Hoplite

Hoplites were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Their main tactic was the phalanx formation. They were primarily free citizens—propertied farmers and artisans—who were able to afford the bronze armor suit and weapons (estimated at a third to a half of its able-bodied adult male population).[1] Hoplites generally received basic military training.
In 690 BC, the Spartan army adopted a military innovation known as the phalanx formation. This new tactic proved successful during the Battle of Marathon in 490 BC and the Battle of Plataea in 479 BC, when the Greeks defeated the Persians. The Persian archers and light troops who fought in the Battle of Marathon failed, in part, because their bows were too weak to penetrate the Greek shields and armour, and their own armour and shields could not stand up to the longer spears and swords of the Greeks.
The word hoplite (Greek: ὁπλίτης hoplitēs; pl. ὁπλίται hoplitai) derives from hoplon (ὅπλον, plural hopla ὅπλα), the type of shield used by the soldiers, although, as a word, hopla could also denote the soldiers' weapons or even their full armament.[2] In later usage, the term hoplite is used to denote any armored infantry such as the Swiss mercenaries during the Burgundian Wars (1474–1477).
History

Ancient Greece
The exact time when hoplitic warfare was developed is uncertain, the prevalent theory being that it was established sometime during the 8th or 7th century BC, when the "heroic age was abandoned and a far more disciplined system introduced" and the Argive shield became popular.[3] Peter Krentz argues that "the ideology of hoplitic warfare as a ritualized contest developed not in the 7th century [BC], but only after 480, when non-hoplite arms began to be excluded from the phalanx".[4] Anagnostis Agelarakis based on recent archaeo-anthropological discoveries of the earliest monumental polyandrion (communal burial of male warriors) at Paros Island in Greece, unveils a last quarter of the 8th century BC date for a hoplitic phalangeal military organization.[5]
The rise and fall of hoplite warfare was tied to the rise and fall of the city-state. As discussed above, hoplites were a solution to the armed clashes between independent city-states. As Greek civilization found itself confronted by the world at large, particularly the Persians, the emphasis in warfare shifted. Confronted by huge numbers of enemy troops, individual city-states could not realistically fight alone. During the Greco-Persian Wars (499–448 BC), alliances between groups of cities (whose composition varied over time) fought against the Persians. This drastically altered the scale of warfare and the numbers of troops involved. The hoplite phalanx proved itself far superior to the Persian infantry at such conflicts as the Battle of Marathon, Thermopylae, and the Battle of Plataea.

During this period, Athens and Sparta rose to a position of political eminence in Greece, and their rivalry in the aftermath of the Persian wars brought Greece into renewed internal conflict. However, the Peloponnesian War was on a scale unlike conflicts before. Fought between leagues of cities, dominated by Athens and Sparta respectively, the pooled manpower and financial resources allowed a diversification of warfare. Hoplite warfare was in decline; there were three major battles in the Peloponnesian War, and none proved decisive. Instead there was increased reliance on navies, skirmishers, mercenaries, city walls, siege engines, and non-set piece tactics. These reforms made wars of attrition possible and greatly increased the number of casualties. In the Persian war, hoplites faced large numbers of skirmishers and missile-armed troops, and such troops (e.g., Peltasts) became much more commonly used by the Greeks during the Peloponnesian War. As a result, hoplites began wearing less armour, carrying shorter swords, and in general adapting for greater mobility; this led to the development of the ekdromoi light hoplite.
Many famous personalities, philosophers, artists, and poets fought as hoplites.[6][7]
Sparta
Sparta is the most famous city-state which had a unique position in ancient Greece. Contrary to other city states, the free citizens of Sparta served as hoplites their entire life, training and exercising also in peacetime, which gave Sparta a professional standing army. Although small, numbering no more than 1,500 to 2,000 men, divided into six mora or battalions, the Spartan army was feared for its discipline and ferocity. Military service was the primary duty of Spartan men, and Spartan society was organized around its army.
Young boys were sent to military school at the age of 7 until the age of 21 when they became full soldiers and moved into their own barracks. These boys who made it endured physical, mental, and spiritual training throughout their education. It is said they were often instructed by their teachers to fight one another. Since the Spartan diet was meagre and not very tasty, stealing food was a necessity, and when caught, the boy would be punished for being captured rather than for stealing. Their graduation included having to live in the wild for a week and killing a slave.
Military service for hoplites lasted until the age of 40, and sometimes even until 60 years of age, depending on a man's physical ability to perform in the battlefield.
Macedonia
Later on in the hoplite era, more sophisticated tactics were developed, in particular by the Theban general Epaminondas. These tactics inspired the future king Philip II of Macedon, who was at the time a hostage in Thebes, and also inspired the development of new kind of infantry, the Macedonian phalanx. After the Macedonian conquests of the 4th century BC, the hoplite was slowly abandoned in favour of the phalangite, armed in the Macedonian fashion, in the armies of the southern Greek states. Although clearly a development of the hoplite, the Macedonian phalanx was tactically more versatile, especially used in the combined arms tactics favoured by the Macedonians. These forces defeated the last major hoplite army, at the Battle of Chaeronea (338 BC), after which Athens and its allies joined the Macedonian empire.
Warfare
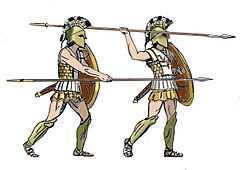
The fragmentary nature of Ancient Greece, with many competing city-states, increased the frequency of conflict, but conversely limited the scale of warfare. Limited manpower did not allow most Greek city-states to form large armies which could operate for long periods, especially in the case of light troops like the psiloi, who were recruited from the lower citizen classes, and as such, they were mainly farmers, workers, even slaves.[citation needed] They were expected to take part in any military campaign when they would be called for duty. The Lacedaemonian citizens of Sparta were renowned for their lifelong combat training and almost mythical military prowess, while their greatest adversaries, the Athenians, were exempted from service only after the 60th year of their lives. This inevitably reduced the potential duration of campaigns, as a large portion of any Greek army would need to return to their own professions as farmers and artisans. Campaigns would therefore often be restricted to summer. Armies marched directly to their target, the battlefield having possibly already been agreed on by the contestants.
If battle was refused by the defender, they would generally retreat to their city, in which case the attackers generally had to content themselves with ravaging the surrounding countryside, since siegecraft was not efficient, at least until the 5th century BC.[citation needed] When battles occurred, they were usually set piece and intended to be decisive. The battlefield would be flat and open to facilitate phalanx warfare. These battles were usually short and required a high degree of discipline. At least in the early classical period, cavalry was usually used to protect the flanks, when present at all, and cover a possible retreat. Light infantry and missile troops took part in the battle, but their role was of a lower importance.
The military structure created by the Spartans was a rectangular phalanx formation. The formation was organized from eight to ten rows deep, stretching down for about a quarter of a mile or more with well heavily armed fighters fighting in a unit. The phalanxes would approach each other in a steady, slow march to keep cohesion or rarely at a run,[citation needed] if the enemy was prone to panic, or if they fought against enemies equipped with bows, as was the case with the Persians at the Battle of Marathon. The two lines would remain at a small distance to be able to effectively use their spears, while the psiloi threw stones and javelins from behind their lines. If the doratismos (spear combat) was not decisive, then the lines would close and swords would be drawn.[citation needed] The shields would clash and the first lines (protostates) would stab at their opponents, at the same time trying to keep in position. The ranks behind them would support them with their own spears and the mass of their shields gently pushing them, not to force them into the enemy formation but to keep them steady and in place.[citation needed] At certain points, a command would be given to the phalanx or a part thereof to collectively take a certain number of steps forward (ranging from half to multiple steps). This was the famed othismos.[8][citation needed]

At this point, the phalanx would put its collective weight to push back the enemy line and thus create fear and panic among its ranks. There could be multiple such instances of attempts to push, but it seems from the accounts of the ancients that these were perfectly orchestrated and attempted organized en masse.[citation needed] Battles rarely lasted more than an hour.[citation needed] Once one of the lines broke, the troops would generally flee from the field, sometimes chased by psiloi, peltasts, or light cavalry.
If a hoplite escaped, he would sometimes be forced to drop his cumbersome aspis, thereby disgracing himself to his friends and family (becoming a ripsaspis, one who threw his shield).[9] To lessen the amount of casualties inflicted by the enemy during battles, soldiers were positioned to stand shoulder to shoulder with their hoplon. Casualties were slight compared to later battles, rarely amounting to more than 5% of the losing side,[citation needed] but the slain often included the most prominent citizens and generals who led from the front. Thus, the whole war could be decided by a single field battle; victory was enforced by ransoming the fallen back to the defeated, called the "Custom of the Greeks".
Individual hoplites carried their shields on their left arm, protecting not only themselves but also the soldier to the left. This meant that the men at the extreme right of the phalanx were only half-protected. In battle, opposing phalanxes would exploit this weakness by attempting to overlap the enemy's right flank.[citation needed] It also meant that, in battle, a phalanx would tend to drift to the right (as hoplites sought to remain behind the shield of their neighbour). The most experienced hoplites were often placed on the right side of the phalanx, to counteract these problems. According to Plutarch's Sayings of Spartans, "a man carried a shield for the sake of the whole line".[10]
The phalanx is an example of a military formation in which single combat and other individualistic forms of battle were suppressed for the good of the whole. In earlier Homeric combat, the words and deeds of supremely powerful heroes turned the tide of battle. With his friends jostling and pushing on both sides and behind, and his enemies forming a solid wall in front of him, the hoplite had little opportunity for feats of technique and weapon skill, but great need for commitment and mental toughness. By forming a human wall to provide a powerful defensive armour, the Hoplites became invincible in the battlefield. The Hoplites were elite soldiers with much disciplined and taught to be loyal and trustworthy. They had to trust their neighbours for mutual protection, so a phalanx was only as strong as its weakest elements. Its effectiveness depended on how well the hoplites could maintain this formation while in combat, and how well they could stand their ground, especially when engaged against another phalanx. The more disciplined and courageous the army, the more likely it was to win—often engagements between the various city-states of Greece would be resolved by one side fleeing before the battle. The Greek word dynamis, "will" or "ability to fight", was used to express the drive that kept hoplites in formation.[citation needed]
Equipment

Each hoplite provided his own equipment. Thus, only those who could afford such weaponry fought as hoplites; as with the Roman Republican army it was the middle classes who formed the bulk of the infantry. Equipment was not standardised, although there were doubtless trends in general designs over time, and between city-states. Hoplites had customized armour, the shield was decorated with family or clan emblems, although in later years these were replaced by symbols or monograms of the city states. The equipment might well be passed down in families, since it would have been expensive to manufacture.
The Hoplite army consisted of heavily armored infantrymen. Their armour, also called panoply, was made of full bronze, weighing nearly 32 kilograms (70 lb). The average farmer-peasant hoplite typically wore no armour, carrying only a shield, a spear, and perhaps a helmet plus a secondary weapon. Some hoplite spears were 9 feet long (2.7 m). A more well-to-do hoplite would have linothorax (sometimes called a cuirass), armour composed of stitched/laminated linen fabrics that was sometimes reinforced with animal skins and/or bronze scales.[citation needed] The linothorax was the most popular type armour worn by the hoplites, since it was cost-effective and provided decent protection. The richer upper-class hoplites typically had a bronze cuirass of either the bell or muscled variety, a bronze helmet with cheekplates, as well as greaves and other armour. The design of the helmets used varied through time. The Corinthian helmet was at first standardised and was a very successful design. Later variants included the Chalcidian helmet, a lightened version of the Corinthian helmet, and the very simple Pilos helmet worn by the later hoplites. Often the helmet was decorated with one, sometimes more horsehair crests, and/or bronze animal horns and ears. Helmets were often painted as well. The Thracian helmet had a large visor to further increase protection. In later periods, linen breastplates called linothorax were used, as they were tougher and cheaper to make. The linen was 0.5-centimetre (0.20 in) thick. Hoplites carried a large concave shield called an aspis (often referred to as a hoplon) made from wood and covered in bronze, measuring roughly 1 metre in diameter and weighing about 16 pounds.[11] This large shield was made possible partly by its shape, which allowed it to be supported on the shoulder. The revolutionary part of the shield was, in fact, the grip. Known as an Argive grip, it placed the handle at the edge of the shield, and was supported by a leather fastening (for the forearm) at the centre. This allowed the hoplite soldier more mobility with the shield, as well as the ability to capitalize on its offensive capabilities and better support the Phalanx. It rested on a man's shoulders, stretching down the knees. These large shields were designed for pushing ahead and was the most essential equipment for the Hoplites.[12]

The main offensive weapon used was an 8 to 15 foot long and an inch in diameter spear called a doru, or dory. It was held with the right hand, the other hand holding the hoplite's shield. Soldiers usually held their spears in an underhand position when approaching but once they came into close contact with their opponents, they were held in an overhand position ready to strike. The spearhead was usually a curved leaf shape, while the rear of the spear had a spike called a sauroter ("lizard-killer") which was used to stand the spear in the ground (hence the name). It was also used as a secondary weapon if the main shaft snapped, or for the rear ranks to finish off fallen opponents as the phalanx advanced over them. In addition to being used as a secondary weapon, the sauroter also doubled to balance the spear, but not for throwing purposes. It is a matter of contention, among historians, whether the hoplite used the spear overarm or underarm. Held underarm, the thrusts would have been less powerful but under more control, and vice versa. It seems likely that both motions were used, depending on the situation. If attack was called for, an overarm motion was more likely to break through an opponent's defence. The upward thrust is more easily deflected by armour due to its lesser leverage. However, when defending, an underarm carry absorbed more shock and could be 'couched' under the shoulder for maximum stability. It should also be said that an overarm motion would allow more effective combination of the aspis and doru if the shield wall had broken down, while the underarm motion would be more effective when the shield had to be interlocked with those of one's neighbours in the battle-line. Hoplites in the rows behind the lead would almost certainly have made overarm thrusts. The rear ranks held their spears underarm, and raised their shields upwards at increasing angles. This was an effective defence against missiles, deflecting their force.
Hoplites also carried a sword, mostly a short sword called a xiphos, but later also longer and heavier types. The short sword was a secondary weapon, used if or when their spears were broken or lost, or if the phalanx broke rank. The xiphos usually had a blade around 2 feet (0.61 m) long, however those used by the Spartans were often only 12–18 inches long. This very short xiphos would be very advantageous in the press that occurred when two lines of hoplites met, capable of being thrust through gaps in the shieldwall into an enemy's unprotected groin or throat, while there was no room to swing a longer sword. Such a small weapon would be particularly useful after many hoplites had started to abandon body armour during the Peloponnesian War. Hoplites could also alternatively carry the kopis, a heavy knife with a forward-curving blade.
By contrast with hoplites, other contemporary infantry (e.g., Persian) tended to wear relatively light armour, use wicker shields, and were armed with shorter spears, javelins, and bows. The most famous are the Peltasts, light-armed troops who wore no armour and were armed with a light shield, javelins and a short sword. The Athenian general Iphicrates developed a new type of armour and arms for his mercenary army, which included light linen armour, smaller shields and longer spears, whilst arming his peltasts with larger shields, helmets and a longer spear, thus enabling them to defend themselves easier against enemy hoplites. With this new type of army he defeated a Spartan army in 392 BC. Nevertheless, most hoplites stuck to the traditional arms and armour.
References
- Notes
- ↑ Gat, Azar (2006). War in Human Civilization. New York, NY: Oxford University Press. pp. 295–298. ISBN 978-0199236633.
- ↑ Diodorus Siculus, 15.44.3 "hoi [men] proteron apo tôn aspidôn hoplitai kaloumenoi tote [de] apo tês peltês peltastai metônomasthêsan"
- ↑ Peter Connoly, Greece and Rome at War, p.37.
- ↑ Peter Krentz, Fighting by the Rules – The Invention of the Hoplite Agon.
- ↑ F. Zafeiropoulou and A. Agelarakis, “Warriors of Paros”, Archaeology 58.1(2005): 30–35
- ↑ Socrates as a hoplite: Plato, Symposium 219e–221b.
- ↑ Epicurus as a hoplite: Diogenes Laertius, Lives of Eminent Philosophers, Book X.
- ↑ othismos. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ↑ ripsaspis. Liddell, Henry George; Scott, Robert; A Greek–English Lexicon at the Perseus Project.
- ↑ Hanson, Victor Davis (1993). Hoplites: Classical Greek Battle Experience. Routledge. p. 303.
- ↑ Zimmel, Girard, Jonathan, Todd. "Hoplites Arms and Armor". Retrieved 22 April 2013.
- ↑ Sage, Michael M (1996). Warfare in Ancient Greece: A Sourcebook. London, GBR: Routledge. p. 281.
- Bibliography
- Crowley, Jason. The Psychology of the Athenian Hoplite: The Culture of Combat in Classical Athens. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2012 (hardcover, ISBN 1-107-02061-1).
- Goldsworthy, A. K. "The Othismos, Myths and Heresies: The Nature of Hoplite Battle", War in History, Vol. 4, Issue 1. (1997), pp. 1–26.
- Hanson, Victor Davis. The Western Way of War: Infantry Battle in Classical Greece. New York: Alfred A. Knopf, 1989 (hardcover, ISBN 0-394-57188-6); New York: Oxford University Press (USA), 1990 (paperback, ISBN 0-19-506588-3); Berkeley: University of California Press, 2000 (paperback, ISBN 0-520-21911-2).
- Hanson, Victor Davis. Warfare and Agriculture in Classical Greece (Biblioteca Di Studi Antichi; 40). Berkeley: University of California Press, 1998 (hardcover, ISBN 0-520-21025-5; paperback, ISBN 0-520-21596-6).
- Hanson, Victor Davis. The Other Greeks: The Family Farm and the Agrarian Roots of Western Civilization. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1999 (paperback, ISBN 0-520-20935-4).
- Krentz, Peter. "Fighting by the Rules: The Invention of the Hoplite Agôn", Hesperia, Vol. 71, No. 1. (2002), pp. 23–39.
- O'Connell, Robert L., Soul of the Sword. Simon and Schuster, 2002, ISBN 0-684-84407-9.
- Roisman, Joseph, and translated by J. C. Yardley, Ancient Greece from Homer to Alexander (Blackwell Publishing Ltd, 2011) ISBN 1-4051-2776-7
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hoplites. |
- Association of Greek Hoplites Historic Studies Club "KORYVANTES"
- Perseus Digital Library database:
- Sparta Pages – web page on Sparta and the Hoplite.
- The Phalanx Hoplite
- Classical Greek Shield Patterns
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||