Inherent viscosity
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Inherent viscosity is the ratio of the natural logarithm of the relative viscosity to the mass concentration of the polymer.[1]
Inherent viscosity is defined as [2]
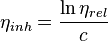
where c is the mass concentration of the polymer (g/dL) and  is the relative viscosity, which is defined as
is the relative viscosity, which is defined as
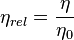 where
where  is the viscosity of the solution and
is the viscosity of the solution and  is the viscosity of the neat solvent.
is the viscosity of the neat solvent.
The unit of inherent viscosity is dL/g.
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.