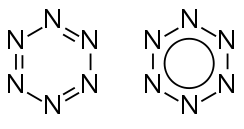
Hexazine
| Hexazine | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Systematic name Hexazine[1] | |
| Other names Hexaazabenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7616-35-5 |
| PubChem | 11966278 |
| ChemSpider | 10140271 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:36869 |
| Gmelin Reference | 1819 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | N6 |
| Molar mass | 84.04 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexazine (also known as hexaazabenzene) is a hypothetical allotrope of nitrogen composed of 6 nitrogen atoms arranged in a ring-like structure analogous to that of benzene. It would be the final member of the azabenzene (azine) series, in which all of the methine groups of the benzene molecule have been replaced with nitrogen atoms. The two last members of this series, hexazine and pentazine, have not been observed, although all other members of the azine series have (such as pyridine, pyrimidine, pyridazine, pyrazine, triazines, and tetrazines).
Stability
The hexazine molecule bears a structural similarity to the very stable benzene molecule. Like benzene, it has been calculated that hexazine is likely an aromatic molecule. Despite this, it has yet to be synthesized. In fact, it has been predicted computationally that the hexazine molecule is highly unstable. It has been suggested that this predicted instability is caused by the lone pairs on the nitrogen atoms, which may repel each other electrostatically and/or cause electron-donation to sigma antibonding orbitals.[2]
See also
- 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom:pyridines
- 6-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms: diazines
- 6-membered rings with three nitrogen atoms: triazines
- 6-membered rings with four nitrogen atoms: tetrazines
- Azide
- Octaazacubane (Nitrogen allotrope with formula N8)
- Pentazole
- Tetranitrogen (Nitrogen allotrope with formula N4)
References
- ↑ "Hexazine - PubChem Public Chemical Database". The PubChem Project. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information.
- ↑ J. Fabian and E. Lewars (2004). "Azabenzenes (azines) — The nitrogen derivatives of benzene with one to six N atoms: Stability, homodesmotic stabilization energy, electron distribution, and magnetic ring current; a computational study". Canadian Journal of Chemistry 82 (1): 50–69. doi:10.1139/v03-178.
- P. Saxe and H. F. Schaefer III (1983). "Cyclic D6h Hexaazabenzene-A Relative Minimum on the N6 Potential Energy Hypersurface?". Journal of the American Chemical Society 105 (7): 1760–1764. doi:10.1021/ja00345a010.
- H. Huber (1982). "Is Hexazine Stable?". Angewandte Chemie International Edition 21 (1): 64–65. doi:10.1002/anie.198200641.
- M. N. Glukhovtsev and P. von Ragué Schleyer (1992). "Structures, bonding and energies of N[6] isomers". Chemical Physics Letters 198 (6): 547–554. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(92)85029-A.
- T.-K. Ha, R. Cimiraglia and M.T. Nguyen (1981). "Can hexazine (N6) be stable?". Chemical Physics Letters 83 (2): 317–319. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(81)85471-1.