Hexamethylenetetramine
| Hexamethylenetetramine | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| IUPAC name 1,3,5,7-Tetraazatricyclo[3.3.1.13,7]decane | |
| Other names Hexamine; Methenamine; | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 100-97-0 |
| PubChem | 4101 |
| ChemSpider | 3959 |
| UNII | J50OIX95QV |
| EC number | 202-905-8 |
| KEGG | D00393 |
| MeSH | Methenamine |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:6824 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL1201270 |
| ATC code | J01 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C6H12N4 |
| Molar mass | 140.186 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.33 g/cm³ (at 20 °C) |
| Boiling point | 280 °C (sublimes) |
| Solubility in water | 85.3 g/100 mL |
| Acidity (pKa) | 4.89[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly flammable, harmful |
| Flash point | 250 °C; 482 °F; 523 K |
| Autoignition temperature | 410 °C; 770 °F; 683 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Hexamethylenetetramine is a heterocyclic organic compound with the formula (CH2)6N4. This white crystalline compound is highly soluble in water and polar organic solvents. It has a cage-like structure similar to adamantane. It is useful in the synthesis of other chemical compounds, e.g. plastics, pharmaceuticals, rubber additives. It sublimes in a vacuum at 280 °C.
The compound was discovered by Aleksandr Butlerov in 1859.[2][3][4]
Synthesis, structure, reactivity
Hexamethylenetetramine is prepared by the reaction of formaldehyde and ammonia.[5] The reaction can be conducted in gas-phase and in solution.
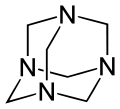
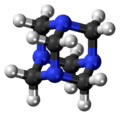
The molecule has a symmetric tetrahedral cage-like structure, similar to adamantane, whose four "corners" are nitrogen atoms and "edges" are methylene bridges. Although the molecular shape defines a cage, no void space is available at the interior for binding other atoms or molecules, unlike crown ethers or larger cryptand structures.
The molecule behaves like an amine base, undergoing protonation and N-alkylation.
When reacted with nitric acid, hexamine forms the explosive RDX (known chemically as cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine).[citation needed] It can also be reacted with hydrogen peroxide, with a catalyst of citric acid or dilute sulfuric acid, to form hexamethylene triperoxide diamine.[citation needed]
Applications
The main use of hexamethylenetetramine is in the production of powdery or liquid preparations of phenolic resins and phenolic resin moulding compounds, where it is added as a hardening component. These products are used as binders, e.g. in brake and clutch linings, abrasive products, non-woven textiles, formed parts produced by moulding processes, and fireproof materials.
Medical uses
As the mandelic acid salt (generic methenamine mandelate, USP[6]) it is used for the treatment of urinary tract infection. It decomposes at an acidic pH to form formaldehyde and ammonia, and the formaldehyde is bactericidal; the mandelic acid adds to this effect. Urinary acidity is typically ensured by co-administering vitamin C (ascorbic acid) or ammonium chloride. Its use had temporarily been reduced in the late 1990s, due to adverse effects, particularly chemically-induced hemorrhagic cystitis in overdose,[7] but its use has now been re-approved because of the prevalence of antibiotic resistance to more commonly used drugs. This drug is particularly suitable for long-term prophylactic treatment of urinary tract infection, because bacteria do not develop resistance to formaldehyde. It should not be used in the presence of renal insufficiency.[medical citation needed]
Histological stains
Methenamine silver stains are used for staining in histology, including the following types:
- Grocott's methenamine silver stain, used widely as a screen for fungal organisms.
- Jones' stain, a methenamine silver-Periodic acid-Schiff that stains for basement membrane, availing to view the "spiked" Glomerular basement membrane associated with membranous glomerulonephritis.
Solid fuel
Together with 1,3,5-trioxane, hexamethylenetetramine is a component of hexamine fuel tablets used by campers, hobbyists, the military and relief organizations for heating camping food or military rations. It burns smokelessly, has a high energy density (30.0 MJ/kg), does not liquify while burning, and leaves no ashes.
Standardized 0.149 g tablets of methenamine (hexamine) are used by fire-protection laboratories as a clean and reproducible fire source to test the flammability of carpets and rugs.[8]
Food additive
Hexamethylene tetramine or hexamine is also used as a food additive as a preservative (INS number 239). It is approved for usage for this purpose in the EU,[9] where it is listed under E number E239, however it is not approved in the USA, Australia, or New Zealand.[10]
Reagent in organic chemistry
Hexamethylenetetramine is a versatile reagent in organic synthesis. It is used in the Duff reaction (formylation of arenes),[11] the Sommelet reaction (converting benzyl halides to aldehydes),[12] and in the Delepine reaction (synthesis of amines from alkyl halides).[13]
Explosives
Hexamethylenetetramine is the base component to produce RDX and consequently, C-4[5] as well as Hexogen, Oktogen, Dinitrohexamine and HMTD.
Producers
Since 1990 the number of European producers has been declining. The French SNPE factory closed in 1990; in 1993, the production of hexamethylenetetramine in Leuna, Germany ceased; in 1996, the Italian facility of Agrolinz closed down; in 2001, the UK producer Borden closed; in 2006, production at Chemko, Slovak Republic, was closed. Remaining producers include INEOS in Germany, Caldic in the Netherlands, and Hexion in Italy. In the US, Eli Lilly and Company stopped producing methenamine tablets in 2002.[8] In Australia, Hexamine Tablets for fuel are made by Thales Australia Ltd.
References
- ↑ Cooney, Aidan P.; Crampton, Michael R.; Golding, Peter (1986). "The acid-base behaviour of hexamine and its N-acetyl derivatives". Journal of the Chemical Society, Perkin Transactions 2 (6): 835. doi:10.1039/P29860000835.
- ↑ A. Butlerow (1859) "Ueber einige Derivate des Jodmethylens" (On some derivatives of methylene iodide), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, vol . 111, pages 242 - 252. In this paper, Butlerov discovered formaldehyde, which he called "Dioxymethylen" (methylene dioxide) [page 247] because his empirical formula for it was incorrect (C4H4O4). On pages 249-250, he reacted formaldehyde with ammonia gas, creating hexamine.
- ↑ See also: A. Butlerow (1860) "Ueber ein neues Methylenderivat" (On a new methylene derivative), Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie, vol. 115, no. 3, pages 322-327.
- ↑ http://library.istu.edu/hoe/books/ruschem.pdf
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Karsten Eller, Erhard Henkes, Roland Rossbacher, Hartmut Höke "Amines, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH Verlag, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001
- ↑ "Methenamine mandelate, USP". Edenbridge Pharmaceuticals.
- ↑ Ross Jr, RR; Conway, GF (1970). "Hemorrhagic cystitis following accidental overdose of methenamine mandelate". American journal of diseases of children (1960) 119 (1): 86–7. PMID 5410299.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Alan H. Schoen (2004), Re: Equialence of methenamine Tablets Standard for Flammability of Carpets and Rugs. U.S. Consumer product Safety Commission, Washington, DC, July 29, 2004. Many other countries who still produce this include Russia, Saudi Arabia, China and Australia.
- ↑ UK Food Standards Agency: "Current EU approved additives and their E Numbers". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- ↑ Australia New Zealand Food Standards Code"Standard 1.2.4 - Labelling of ingredients". Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- ↑ A. T. Bottini, Vasu Dev, and Jane Klinck (1963), "Syringic Aldehyde", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 4: 866
- ↑ Kenneth B. Wiberg (1963), "2-Thiophenaldehyde", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 3: 811
- ↑ A. T. Bottini, Vasu Dev, and Jane Klinck (1963), "2-Bromoallylamine", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 5: 121
| |||||