Intercondylar eminence
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Intercondyloid eminence | |
|---|---|
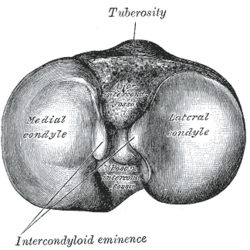 | |
| Upper surface of right tibia. | |
| Latin | Eminentia intercondylaris |
| Gray's | p.256 |
The intercondylar eminence, or tibial spine, is a structure of the tibia.
Anatomy
Between the articular facets of the proximal tibia, but nearer the posterior than the anterior aspect of the bone, is the intercondyloid eminence (intercondylar eminence, spine of tibia), surmounted on either side by a prominent tubercle, on to the sides of which the articular facets are prolonged; in front of and behind the intercondyloid eminence are rough depressions for the attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament and posterior cruciate ligament and the menisci.
Clinical significance
It can be involved in fractures.[1][2]
References
- ↑ Park HJ, Urabe K, Naruse K, Aikawa J, Fujita M, Itoman M (November 2007). "Arthroscopic evaluation after surgical repair of intercondylar eminence fractures". Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 127 (9): 753–7. doi:10.1007/s00402-006-0282-7. ISBN [[Special:BookSources/0040200602827 |0040200602827 [[Category:Articles with invalid ISBNs]] [[Category:Articles with invalid ISBNs]]]] Check
|isbn=value (help). PMID 17310373. - ↑ "Intercondylar Eminence Fracture - Wheeless' Textbook of Orthopaedics". Retrieved 2008-12-04.
External links
- lljoints at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (topoftibia)
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.