Imino acid
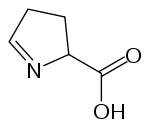
In chemistry, an imino acid is any molecule that contains both imino (>C=NH) and carboxyl (-C(=O)-OH) functional groups.[1]
Imino acids are related to amino acids, which contain both amino (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, differing in the bonding to the nitrogen.
The amino acid oxidase enzymes are able to convert amino acids into imino acids. Also the direct biosynthetic precursor to the amino acid proline is the imino acid (S)-Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate (P5C).
Related terminology
Amino acids containing a secondary amine group (the only proteinogenic amino acid of this type is proline) are sometimes named imino acids,[2][3] though this usage is obsolescent .[1]
The term imino acid is also the obsolete term for imidic acids, containing the -C(=NH)-OH group, and should not be used for them.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "Imino acids".
- ↑ Proline at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ http://opbs.okstate.edu/5753/Amino%20Acids.html
External links
- imino acids at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)


