Histrionicotoxin

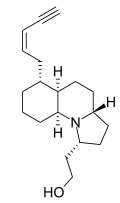
Histrionicotoxins are a group of related toxins found in the skin of poison frogs from the Dendrobatidae family, notably Oophaga histrionica.[1] It is likely that as with other poison frog alkaloids, histrionicotoxins are not manufactured by the amphibians, but absorbed from insects in their diet and stored in glands in their skin.[2]
Histrionicotoxins are less powerful toxins compared to many of the other alkaloids found in poison frogs; however, they have an unusual chemical structure and a distinct mechanism of action, acting as a potent non-competitive antagonists of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, binding to a regulatory site on the delta subunit of the ion channel complex.[3][4] They also have some affinity for sodium and potassium channels, although they are much less potent for these targets.[5] The synthesis of histrionicotoxins and various homologues is synthetically challenging and has been the subject of many different attempts.[6]
See also
References
- ↑ Daly, JW (1982). "Alkaloids of neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae)". Fortschritte der Chemie organischer Naturstoffe. Progress in the chemistry of organic natural products. Progres dans la chimie des substances organiques naturelles 41: 205–340. PMID 7049875.
- ↑ Daly, JW (1995). "The chemistry of poisons in amphibian skin". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92 (1): 9–13. Bibcode:1995PNAS...92....9D. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.1.9. PMC 42808. PMID 7816854.
- ↑ Oberthür, W; Muhn, P; Baumann, H; Lottspeich, F; Wittmann-Liebold, B; Hucho, F (1986). "The reaction site of a non-competitive antagonist in the delta-subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor". The EMBO Journal 5 (8): 1815–9. PMC 1167045. PMID 3758027.
- ↑ Johnson, DA; Nuss, JM (1994). "The histrionicotoxin-sensitive ethidium binding site is located outside of the transmembrane domain of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: a fluorescence study". Biochemistry 33 (31): 9070–7. doi:10.1021/bi00197a007. PMID 8049208.
- ↑ Lovenberg, T; Daly, JW (1986). "Histrionicotoxins: effects on binding of radioligands for sodium, potassium, and calcium channels in brain membranes". Neurochemical research 11 (11): 1609–21. doi:10.1007/BF00965779. PMID 2446155.
- ↑ Sinclair, A; Stockman, RA (2007). "Thirty-five years of synthetic studies directed towards the histrionicotoxin family of alkaloids". Natural product reports 24 (2): 298–326. doi:10.1039/b604203c. PMID 17389999.
External links
- Frog Poison – Histrionicotoxin at The Periodic Table of Videos (University of Nottingham)
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||