Hybrid automaton
In automata theory, a hybrid automaton (plural: hybrid automata or hybrid automatons) is a mathematical model for precisely describing systems in which digital computational processes interact with analog physical processes. A hybrid automaton is a finite state machine with a finite set of continuous variables whose values are described by a set of ordinary differential equations. This combined specification of discrete and continuous behaviors enables dynamic systems that comprise both digital and analog components to be modeled and analyzed.
Examples
A simple example is a room-thermostat-heater system where the temperature of the room evolves according to laws of thermodynamics and the state of the heater (on/off); the thermostat senses the temperature, performs certain computations and turns the heater on and off. In general, hybrid automata have been used to model and analyze a variety of embedded systems including vehicle control systems, air traffic control systems, mobile robots, and processes from systems biology.
Formal Definition
An Alur-Henzinger hybrid automaton 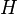 comprises the following components:[1]
comprises the following components:[1]
- A finite set
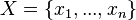 of real-numbered variables. The number
of real-numbered variables. The number  is called the dimension of
is called the dimension of 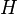 . Let
. Let  be the set
be the set  of dotted variables that represent first derivatives during continuous change, and let
of dotted variables that represent first derivatives during continuous change, and let 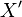 be the set
be the set 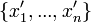 of primed variables that represent values at the conclusion of discrete change.
of primed variables that represent values at the conclusion of discrete change. - A finite multidigraph
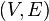 . The vertices in
. The vertices in  are called control modes. The edges in
are called control modes. The edges in  are called control switches.
are called control switches. - Three vertex labeling functions init, inv, and flow that assign to each control mode
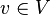 three predicates. Each initial condition init
three predicates. Each initial condition init is a predicate whose free variables are from
is a predicate whose free variables are from  . Each invariant condition inv
. Each invariant condition inv is a predicate whose free variables are from
is a predicate whose free variables are from  . Each flow condition flow
. Each flow condition flow is a predicate whose free variables are from
is a predicate whose free variables are from 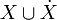 .
.
So this is a labeled multidigraph.
- An edge labeling function jump that assigns to each control switch
 a predicate. Each jump condition jump
a predicate. Each jump condition jump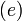 is a predicate whose free variables are from
is a predicate whose free variables are from  .
. - A finite set
 of events, and an edge labeling function event:
of events, and an edge labeling function event: 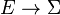 that assigns to each control switch an event.
that assigns to each control switch an event.
Related models
Hybrid automata come in several flavors: The Alur-Henzinger hybrid automaton is a popular model; it was developed primarily for algorithmic analysis of hybrid systems model checking. The HyTech model checking tool is based on this model. The Hybrid Input/Output Automaton model has been developed more recently. This model enables compositional modeling and analysis of hybrid systems. Another formalism which is useful to model implementations of hybrid automaton is the lazy linear hybrid automaton. A sub-class of hybrid automata are timed automata in which all continuous variables have derivative 1. State reachability is decidable for this sub-class, which is why it is an interesting formalism for formal verification.
References
- ↑ Henzinger, T.A. "The Theory of Hybrid Automata". Proceedings of the Eleventh Annual IEEE Symposium on Logic in Computer Science (LICS), pages 278-292, 1996.
Further reading
- Rajeev Alur, Costas Courcoubetis, Nicolas Halbwachs, Thomas A. Henzinger, Pei-Hsin Ho, Xavier Nicollin, Alfredo Olivero, Joseph Sifakis, and Sergio Yovine The algorithmic analysis of hybrid systems. Theoretical Computer Science, volume 138(1), pages 3–34, 1995.
- Nancy Lynch, Roberto Segala, Frits Vaandrager, Hybrid I/O Automata. Information and Computation, volume 185(1), pages 103–157, 2003.