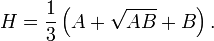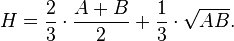Heronian mean
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, the Heronian mean H of two non-negative real numbers A and B is given by the formula:
It is named after Hero of Alexandria, and used in finding the volume of a frustum of a pyramid or cone. The volume is equal to the product of the height of the frustum and the Heronian mean of the areas of the opposing parallel faces.
The Heronian mean of the numbers A and B is a weighted mean of their arithmetic and geometric means:
References
- Bullen, P.S. (2003), Handbook of Means and Their Inequalities, Mathematics and Its Applications (2nd ed.), Berlin, New York: Springer Science+Business Media, ISBN 978-1-4020-1522-9
- Eves, Howard Whitley (1980), Great Moments in Mathematics (Before 1650), Mathematical Association of America, ISBN 978-0-88385-310-8
External links
- Mean-Trapezoids Geometric comparison of some mathematical means
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.