Hurthle cell
| Hürthle cell | |
|---|---|
| Classification and external resources | |
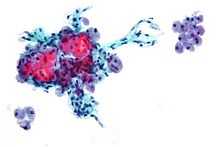 Micrograph showing Hürthle cells in a Hürthle cell neoplasm. Pap stain. | |
| ICD-10 | C73.9 |
| ICD-O: | 8290/0 |
| DiseasesDB | 31956 |
| eMedicine | med/1045 |
| MeSH | D018249 |
A Hürthle cell is a cell in the thyroid that is often associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis[1] as well as follicular thyroid cancer.
Histology
Hürthle cells are characterized as enlarged epithelial cells with abundant eosinophilic granular cytoplasm as a result of altered mitochondria.[2] They generally stain pink and are prominently found in histological sections of thyroid glands affected with Hashimoto's.
Clinical significance
A Hürthle cell adenoma is a type of thyroid benign tumor[3] that, in rare cases, has the potential to become malignant[4] and metastasize (Hürthle cell carcinoma). Hürthle cells are also found in Hashimoto's thyroiditis and toxic and nontoxic nodular goiter. Hürthle cells are hypothesized to be of follicular epithelial origin.
Eponym
It is named for Karl Hürthle.[5][6]
See also
References
- ↑ "Endocrine Pathology". Retrieved 2009-05-07.
- ↑ Aytug, Serhat (June 13, 2006). "Hurthle Cell Carcinoma". eMedicine.
- ↑ "Hürthle cell tumor" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Qian L, Pucci R, Castro CY, Eltorky MA (October 2004). "Renal cell carcinoma metastatic to Hürthle cell adenoma of thyroid". Ann Diagn Pathol 8 (5): 305–8. doi:10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2004.07.011. PMID 15494939.
- ↑ synd/2742 at Who Named It?
- ↑ M. Askanazy. Pathologisch-anatomische Beiträge zur Kenntniss des morbus basedowii, insbesondere uber die dabei auftretende Muskelerkrankkung. Deutsches Archiv für klinische Medicin, Leipzig, 1898, 61:118-186.
External links
- The Doctor's Doctor at thedoctorsdoctor.com
- Illustration at thyroidmanager.org
- EndocrineWeb at endocrineweb.com
- HKU at hku.hk
- Image at upmc.edu
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||