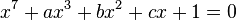Hilbert's thirteenth problem
Hilbert's thirteenth problem is one of the 23 Hilbert problems set out in a celebrated list compiled in 1900 by David Hilbert. It entails proving whether or not a solution exists for all 7th-degree equations using functions of two arguments. It was first presented in the context of nomography, and in particular "nomographic construction" — a process whereby a function of several variables is constructed using functions of two variables. The actual question is more easily posed however in terms of continuous functions. Hilbert considered the general seventh-degree equation
and asked whether its solution, x, a function of the three variables a, b and c, can be expressed using a finite number of two-variable functions.
A more general question is: can every continuous function of three variables be expressed as a composition of finitely many continuous functions of two variables? The affirmative answer to this general question was given in 1957 by Vladimir Arnold, then only nineteen years old and a student of Andrey Kolmogorov. Kolmogorov had shown in the previous year that any function of several variables can be constructed with a finite number of three-variable functions. Arnold then expanded on this work to show that only two-variable functions were in fact required, thus answering Hilbert's question.
Arnold later returned to the question, jointly with Goro Shimura (V. I. Arnold and G. Shimura, Superposition of algebraic functions (1976), in Mathematical Developments Arising From Hilbert's Problems).
References
- G. G. Lorentz, Approximation of Functions (1966), Ch. 11