Hypochondrium
| Hypochondrium | |
|---|---|
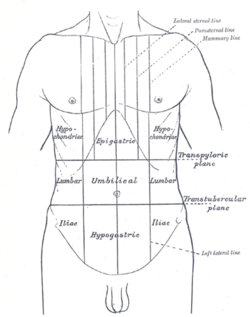 | |
| Thorax and abdomen. This image shows an older definition of hypochondrium, where it is the abdominal region inferior to (beneath) the lowest ribs of the thorax. | |
 | |
| Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for liver, stomach, and great intestine. | |
| Latin | regio hypochondriaca |
| Gray's | subject #246 1149 |
The hypochondrium is the upper part of the abdomen interior to the lowest ribs of the thorax.[1] The word derives from Greek: ὑποχονδρος: hupochondros, meaning abdomen, or literally under cartilage.
The liver is found in the right hypochondrium.
Controversies
Some sources have disputed usage of the term to the parts of the anterior abdominal wall below the costal margins. The region named the right hypochondrium exists anatomically, but is almost totally under the chest wall. In clinical situations, the part of the abdominal wall just below the right and left costal margins are referred to as the right and left hypochondriac regions respectively. Clinically speaking, symptoms and signs arising from this region are of great importance and have a specific list of diseases in their differential diagnoses.[2]
See also
Additional images
-
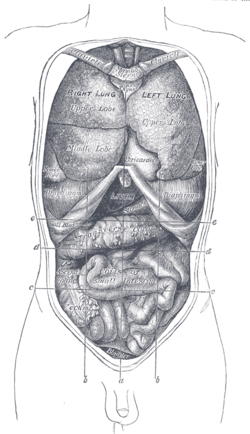
Front view of the thoracic and abdominal viscera
References
- ↑ thefreedictionary.com
- ↑ M. Aroon Kamath, M.D.. The right hypochondrium… Is it really “right”? A territorial dispute. Doctors Lounge Website. Available at: http://www.doctorslounge.com/index.php/blogs/page/13346. Accessed August 18 2010.
External links
- Abdominal Viscera Basics - Page 1 of 10 anatomy module at med.umich.edu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||