressure, 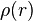 is the density of the gas at
is the density of the gas at  ,
,  is the gravitational constant and
is the gravitational constant and  is the radius. The equilibrium is stable if small perturbations are damped and unstable if they are amplified. In general, the cloud is unstable if it is either very massive at a given temperature or very cool at a given mass for gravity to overcome the gas pressure.
is the radius. The equilibrium is stable if small perturbations are damped and unstable if they are amplified. In general, the cloud is unstable if it is either very massive at a given temperature or very cool at a given mass for gravity to overcome the gas pressure.
Jeans mass
The Jeans mass is named after the British physicist Sir James Jeans, who considered the process of gravitational collapse within a gaseous cloud. He was able to show that, under appropriate conditions, a cloud, or part of one, would become unstable and begin to collapse when it lacked sufficient gaseous pressure support to balance the force of gravity. The cloud is stable for sufficiently small mass (at a given temperature and radius), but once this critical mass is exceeded, it will begin a process of runaway contraction until some other force can impede the collapse. He derived a formula for calculating this critical mass as a function of its density and temperature. The greater the mass of the cloud, the smaller its size, and the colder its temperature, the less stable it will be against gravitational collapse.
The approximate value of the Jeans mass may be derived through a simple physical argument. One begins with a spherical gaseous region of radius  , mass
, mass  , and with a gaseous sound speed
, and with a gaseous sound speed 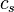 . Imagine that we compress the region slightly. It takes a time,
. Imagine that we compress the region slightly. It takes a time,
for sound waves to cross the region, and attempt to push back and re-establish the system in pressure balance. At the same time, gravity will attempt to contract the system even further, and will do so on a free-fall time,
where  is the universal gravitational constant,
is the universal gravitational constant,  is the gas density within the region, and
is the gas density within the region, and 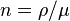 is the gas number density for mean mass per particle
is the gas number density for mean mass per particle 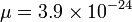 g, appropriate for molecular hydrogen with 20% helium by number. Now, when the sound-crossing time is less than the free-fall time, pressure forces win, and the system bounces back to a stable equilibrium. However, when the free-fall time is less than the sound-crossing time, gravity wins, and the region undergoes gravitational collapse. The condition for gravitational collapse is therefore:
g, appropriate for molecular hydrogen with 20% helium by number. Now, when the sound-crossing time is less than the free-fall time, pressure forces win, and the system bounces back to a stable equilibrium. However, when the free-fall time is less than the sound-crossing time, gravity wins, and the region undergoes gravitational collapse. The condition for gravitational collapse is therefore:
The resultant Jeans length  is approximately:
is approximately:
This length scale is known as the Jeans length. All scales larger than the Jeans length are unstable to gravitational collapse, whereas smaller scales are stable. The Jeans mass  is just the mass contained in a sphere of radius
is just the mass contained in a sphere of radius 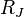 (
(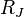 is half the Jeans length):
is half the Jeans length):
It was later pointed out by other astrophysicists that in fact, the original analysis used by Jeans was flawed, for the following reason. In his formal analysis, Jeans assumed that the collapsing region of the cloud was surrounded by an infinite, static medium. In fact, because all scales greater than the Jeans length are also unstable to collapse, any initially static medium surrounding a collapsing region will in fact also be collapsing. As a result, the growth rate of the gravitational instability relative to the density of the collapsing background is slower than that predicted by Jeans' original analysis. This flaw has come to be known as the "Jeans swindle".
The Jeans instability likely determines when star formation occurs in molecular clouds.
Jeans length
Jeans' length is the critical radius of a cloud (typically a cloud of interstellar dust) where thermal energy, which causes the cloud to expand, is counteracted by gravity, which causes the cloud to collapse. It is named after the British astronomer Sir James Jeans, who concerned himself with the stability of spherical nebula in the early 1900s.[1]
The formula for Jeans Length is:
where  is Boltzmann's constant,
is Boltzmann's constant,  is the temperature of the cloud,
is the temperature of the cloud,  is the radius of the cloud,
is the radius of the cloud,  is the mass per particle in the cloud,
is the mass per particle in the cloud,  is the Gravitational Constant and
is the Gravitational Constant and  is the cloud's mass density (i.e. the cloud's mass divided by the cloud's volume).
is the cloud's mass density (i.e. the cloud's mass divided by the cloud's volume).
Perhaps the easiest way to conceptualize Jeans' Length is in terms of a close approximation, in which we discard the factors 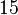 and
and  and in which we rephrase
and in which we rephrase  as
as 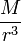 . The formula for Jeans' Length then becomes:
. The formula for Jeans' Length then becomes:
It follows immediately that 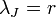 when
when 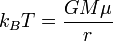 i.e. the cloud's radius is the Jeans' Length when thermal energy per particle equals gravitational work per particle. At this critical length the cloud neither expands nor contracts. It is only when thermal energy is not equal to gravitational work that the cloud either expands and cools or contracts and warms, a process that continues until equilibrium is reached.
i.e. the cloud's radius is the Jeans' Length when thermal energy per particle equals gravitational work per particle. At this critical length the cloud neither expands nor contracts. It is only when thermal energy is not equal to gravitational work that the cloud either expands and cools or contracts and warms, a process that continues until equilibrium is reached.
Jeans' Length as oscillation wavelength
The Jeans' Length is the oscillation wavelength below which stable oscillations rather than gravitational collapse will occur.
where G is the gravitational constant, 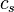 is the sound speed, and
is the sound speed, and  is the enclosed mass density.
is the enclosed mass density.
It is also the distance a sound wave would travel in the collapse time.
Fragmentation
Jeans instability can also give rise to fragmentation in certain conditions. To derive the condition for fragmentation an adiabatic process is assumed in an ideal gas and also a polytropic equation of state is taken. The derivation is showed below through a dimensional analysis:
- For adiabatic processes,
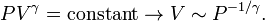
- For an ideal gas,

- Jeans mass,
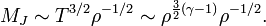
- Thus,
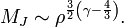
If adiabatic index, 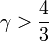 Jeans mass increases with increasing density while if
Jeans mass increases with increasing density while if 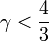 Jeans mass decreases with increasing density. During gravitational collapse density always increases, thus in the second case Jeans mass will decrease during collapse allowing smaller overdense regions to collapse leading to fragmentation of the giant molecular cloud. For an ideal monatomic gas, the adiabatic index is 5/3 but in astrophysical objects this value is usually even lower than 1. So the second case is the rule rather than an exception in stars. This is the reason why stars usually form in clusters.
Jeans mass decreases with increasing density. During gravitational collapse density always increases, thus in the second case Jeans mass will decrease during collapse allowing smaller overdense regions to collapse leading to fragmentation of the giant molecular cloud. For an ideal monatomic gas, the adiabatic index is 5/3 but in astrophysical objects this value is usually even lower than 1. So the second case is the rule rather than an exception in stars. This is the reason why stars usually form in clusters.
See also
- Bonnor–Ebert mass
- Langmuir waves (similar waves in a plasma)
References
- ↑ "The Stability of a Spherical Nebula". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society. 1902. JSTOR 90845.
- Jeans, J. H. (1902). "The Stability of a Spherical Nebula". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 199: 1–53. JSTOR 90845.
- Longair, Malcolm S. (1998). Galaxy Formation. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-63785-0.
- Clarke, Cathie; Carswell, Bob (2007). Astrophysical Fluid Dynamics. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-85331-6.