Iron tetracarbonyl hydride
| Iron tetracarbonyl hydride | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Tetracarbonyldihydroiron[citation needed] | |
| Other names Iron tetracarbonyl dihydride, tetracarbonyldihydroiron[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 12002-28-7 |
| PubChem | 518470 |
| ChemSpider | 452380 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[O+]#[C-].[Fe]|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | FeC 4H 2O 4 |
| Molar mass | 169.901 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Liquid (at -20 °C) |
| Melting point | −70 °C; −94 °F; 203 K |
| Boiling point | −20 °C; −4 °F; 253 K (decomposes) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Iron tetracarbonyl hydride is the organometallic compound with the formula H2Fe(CO)4. Also known as tetracarbonyldihydridoiron, tetracarbonyldihydroiron, or iron tetracarbonyl dihydride, this compound was the first metal hydride discovered. The complex is only stable at low temperatures and decomposes rapidly at temperatures above –20 °C.
Preparation
Iron tetracarbonyl hydride was originally produced by Hieber and Leutert, who developed a two-step process starting from iron pentacarbonyl:[2][3]
- Fe(CO)5 + 2OH- → HFe(CO)4- + HCO3-
- HFe(CO)4- + H+ → H2Fe(CO)4
Current procedures consist of treatment of iron pentacarbonyl with potassium hydroxide and barium hydroxide to yield an orange solution. From this point in the reaction, ideal conditions consist of a cold dark environment, thus dubbing the method the "polar night synthesis".[4] This dark, cold environment stabilizes the dianion species Fe(CO)42-, which is light and temperature sensitive. The orange solution is then treated with sulfuric acid to protonate the anionic intermediate, giving the neutral product.
Structure and properties
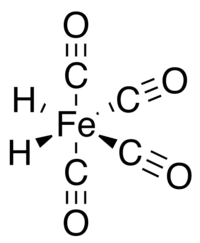
In iron tetracarbonyl hydride the Fe(CO)4 group has C2v molecular symmetry with a geometry intermediate between octahedral and tetrahedral. Viewed as an octahedral complex, the hydride ligands are cis. Viewed as a tetrahedral Fe(CO)4 complex, the hydrides occupy adjacent faces of the tetrahedron.[5] Although the structure of tetracarbonyliron with the hydrogen atoms bound as a single H2 ligand has been proposed as an intermediate in some rearrangement reactions,[6] the stable state for the compound has the two atoms as independent ligands.[7]
Chemistry
Iron tetracarbonyl hydride undergoes rapid ligand substitutions. Upon warming, the complex liberates H2, giving trans tetracarbonyliron.[8]
- H2Fe(CO)4 + PPh3 → H2Fe(CO)3PPh3
- H2Fe(CO)3PPh3 → trans-Fe(CO)3PPh3 + H2
The hydrides in tetracarbonyldihydroiron have a pK1 of 6.8 and pK2 of 15.[9] The monoanion itself has been reviewed extensively.[10] The monoanion is an important intermediate in the water-gas shift reaction (WGSR). The slow step in the iron carbonyl-catalyzed WGSR is the proton transfer from water to the iron hydride anion.[11]
- HFe(CO)4- + H2O → H2Fe(CO)4 + OH-
Another way the complex has been used is for cooperative bimetallic activation of CO2.[12]
- Cp2MoCO2 + H2Fe(CO)4 → Cp2MoHCO+ HFe3(CO)11- + H2O
References
- ↑ SciFinder entry for CAS #12002-28-7, accessed 2012-06-14
- ↑ Hieber, W.; Leutert, F. (1931). "Zur Kenntnis des koordinative gebundene Kohlenoxyds: Bildung von Eisencarbonylwasserstoff". Naturwissenschaften 19 (17): 360. doi:10.1007/BF01522286.
- ↑ Rittmeyer, P.; Wietelmann, U. (2005), "Hydrides", Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, doi:10.1002/14356007.a13_199
- ↑ Vancea, L.; Graham, W.A.G. (1977). "Stereochemically Nonrigid Six-Coordinate Metal Carbonyl Complexes". J. Organomet. Chem. 134 (2): 219. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)81421-7.
- ↑ McNeill, E. A.; Scholer, F. R. (1977). "Molecular structure of the gaseous metal carbonyl hydrides of manganese, iron, and cobalt". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 99 (19): 6243. doi:10.1021/ja00461a011.
- ↑ Soubra, C.; Oishi, Y.; Albright, T. A.; Fujimoto, H. (2001). "Intramolecular Rearrangements in Six-Coordinate Ruthenium and Iron Dihydrides". Inorg. Chem. 40 (4): 620–627. doi:10.1021/ic0006089.
- ↑ Drouin, B. J.; Kukolich, S. G. (1998). "Molecular Structure of Tetracarbonyldihydroiron: Microwave Measurements and Density Functional Theory Calculations". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120 (27): 6774–6780. doi:10.1021/ja9741584.
- ↑ Peason, R. G.; Walker, H. W.; Mauermann, H.; Ford, P.C. (1981). "Hydrogen migration mechanism for ligand substitution reactions in metal carbonyl hydrides". Inorg. Chem. 20 (8): 2741. doi:10.1021/ic50222a078.
- ↑ Walker, H.W.; Kresge, C.T.; Ford, P.C.; Pearson, R. G. (1979). "Rates of Deprotonation and pKa Values of Transition Metal Carbonyl Hydrides". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101 (24): 7428. doi:10.1021/ja00518a061.
- ↑ Brunet, J.J. (1990). "Tetracarbonylhydridoferrates, MHFe(CO)4: Versatile tools in Organic Synthesis and Catalysis". Chem. Rev. 90 (6): 1041. doi:10.1021/cr00104a006.
- ↑ Crabtree R.H.; Mingos D.M.P. 2007. Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry III From Fundamentals to Applications. Elsevier Ltd.
- ↑ Tsai, J.-C.; Khan, M.A.; Nicholas, K.M. (1991). "Reduction of Coordinated Carbon Dioxide by Transition-Metal Hydrides". Organometallics 10: 29. doi:10.1021/om00047a016.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||