Humboldt Penguin
| Humboldt Penguin | |
|---|---|
 | |
| At Islas Ballestas, Peru | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Sphenisciformes |
| Family: | Spheniscidae |
| Genus: | Spheniscus |
| Species: | S. humboldti |
| Binomial name | |
| Spheniscus humboldti Meyen, 1834 | |
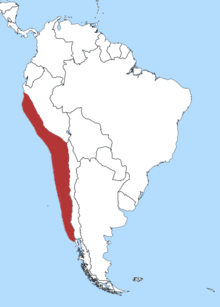 | |
| Distribution of the Humboldt Penguin | |
The Humboldt Penguin (Spheniscus humboldti) (also termed Peruvian Penguin, or Patranca) is a South American penguin, that breeds in coastal Peru and Chile. Its nearest relatives are the African Penguin, the Magellanic Penguin and the Galápagos Penguin. The penguin is named after the cold water current it swims in, which is itself named after Alexander von Humboldt, an explorer.
Humboldt Penguins are medium-sized penguins, growing to 56–70 cm (22–28 in) long and a weight of 3.6-5.9 kg (8-13 lbs).[2][3] They have a black head with a white border that runs from behind the eye, around the black ear-coverts and chin, and joins at the throat. They have blackish-grey upperparts and whitish underparts, with a black breast-band that extends down the flanks to the thigh. They have a fleshy-pink base to the bill. Juveniles have dark heads and no breast-band. They have spines on their tongue which they use to hold their prey.
Range and habitat
Humboldt Penguins nest on islands and rocky coasts, burrowing holes in guano and sometimes using scrapes or caves. In South America the Humboldt Penguin is found only along the Pacific coast,[4] and the range of the Humboldt Penguin overlaps that of the Magellanic Penguin on the central Chilean coast. It is vagrant in Ecuador, Colombia and Argentina.[5]
Conservation
Due to a declining population caused in part by over-fishing, climate change, and ocean acidification, the current status of the Humboldt penguin is threatened,[6] Historically it was the victim of guano over-exploitation. Penguins are also declining in numbers due to habitat destruction. The current population is estimated at between 3,300 and 12,000. In August 2010 the Humboldt penguin of Chile and Peru, was granted protection under the U.S. Endangered Species Act.[6]
Raising of young
In 2009 at a zoo in Bremerhaven, Germany, two adult male Humboldt penguins adopted an egg that had been abandoned by its biological parents. After the egg hatched, the two male penguins raised, protected, cared for, and fed the chick in the same manner that regular penguin couples raise their own biological offspring.
Escape from Tokyo Zoo
One of the 135 Humboldt penguins from Tokyo Sea Life Park (Kasai Rinkai Suizokuen) thrived in Tokyo Bay for 82 days after apparently scaling the 13 feet high wall and through the fence into the bay.[7] The penguin, known only by its number (#337), was recaptured by the zoo keepers in late May 2012.[8]
Gallery
-
-upper_body.jpg)
Upper body
-

Humboldt Penguin Spheniscus Humboldti at Newquay Zoo
-
.jpg)
St Louis Zoo
-

A pair "kissing" at Cotswold Wildlife Park
-

Swimming underwater
-

Back
-

At Dublin Zoo
-
Humboldt Penguin underwater at "Zoo am Meer" Bremerhaven
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2013). "Spheniscus humboldti". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
- ↑ "Invalid license key". .philadelphiazoo.org. Retrieved 2012-02-12.
- ↑ "Humboldt Penguin - Spheniscus humboldti : WAZA : World Association of Zoos and Aquariums". WAZA. Retrieved 2012-02-12.
- ↑ "Humboldt penguins from the International Penguin Conservation Web Site". Penguins.cl. Retrieved 2012-02-12.
- ↑ C. Michael Hogan (2008) Magellanic Penguin, GlobalTwitcher.com, ed. N. Stromberg
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Five Penguins Win U.S. Endangered Species Act Protection Turtle Island Restoration Network
- ↑ 'Escape' into the Tokyo Bay, CNN, May 17, 2012
- ↑
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Spheniscus humboldti. |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||

