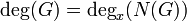Imaginary hyperelliptic curve
A hyperelliptic curve is a particular kind of algebraic curve.
There exist hyperelliptic curves of every genus 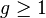 . If the genus of a hyperelliptic curve equals 1, we simply call the curve an elliptic curve. Hence we can see hyperelliptic curves as generalizations of elliptic curves. There is a well-known group structure on the set of points lying on an elliptic curve over some field
. If the genus of a hyperelliptic curve equals 1, we simply call the curve an elliptic curve. Hence we can see hyperelliptic curves as generalizations of elliptic curves. There is a well-known group structure on the set of points lying on an elliptic curve over some field  , which we can describe geometrically with chords and tangents. Generalizing this group structure to the hyperelliptic case is not straightforward. We cannot define the same group law on the set of points lying on a hyperelliptic curve, instead a group structure can be defined on the so-called Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve. The computations differ depending on the number of points at infinity. This article is about imaginary hyperelliptic curves, these are hyperelliptic curves with exactly 1 point at infinity. Real hyperelliptic curves have two points at infinity.
, which we can describe geometrically with chords and tangents. Generalizing this group structure to the hyperelliptic case is not straightforward. We cannot define the same group law on the set of points lying on a hyperelliptic curve, instead a group structure can be defined on the so-called Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve. The computations differ depending on the number of points at infinity. This article is about imaginary hyperelliptic curves, these are hyperelliptic curves with exactly 1 point at infinity. Real hyperelliptic curves have two points at infinity.
Formal definition
Hyperelliptic curves can be defined over fields of any characteristic. Hence we consider an arbitrary field  and its algebraic closure
and its algebraic closure  . An (imaginary) hyperelliptic curve of genus
. An (imaginary) hyperelliptic curve of genus 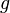 over
over  is given by an equation of the form
is given by an equation of the form
![C:y^{2}+h(x)y=f(x)\in K[x,y]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/5/2/b/252b4fed5ce380e3d65e431df51c2f27.png)
where ![h(x)\in K[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/3/b/c/f3bc4d0e4cbb736b8ec9180b21a4d191.png) is a polynomial of degree not larger than
is a polynomial of degree not larger than 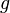 and
and ![f(x)\in K[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/c/2/b/cc2b444b908aa370fabb8e7c785249e3.png) is a monic polynomial of degree
is a monic polynomial of degree 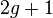 . Furthermore we require the curve to have no singular points. In our setting, this entails that no point
. Furthermore we require the curve to have no singular points. In our setting, this entails that no point  satisfies both
satisfies both 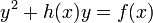 and the equations
and the equations 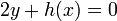 and
and 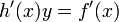 . This definition differs from the definition of a general hyperelliptic curve in the fact that
. This definition differs from the definition of a general hyperelliptic curve in the fact that  can also have degree
can also have degree 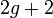 in the general case. From now on we drop the adjective imaginary and simply talk about hyperelliptic curves, as is often done in literature. Note that the case
in the general case. From now on we drop the adjective imaginary and simply talk about hyperelliptic curves, as is often done in literature. Note that the case  corresponds to
corresponds to  being a cubic polynomial, agreeing with the definition of an elliptic curve. If we view the curve as lying in the projective plane
being a cubic polynomial, agreeing with the definition of an elliptic curve. If we view the curve as lying in the projective plane  with coordinates
with coordinates 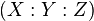 , we see that there is a particular point lying on the curve, namely the point at infinity
, we see that there is a particular point lying on the curve, namely the point at infinity 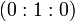 denoted by
denoted by  . So we could write
. So we could write  .
.
Suppose the point 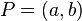 not equal to
not equal to  lies on the curve and consider
lies on the curve and consider  . As
. As 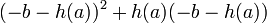 can be simplified to
can be simplified to 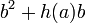 , we see that
, we see that 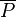 is also a point on the curve.
is also a point on the curve. 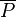 is called the opposite of
is called the opposite of  and
and  is called a Weierstrass point if
is called a Weierstrass point if  , i.e.
, i.e. 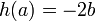 . Furthermore, the opposite of
. Furthermore, the opposite of  is simply defined as
is simply defined as 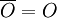 .
.
Alternative definition
The definition of a hyperelliptic curve can be slightly simplified if we require that the characteristic of  is not equal to 2. To see this we consider the change of variables
is not equal to 2. To see this we consider the change of variables  and
and 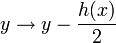 , which makes sense if char
, which makes sense if char . Under this change of variables we rewrite
. Under this change of variables we rewrite 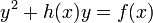 to
to  which, in turn, can be rewritten to
which, in turn, can be rewritten to  . As
. As 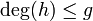 we know that
we know that 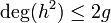 and hence
and hence 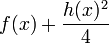 is a monic polynomial of degree
is a monic polynomial of degree 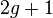 . This means that over a field
. This means that over a field  with char
with char every hyperelliptic curve of genus
every hyperelliptic curve of genus 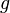 is isomorphic to one given by an equation of the form
is isomorphic to one given by an equation of the form 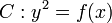 where
where  is a monic polynomial of degree
is a monic polynomial of degree 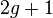 and the curve has no singular points. Note that for curves of this form it is easy to check whether the non-singularity criterion is met. A point
and the curve has no singular points. Note that for curves of this form it is easy to check whether the non-singularity criterion is met. A point 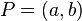 on the curve is singular if and only if
on the curve is singular if and only if 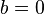 and
and 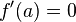 . As
. As 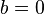 and
and 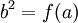 , it must be the case that
, it must be the case that 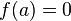 and thus
and thus  is a multiple root of
is a multiple root of  . We conclude that the curve
. We conclude that the curve 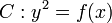 has no singular points if and only if
has no singular points if and only if  has no multiple roots. Even though the definition of a hyperelliptic curve is quite easy when char
has no multiple roots. Even though the definition of a hyperelliptic curve is quite easy when char , we should not forget about fields of characteristic 2 as hyperelliptic curve cryptography makes extensive use of such fields.
, we should not forget about fields of characteristic 2 as hyperelliptic curve cryptography makes extensive use of such fields.
Example
As an example consider 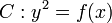 where
where  over
over 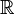 . As
. As  has degree 5 and the roots are all distinct,
has degree 5 and the roots are all distinct,  is a curve of genus
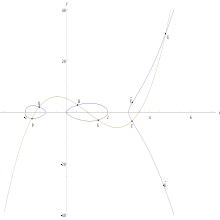
is a curve of genus 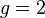 . Its graph is depicted in Figure 1.
. Its graph is depicted in Figure 1.

From this picture it is immediately clear that we cannot use the chords and tangents method to define a group law on the set of points of a hyperelliptic curve. The group law on elliptic curves is based on the fact that a straight line through two points lying on an elliptic curve has a unique third intersection point with the curve. Note that this is always true since  lies on the curve. From the graph of
lies on the curve. From the graph of  it is clear that this does not need to hold for an arbitrary hyperelliptic curve. Actually, Bézout's theorem states that a straight line and a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 intersect in 5 points. So, a straight line through two point lying on
it is clear that this does not need to hold for an arbitrary hyperelliptic curve. Actually, Bézout's theorem states that a straight line and a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 intersect in 5 points. So, a straight line through two point lying on  does not have a unique third intersection point, it has three other intersection points.
does not have a unique third intersection point, it has three other intersection points.
Coordinate ring
The coordinate ring of C over K is defined as
![\;K[C]=K[x,y]/(y^{2}+h(x)y-f(x))](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/b/d/a/1/bda1ff667fe8ebc1455ccb1a97fc81b3.png) .
.
The polynomial  is irreducible over
is irreducible over  , so
, so
is an integral domain.
Proof. If r (x,y) were reducible over  , it would factor as (y - u(x)) · (y - v(x)) for some u,v ∈
, it would factor as (y - u(x)) · (y - v(x)) for some u,v ∈  . But then u(x) · v(x)= f(x) so it has degree 2g + 1, and u(x) + v(x) = h(x) so it has degree smaller than g, which is impossible.
. But then u(x) · v(x)= f(x) so it has degree 2g + 1, and u(x) + v(x) = h(x) so it has degree smaller than g, which is impossible.
Note that any polynomial function 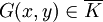 can be written uniquely as
can be written uniquely as
 with
with  ,
,  ∈
∈ ![\overline {K}[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/d/9/1/ad91c07c9874968d383fce9563280779.png)
Norm and degree
The conjugate of a polynomial function G(x,y) = u(x) - v(x)y in ![\overline {K}[C]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/b/3/8/ab384ad52307fc5028e54e94dce0f923.png) is defined to be
is defined to be
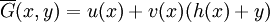 .
.
The norm of G is the polynomial function  . Note that N(G) = u(x)2 + u(x)v(x)h(x) - v(x)2f(x), so N(G) is a polynomial in only one variable.
. Note that N(G) = u(x)2 + u(x)v(x)h(x) - v(x)2f(x), so N(G) is a polynomial in only one variable.
If G(x,y) = u(x) - v(x) · y, then the degree of G is defined as
![\,\deg(G)=\max[2\deg(u),2g+1+2\deg(v)]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/c/5/a/5c5a305212a68e67de7ae6426975e471.png) .
.
Properties:
Function field
The function field K(C) of C over K is the field of fractions of K[C], and the function field 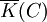 of C over
of C over  is the field of fractions of
is the field of fractions of ![\overline {K}[C]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/b/3/8/ab384ad52307fc5028e54e94dce0f923.png) . The elements of
. The elements of 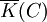 are called rational functions on C.
For R such a rational function, and P a finite point on C, R is said to be defined at P if there exist polynomial functions G, H such that R = G/H and H(P) ≠ 0, and then the value of R at P is
are called rational functions on C.
For R such a rational function, and P a finite point on C, R is said to be defined at P if there exist polynomial functions G, H such that R = G/H and H(P) ≠ 0, and then the value of R at P is
 .
.
For P a point on C that is not finite, i.e. P =  , we define R(P) as:
, we define R(P) as:
- If
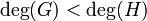 then
then 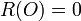 , i.e. R has a zero at O.
, i.e. R has a zero at O. - If
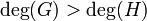 then
then 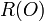 is not defined, i.e. R has a pole at O.
is not defined, i.e. R has a pole at O. - If
 then
then 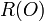 is the ratio of the leading coefficients of G and H.
is the ratio of the leading coefficients of G and H.
For  and
and 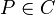 ,
,
- If
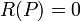 then R is said to have a zero at P,
then R is said to have a zero at P, - If R is not defined at P then R is said to have a pole at P, and we write
 .
.
Order of a polynomial function at a point
For ![G=u(x)-v(x)\cdot y\in \overline {K}[C]^{2}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/a/3/7/5a37133677590496f5c5cd8663288c06.png) and
and 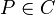 , the order of G at P is defined as:
, the order of G at P is defined as:
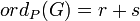 if P = (a,b) is a finite point which is not Weierstrass. Here r is the highest power of (x-a) which divides both u(x) and v(x). Write G(x,y) = (x - a)r(u0(x) - v0(x)y) and if u0(a) - v0(a)b = 0, then s is the highest power of (x - a) which divides N(u0(x) - v0(x)y) = u02 + u0v0h - v02f, otherwise, s = 0.
if P = (a,b) is a finite point which is not Weierstrass. Here r is the highest power of (x-a) which divides both u(x) and v(x). Write G(x,y) = (x - a)r(u0(x) - v0(x)y) and if u0(a) - v0(a)b = 0, then s is the highest power of (x - a) which divides N(u0(x) - v0(x)y) = u02 + u0v0h - v02f, otherwise, s = 0.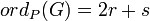 if P = (a,b) is a finite Weierstrass point, with r and s as above.
if P = (a,b) is a finite Weierstrass point, with r and s as above.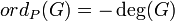 if P = O.
if P = O.
The divisor and the Jacobian
In order to define the Jacobian, we first need the notion of a divisor. Consider a hyperelliptic curve  over some field
over some field  . Then we define a divisor
. Then we define a divisor  to be a formal sum of points in
to be a formal sum of points in  , i.e.
, i.e. ![D=\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/4/d/2/14d247758d7cb461f30eac6f9128f141.png) where
where  and furthermore
and furthermore  is a finite set. This means that a divisor is a finite formal sum of scalar multiples of points. Note that there is no simplification of
is a finite set. This means that a divisor is a finite formal sum of scalar multiples of points. Note that there is no simplification of ![c_{P}[P]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/7/5/d/575d2d99be5fbf6432c8481e4b0aa145.png) given by a single point (as one might expect from the analogy with elliptic curves). Furthermore we define the degree of
given by a single point (as one might expect from the analogy with elliptic curves). Furthermore we define the degree of  as
as  . The set of all divisors
. The set of all divisors 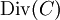 of the curve
of the curve  forms an Abelian group where the addition is defined pointwise as follows
forms an Abelian group where the addition is defined pointwise as follows ![\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}[P]}+\sum _{{P\in C}}{d_{P}[P]}=\sum _{{P\in C}}{(c_{P}+d_{P})[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/b/d/e/fbde7fdca1b678f6c491630037378b68.png) . It is easy to see that
. It is easy to see that ![0=\sum _{{P\in C}}{0[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/a/5/d/ca5d336a6b09fa0c0f7a64ec78815e90.png) acts as the identity element and that the inverse of
acts as the identity element and that the inverse of ![\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/9/5/1/6951d2de6b094b511a22de7c00a15d4d.png) equals
equals ![\sum _{{P\in C}}{-c_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/0/1/7/4017868e3b4d61856500983cc2fce86f.png) . The set
. The set  of all divisors of degree 0 can easily be checked to be a subgroup of
of all divisors of degree 0 can easily be checked to be a subgroup of 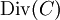 .
.
Proof. Consider the map  defined by
defined by  , note that
, note that  forms a group under the usual addition. Then
forms a group under the usual addition. Then ![\varphi (\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}[P]}+\sum _{{P\in C}}{d_{P}[P]})=\varphi (\sum _{{P\in C}}{(c_{P}+d_{P})[P]})=\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}+d_{P}}=\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{p}}+\sum _{{P\in C}}{d_{p}}=\varphi (\sum _{{P\in C}}{c_{P}[P]})+\varphi (\sum _{{P\in C}}{d_{P}[P]})](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/c/5/e/6c5e295a5c50f51d2346afb083bafe86.png) and hence
and hence  is a group homomorphism. Now,
is a group homomorphism. Now, 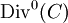 is the kernel of this homomorphism and thus it is a subgroup of
is the kernel of this homomorphism and thus it is a subgroup of 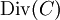 .
.
Consider a function 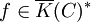 , then we can look at the formal sum div
, then we can look at the formal sum div![(f)=\sum _{{P\in C}}{{\mathrm {ord}}_{{P}}(f)[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/6/4/3/26435ff361b3522fe499922aee8eb938.png) . Here ord
. Here ord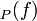 denotes the order of
denotes the order of  at
at  . We have that ord
. We have that ord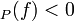 if
if  has a pole of order -ord
has a pole of order -ord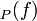 at
at  , ord
, ord if
if  is defined and non-zero at
is defined and non-zero at  and ord
and ord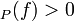 if
if  has a zero of order ord
has a zero of order ord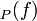 at
at  .[1] It can be shown that
.[1] It can be shown that  has only a finite number of zeroes and poles,[2] and thus only finitely many of the ord
has only a finite number of zeroes and poles,[2] and thus only finitely many of the ord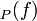 are non-zero. This implies that div
are non-zero. This implies that div is a divisor. Moreover, as
is a divisor. Moreover, as  ,[2] it is the case that div
,[2] it is the case that div is a divisor of degree 0. Such divisors, i.e. divisors coming from some rational function
is a divisor of degree 0. Such divisors, i.e. divisors coming from some rational function  , are called principal divisors and the set of all principal divisors
, are called principal divisors and the set of all principal divisors  is a subgroup of
is a subgroup of 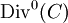 .
.
Proof. The identity element ![0=\sum _{{P\in C}}{0[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/a/5/d/ca5d336a6b09fa0c0f7a64ec78815e90.png) comes from a constant function which is non-zero. Suppose
comes from a constant function which is non-zero. Suppose ![D_{1}=\sum _{{P\in C}}{{\mathrm {ord}}_{{P}}(f)[P]},D_{2}=\sum _{{P\in C}}{{\mathrm {ord}}_{{P}}(g)[P]}\in {\mathrm {Princ}}(C)](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/0/e/6/50e65530dd11d6f8b45dea1bf72d53e3.png) are two principal divisors coming from
are two principal divisors coming from  and
and 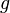 respectively. Then
respectively. Then ![D_{1}-D_{2}=\sum _{{P\in C}}{({\mathrm {ord}}_{{P}}(f)-{\mathrm {ord}}_{P}(g))[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/1/7/3/21734484f1188da5ebb906ad02d9de80.png) comes from the function
comes from the function 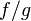 , and thus
, and thus  is a principal divisor, too. We conclude that
is a principal divisor, too. We conclude that  is closed under addition and inverses, making it into a subgroup.
is closed under addition and inverses, making it into a subgroup.
We can now define the quotient group  which is called the Jacobian or the Picard group of
which is called the Jacobian or the Picard group of  . Two divisors
. Two divisors 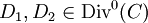 are called equivalent if they belong to the same element of
are called equivalent if they belong to the same element of 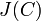 , this is the case if and only if
, this is the case if and only if  is a principal divisor. Consider for example a hyperelliptic curve
is a principal divisor. Consider for example a hyperelliptic curve  over a field
over a field  and a point
and a point 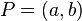 on
on  . For
. For  the rational function
the rational function  has a zero of order
has a zero of order  at both
at both  and
and 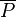 and it has a pole of order
and it has a pole of order  at
at  . Therefore we find div
. Therefore we find div and we can simplify this to div
and we can simplify this to div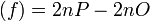 if
if  is a Weierstrass point.
is a Weierstrass point.
Example: the Jacobian of an elliptic curve
For elliptic curves the Jacobian turns out to simply be isomorphic to the usual group on the set of points on this curve, this is basically a corollary of the Abel-Jacobi theorem. To see this consider an elliptic curve  over a field
over a field  . The first step is to relate a divisor
. The first step is to relate a divisor  to every point
to every point  on the curve. To a point
on the curve. To a point  on
on  we associate the divisor
we associate the divisor ![D_{P}=1[P]-1[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/b/0/6/3/b063a29106373d5bc7ca8d8b621c82f5.png) , in particular
, in particular  in linked to the identity element
in linked to the identity element  . In a straightforward fashion we can now relate an element of
. In a straightforward fashion we can now relate an element of 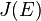 to each point
to each point  by linking
by linking  to the class of
to the class of 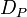 , denoted by
, denoted by ![[D_{P}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/0/1/4/c014ca527719c972b0a89d0b5037fa10.png) . Then the map
. Then the map  from the group of points on
from the group of points on  to the Jacobian of
to the Jacobian of  defined by
defined by ![\varphi (P)=[D_{P}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/9/e/9/9/9e997b9cf46d8bfa6521679fe1bf1cc8.png) is a group homomorphism. This can be shown by looking at three points on
is a group homomorphism. This can be shown by looking at three points on  adding up to
adding up to  , i.e. we take
, i.e. we take  with
with 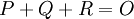 or
or 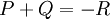 . We now relate the addition law on the Jacobian to the geometric group law on elliptic curves. Adding
. We now relate the addition law on the Jacobian to the geometric group law on elliptic curves. Adding  and
and  geometrically means drawing a straight line through
geometrically means drawing a straight line through  and
and  , this line intersects the curve in one other point. We then define
, this line intersects the curve in one other point. We then define 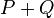 as the opposite of this point. Hence in the case
as the opposite of this point. Hence in the case 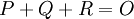 we have that these three points are collinear, thus there is some linear
we have that these three points are collinear, thus there is some linear ![f\in K[x,y]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/5/1/5/7515ee1f3a1bbcd818a6f836609e9265.png) such that
such that  ,
,  and
and  satisfy
satisfy  . Now,
. Now, ![\varphi (P)+\varphi (Q)+\varphi (R)=[D_{P}]+[D_{Q}]+[D_{R}]=[[P]+[Q]+[R]-3[O]]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/8/0/f/e80fa3c7a1d81f7883f9f4e3e3d4535d.png) which is the identity element of
which is the identity element of 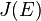 as
as ![[P]+[Q]+[R]-3[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/3/6/9/4/3694b0fd93aa8799e3cd5399f7be047a.png) is the divisor on the rational function
is the divisor on the rational function  and thus it is a principal divisor. We conclude that
and thus it is a principal divisor. We conclude that  .
.
The Abel-Jacobi theorem states that a divisor ![D=\sum _{{P\in E}}{c_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/d/7/0/6d704c75e2829c29e843c8617cca5838.png) is principal if and only if
is principal if and only if  has degree 0 and
has degree 0 and  under the usual addition law for points on cubic curves. As two divisors
under the usual addition law for points on cubic curves. As two divisors  are equivalent if and only if
are equivalent if and only if  is principal, we conclude that
is principal, we conclude that ![D_{1}=\sum _{{P\in E}}{c_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/d/e/3/ade362da98a93297d182c20f04c352d2.png) and
and ![D_{2}=\sum _{{P\in E}}{d_{P}[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/0/e/1/70e1c3d809c183d63cb210ede6074f4b.png) are equivalent if and only if
are equivalent if and only if  . Now, every nontrivial divisor of degree 0 is equivalent to a divisor of the form
. Now, every nontrivial divisor of degree 0 is equivalent to a divisor of the form ![[P]-[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/d/6/2/1/d621c55af76829c2bb9f39edf18b22ce.png) , this implies that we have found a way to ascribe a point on
, this implies that we have found a way to ascribe a point on  to every class
to every class ![[D_{P}]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/0/1/4/c014ca527719c972b0a89d0b5037fa10.png) . Namely, to
. Namely, to ![[D_{P}]=[1[P]-1[O]]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/8/1/5/f815e8aa28c3773571ca59ca132a40a6.png) we ascribe the point
we ascribe the point  . This maps extends to the neutral element 0 which is maped to
. This maps extends to the neutral element 0 which is maped to  . As such the map
. As such the map 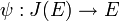 defined by
defined by ![\psi ([D_{P}])=P](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/e/e/b/aeeb3223a12b7c79838d131627d34aef.png) is the inverse of
is the inverse of  . So
. So  is in fact a group isomorphism, proving that
is in fact a group isomorphism, proving that  and
and 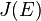 are isomorphic.
are isomorphic.
The Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve
The general hyperelliptic case is a bit more complicated. Consider a hyperelliptic curve  of genus
of genus 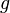 over a field
over a field  . A divisor
. A divisor  of
of  is called reduced if it has the form
is called reduced if it has the form ![D=\sum _{{i=1}}^{{k}}{[P_{i}]}-k[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/3/3/b/0/33b06bd35a246b2deac6aa79a869dc4c.png) where
where  ,
,  for all
for all 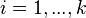 and
and 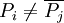 for
for 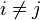 . Note that a reduced divisor always has degree 0, also it is possible that
. Note that a reduced divisor always has degree 0, also it is possible that 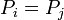 if
if 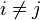 , but only if
, but only if  is not a Weierstrass point. It can be proven that for each divisor
is not a Weierstrass point. It can be proven that for each divisor  there is a unique reduced divisor
there is a unique reduced divisor  such that
such that  is equivalent to
is equivalent to  .[3] Hence every class of the quotient group
.[3] Hence every class of the quotient group 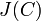 has precisely one reduced divisor. Instead of looking at
has precisely one reduced divisor. Instead of looking at 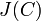 we can thus look at the set of all reduced divisors.
we can thus look at the set of all reduced divisors.
Reduced divisors and their Mumford representation
A convenient way to look at reduced divisors is via their Mumford representation. A divisor in this representation consists of a pair of polynomials ![u,v\in K[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/f/0/9/6f0963e441e7e793d1a230cc6a757b65.png) such that
such that  is monic,
is monic,  and
and 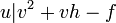 . Every non-trivial reduced divisor can be represented by a unique pair of such polynomials. This can be seen by factoring
. Every non-trivial reduced divisor can be represented by a unique pair of such polynomials. This can be seen by factoring  in
in  which can be done as such as
which can be done as such as  is monic. The last condition on
is monic. The last condition on  and
and  then implies that the point
then implies that the point 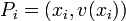 lies on
lies on  for every
for every 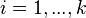 . Thus
. Thus ![D=\sum _{{i=1}}^{{k}}{[P_{i}]}-k[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/3/3/b/0/33b06bd35a246b2deac6aa79a869dc4c.png) is a divisor and in fact it can be shown to be a reduced divisor. For example the condition
is a divisor and in fact it can be shown to be a reduced divisor. For example the condition 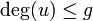 ensures that
ensures that  . This gives the 1-1 correspondence between reduced divisors and divisors in Mumford representation. As an example,
. This gives the 1-1 correspondence between reduced divisors and divisors in Mumford representation. As an example, ![0=\sum _{{P\in C}}{0[P]}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/c/a/5/d/ca5d336a6b09fa0c0f7a64ec78815e90.png) is the unique reduced divisor belonging to the identity element of
is the unique reduced divisor belonging to the identity element of 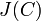 . Its Mumford representation is
. Its Mumford representation is  and
and 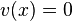 . Going back and forth between reduced divisors and their Mumford representation is now an easy task. For example consider the hyperelliptic curve
. Going back and forth between reduced divisors and their Mumford representation is now an easy task. For example consider the hyperelliptic curve 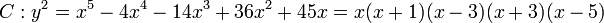 of genus 2 over the real numbers. We can find the following points on the curve
of genus 2 over the real numbers. We can find the following points on the curve  ,
, 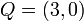 and
and  . Then we can define reduced divisors
. Then we can define reduced divisors ![D=[P]+[Q]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/5/2/7/152717cb0e9aef2d66f9edba4e2483cf.png) and
and ![D'=[P]+[R]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/2/7/b/227b2c2f09be19ec2aba20c82fe8cb20.png) . The Mumford representation of
. The Mumford representation of  consists of polynomials
consists of polynomials  and
and  with
with 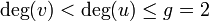 and we know that the first coordinates of
and we know that the first coordinates of  and
and  , i.e. 1 and 3, must be zeroes of
, i.e. 1 and 3, must be zeroes of  . Hence we have
. Hence we have 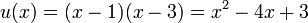 . As
. As 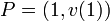 and
and  it must be the case that
it must be the case that  and
and  and thus
and thus  has degree 1. There is exactly one polynomial of degree 1 with these properties, namely
has degree 1. There is exactly one polynomial of degree 1 with these properties, namely 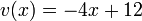 . Thus the Mumford representation of
. Thus the Mumford representation of  is
is  and
and 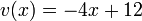 . In a similar fashion we can find the Mumford representation
. In a similar fashion we can find the Mumford representation 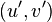 of
of  , we have
, we have 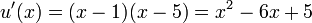 and
and 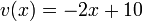 . If a point
. If a point  appears with multiplicity n, the polynomial v needs to satisfy
appears with multiplicity n, the polynomial v needs to satisfy
![\left({\frac {d}{dt}}\right)^{j}\left[v(x)^{2}+v(x)h(x)-f(x)\right]_{{|_{{x=x_{i}}}}}=0](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/2/0/1/42014f41d447aaff0b47039f90d82a22.png) for
for  .
.
Cantor's algorithm
There is an algorithm which takes two reduced divisors  and
and  in their Mumford representation and produces the unique reduced divisor
in their Mumford representation and produces the unique reduced divisor  , again in its Mumford representation, such that
, again in its Mumford representation, such that  is equivalent to
is equivalent to 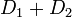 .[4] As every element of the Jacobian can be represented by the one reduced divisor it contains, the algorithm allows to perform the group operation on these reduced divisors given in their Mumford representation. The algorithm was originally developed by David G. Cantor (not to be confused with Cantor), explaining the name of the algorithm. Cantor only looked at the case
.[4] As every element of the Jacobian can be represented by the one reduced divisor it contains, the algorithm allows to perform the group operation on these reduced divisors given in their Mumford representation. The algorithm was originally developed by David G. Cantor (not to be confused with Cantor), explaining the name of the algorithm. Cantor only looked at the case  , the general case is due to Koblitz. The input is two reduced divisors
, the general case is due to Koblitz. The input is two reduced divisors  and
and  in their Mumford representation of the hyperelliptic curve
in their Mumford representation of the hyperelliptic curve  of genus
of genus 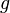 over the field
over the field  . The algorithm works as follows
. The algorithm works as follows
- Using the extended Euclidean algorithm compute the polynomials
![d_{1},e_{1},e_{2}\in K[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/c/1/f/ac1f36969d354fb225c6e4b833887247.png) such that
such that 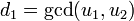 and
and  .
. - Again with the use of the extended Euclidean algorithm compute the polynomials
![d,c_{1},c_{2}\in K[x]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/1/9/0/7190850f27a8fec94b554aabf3c72d84.png) with
with 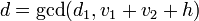 and
and  .
. - Put
 ,
,  and
and 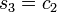 , which gives
, which gives  .
. - Set
 and
and 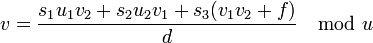 .
. - Set
 and
and 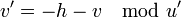 .
. - If
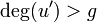 , then set
, then set  and
and 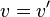 and repeat step 5 until
and repeat step 5 until  .
. - Make
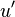 monic by dividing through its leading coefficient.
monic by dividing through its leading coefficient. - Output
 .
.
The proof that the algorithm is correct can be found in
.[5] As an example look again at 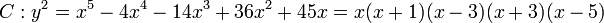 of genus 2 over the real numbers. For the points
of genus 2 over the real numbers. For the points  ,
, 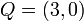 and
and  and the reduced divisors
and the reduced divisors ![D_{1}=[P]+[Q]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/d/a/a/2daaade6287aab1d083607a744e18ee4.png) and
and ![D_{2}=[P]+[R]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/3/3/e/f33ebbeba1dff3f198d47e571ca92afd.png) we know that
we know that 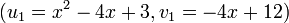 and
and 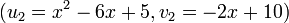 are the Mumford representations of
are the Mumford representations of  and
and  respectively. We can compute their sum using Cantor's algorithm. We begin by computing
respectively. We can compute their sum using Cantor's algorithm. We begin by computing  and
and  for
for  and
and 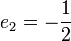 . In the second step we find
. In the second step we find  and
and  for
for 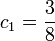 and
and  . Now we can compute
. Now we can compute  ,
, 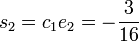 and
and 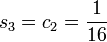 . So
. So  and
and 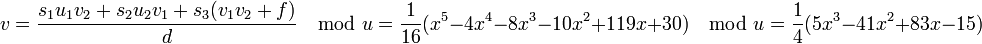 . Lastly we find
. Lastly we find 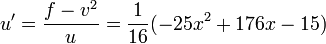 and
and 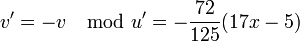 and after making
and after making 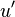 monic we conclude that
monic we conclude that  is equivalent to
is equivalent to 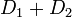 .
.
Cantor's algorithm as presented here has a general form, it holds for hyperelliptic curves of any genus and over any field. However, the algorithm is not very efficient. For example, it requires the use of the extended Euclidean algorithm. If we fix the genus of the curve or the characteristic of the field (or both), we can make the algorithm more efficient. For some special cases we even get explicit addition and doubling formulas which are very fast. For example, there are explicit formulas for hyperelliptic curves of genus 2[6]
[7]
and genus 3.
For hyperelliptic curves it is also fairly easy to visualize the adding of two reduced divisors. Suppose we have a hyperelliptic curve of genus 2 over the real numbers of the form 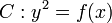 and two reduced divisors
and two reduced divisors ![D_{1}=[P]+[Q]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/d/a/a/2daaade6287aab1d083607a744e18ee4.png) and
and ![D_{2}=[R]+[S]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/9/7/f/9/97f92efa9ec257779bd8705ca28f8586.png) . Assume that
. Assume that  , this case has to be treated separately. There is exactly 1 cubic polynomial
, this case has to be treated separately. There is exactly 1 cubic polynomial  going through the four points
going through the four points 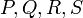 . Note here that it could be possible that for example
. Note here that it could be possible that for example 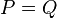 , hence we must take multiplicities into account. Putting
, hence we must take multiplicities into account. Putting 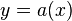 we find that
we find that  and hence
and hence 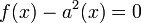 . As
. As 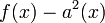 is a polynomial of degree 6, we have that
is a polynomial of degree 6, we have that 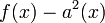 has six zeroes and hence
has six zeroes and hence  has besides
has besides  two more intersection points with
two more intersection points with  , call them
, call them  and
and  , with
, with  . Now,
. Now,  are intersection points of
are intersection points of  with an algebraic curve. As such we know that the divisor
with an algebraic curve. As such we know that the divisor ![D=[P]+[Q]+[R]+[S]+[T]+[U]-6[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/9/2/c/a92c233cbbdb49ebadc2e1384ae28739.png) is principal which implies that the divisor
is principal which implies that the divisor ![[P]+[Q]+[R]+[S]-4[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/2/b/c/12bc8dd3b642af7d08912bb86f5d5c19.png) is equivalent to the divisor
is equivalent to the divisor ![-([T]+[U]-2[O])](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/3/c/d/23cd2cfc1b324a599927b8e89bd005b7.png) . Furthermore the divisor
. Furthermore the divisor ![[P]+[\overline {P}]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/4/7/6/e476172c3527eac22364e0f6e6b44374.png) is principal for every point
is principal for every point 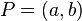 on
on  as it comes from the rational function
as it comes from the rational function  . This gives that
. This gives that ![-([P]-[O])](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/8/a/3/f8a31fe516efe6bcec2ad01e481f74b7.png) and
and ![[\overline {P}]-[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/f/8/5/ff85c11ae143b16779b433062fd77e9c.png) are equivalent. Combining these two properties we conclude that
are equivalent. Combining these two properties we conclude that ![D_{1}+D_{2}=([P]+[Q]-2[O])+([R]+[S]-2[O])](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/3/2/2/7322197af11845c6067267ce8658c7af.png) is equivalent to the reduced divisor
is equivalent to the reduced divisor ![[\overline {T}]+[\overline {U}]-2[O]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/f/4/5/5f450923722238563396daf46fdfd8f1.png) . In a picture this looks like Figure 2. It is possible to explicitly compute the coefficients of
. In a picture this looks like Figure 2. It is possible to explicitly compute the coefficients of  , in this way we can arrive at explicit formulas for adding two reduced divisors.
, in this way we can arrive at explicit formulas for adding two reduced divisors.
References
- ↑ Isabelle Déchène, The Picard Group, or how to build a group from a set
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Alfred J. Menezes, Yi-Hong Wu, Robert J. Zuccherato, An elementary introduction to hyperelliptic curves, page 15
- ↑ Alfred J. Menezes, Yi-Hong Wu, Robert J. Zuccherato, An elementary introduction to hyperelliptic curves, page 20
- ↑ Alfred J. Menezes, Yi-Hong Wu, Robert J. Zuccherato, An elementary introduction to hyperelliptic curves, page 22–27
- ↑ D. Cantor (1987). "Computing in the Jacobian of a hyperelliptic curve". Mathematics of Computation 48: 95–101. doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-1987-0866101-0.
- ↑ Frank Leitenberger, About the Group Law for the Jacobi Variety of a Hyperelliptic Curve
- ↑ T. Lange (2005). "Formulae for Arithmetic on Genus $2$ Hyperelliptic Curves". Applicable Algebra in Engineering, Communication and Computing (AAECC) 15: 295–328. doi:10.1007/s00200-004-0154-8.
![\overline {K}[C]=\overline {K}[x,y]/(y^{2}+h(x)y-f(x))](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/9/5/d/d/95dd2bb49e0b3a259b87958163be2d6c.png)