Heinkel He 219
The Heinkel He 219 Uhu ("Eagle-Owl") was a night fighter that served with the German Luftwaffe in the later stages of World War II. A relatively sophisticated design, the He 219 possessed a variety of innovations, including an advanced VHF-band intercept radar. It was also the first operational military aircraft in the world to be equipped with ejection seats, and the first operational German World War II-era aircraft with tricycle landing gear. Had the Uhu been available in quantity, it might have had a significant effect on the strategic night bombing offensive of the Royal Air Force; but only 294 of all models were built by the end of the war, and these saw only limited service.[1]
Design and development
Development and production of the He 219 was protracted and tortuous, due to political rivalries between Josef Kammhuber, commander of the German night fighter forces, Ernst Heinkel, the manufacturer, and Erhard Milch, responsible for aircraft construction in the Reichsluftfahrtministerium (RLM — the German Aviation Ministry). The aircraft was also complicated and expensive to build; these factors further limited the number of aircraft produced.
When engineer Robert Lusser returned to Heinkel from Messerschmitt, he began work on a new high-speed bomber project called P.1055. This was an advanced design with a pressurized cockpit, twin ejection seats (the first to be planned for use in any combat aircraft), tricycle landing gear (featuring a nose gear that rotated its main strut through 90° during retraction to fit flat within the forward fuselage), and remotely controlled defensive gun turrets similar to those used by the Messerschmitt Me 210. Power was to be provided by two DB 610 "coupled" engines then under development, weighing on the order of about 1-1/2 tonnes apiece, producing (2,200 kW/2,950 hp) each, delivering excellent performance with a top speed of approximately 750 km/h (470 mph) and a 4,000 km (2,500 mi) range with a 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) bomb load.
The RLM rejected the design in August 1940 as too complex and risky. Lusser quickly offered four versions of the fighter with various wingspans and engine choices in order to balance the performance and risk. At the same time, he offered the P.1056 dedicated night fighter with four 20 mm cannons in the wings and fuselage. The RLM rejected all of these on the same grounds in 1941. Heinkel was furious and fired Lusser on the spot.
About the same time as Lusser was designing the P.1055, Kammhuber had started looking for a dedicated aircraft for his rapidly growing night fighter force. Heinkel quickly re-designed the P.1055 for this role as the P.1060. This design was similar in layout, but somewhat smaller and powered by two of the largest displacement (at 44.5 litres/2,700 cu. in.) liquid-cooled aviation engines placed in mass production in Germany, the DB 603 inverted V12 engine, using annular radiators similar to the ones on the Jumo 211-powered Junkers Ju 88A but considerably more streamlined in appearance. This engine was not known for its altitude performance, which was a problem for Heinkel's short-winged design, but Daimler offered a new "G" version then under development to address the issue. Heinkel was sure he had a winner and sent the design off to the RLM in January 1942 while he funded the first prototype himself. Nevertheless, the RLM again rejected the He 219 in favour of new Ju 88- and Me 210-based designs.
Construction of the prototype started in February 1942 but suffered a serious setback in March, when Daimler said that the DB 603G engine would not be ready in time. Instead, they would deliver a 603A engine with a new gear ratio to the propellers, with the new designation DB 603C, and offering the choice of using four-blade propellers. Even these took until August to arrive, and the prototype did not fly until 6 November 1942.[2] When Kammhuber saw the prototype on the 19th, he was so impressed he immediately ordered it into production over Milch's objections. Milch — who had rejected the He 219 in January — was enraged.
Stability problems with the aircraft were noted, but Heinkel overcame these by offering a cash prize to engineers who could fix them. Further changes were made to the armament during the prototype He 219V-series airframes' development: the dorsal rear defensive guns — mounted atop the fuselage, and firing directly rearward from a fixed, internally mounted, rear-facing dorsal "step" position at a point just aft of the wings' trailing edge — were removed due to their ineffectiveness. The forward-firing armament was increased to two 20 mm cannons in the wing roots and four more guns mounted in the ventral tray, which had originally ended in a rearwards-facing "step" for a fixed mount for rearwards ventral defensive fire almost directly under the deleted rear dorsal "step", but was also deleted for similar reasons. The A-0 model also featured a bulletproof shield that could be raised in the front interior cockpit, hiding the entire bottom portion of windscreen, providing temporary pilot protection, leaving a slot by which the gunsight could be aimed at a bomber and fired. Production prototypes were then ordered as the He 219 A-0 and quickly progressed to the point where V7, V8 and V9 were handed over to operational units in June 1943 for testing. The earlier prototypes, fitted out with four-blade propellers for at least the first five prototypes for their DB 603 engines (also used on the Fw 190C prototypes, with the same DB 603 engine) and the quartet of Matratze 32-dipole radar antennas for an early UHF-band Lichtenstein radar installation also possessed cockpit canopies that did not smoothly taper on their upper line going from the rear of the pilot's canopy hatch aftwards, but ended in a nearly semi-spherical enclosure forming the rear of the canopy glazing.
Milch repeatedly tried to have the He 219 program killed and in the process, Kammhuber was removed from office. Production ceased for a time but was restarted because the new Junkers Ju 388s were taking too long to get into service.
Operational history

The He 219 had an auspicious combat debut. On the night of 11–12 June 1943, Werner Streib flew the V9 and shot down five bombers between 01:05 and 02:22 hours,[3] before crashing on landing.[4] Claims have been made that, "In the next 10 days the three Heinkel He 219A-0 pre-production aircraft would shoot down a total of 20 RAF aircraft, including six of the previously "untouchable" de Havilland Mosquito fighter-bombers. Greatly encouraged, Kammhuber continued to press for immediate production."[5] No record of corresponding Mosquito losses or any documentary evidence exists, however, to suggest that He 219 pilots actually made claims for six Mosquitos during this time.[6][7][8][9]
The first major production series was the He 219 A-0, although initially the preproduction series, it matured into a long running production series due to numerous changes incorporated into the design, along with the cancellation of several planned variants. Production problems as a result of Allied bombing in March[10] meant the A-0 did not reach Luftwaffe units until October 1943. The A-0 were usually armed with two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots and up to four 20 mm or 30 mm cannon in a ventral weapons bay. The first 10 to 15 aircraft were delivered with the 490 MHz UHF-band FuG 212 "Lichtenstein" C-1 radar set, complete with its 4 x 8-dipole element Matratze antenna array. A total of 104 He 219 A-0s were built until the summer of 1944, the majority of them at EHW or Heinkel-Süd in Wien-Schwechat.
The first planned version to reach production was the He 219 A-2 model, which had longer engine nacelles containing extra fuel tanks, 1670 PS DB 603AA engines with higher critical altitude and often also two 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 108 cannons as an offensive Schräge Musik upward-firing system in the rear fuselage. With the Schräge Musik system installed, the ventral weapons bay was only capable of holding two cannon due to space limitations.[11] The A-2 featured an updated, 90 MHz VHF-band Telefunken FuG 220 Lichtenstein SN-2 radar system, complete with their larger, high-drag 4 x 2-dipole element Hirschgeweih aerials. It initially had less range than the C-1 radar, but improved accuracy and resolution and was also less vulnerable to chaff jamming through the late summer of 1944. A total of 85 He 219 A-2s were built until November 1944, the majority of them at EHR or Heinkel-Nord in Rostock-Marienehe (today's Rostock-Schmarl).
The He 219 was a capable fighter aircraft, allowing the pilots a large degree of autonomy. Ground control simply sent the aircraft into the right area and then the pilots took over and hunted down the bombers on their own; the SN-2 radar's 4 km (3 mi) range was greater than the distance between the bombers. While the performance of the A-2 was not extraordinary — approximately 580 km/h (360 mph) speed — it was enough of an advance over the Messerschmitt Bf 110Gs and Dornier Do 217Ns to allow the aircraft to chase several bombers in one sortie.
In order to combat the Mosquito, the He 219 had all excess weight removed. With some weapon and radio systems deleted, the aircraft was able to attain a speed of 650 km/h (400 mph). This version was given the designation A-6. None of these were produced but weight saving measures could be done at the unit level.
The last major production version was the A-7 with improved DB 603E engines. The A-7 was typically outfitted with two 20 mm MG 151/20 cannon in the wing roots (inboard of the propeller arcs), two 20 mm MG 151/20 in the ventral weapons bay, and two 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 108s as Schräge Musik. The production was to start in November/December 1944 with 210 aircraft ordered. The number produced is not exactly known as the original documents have either been lost or contained no subversion number.
The follow-on series was to be the He 219B fitted with the new, but very troublesome, 1,864 kW (2,500 hp) Junkers Jumo 222A/B 24-cylinder engines - a multibank inline engine, with six rows of cylinder blocks having four cylinders each - which would have allowed the He 219 to reach 700 km/h (440 mph), each of which were almost the same displacement and only very slightly heavier apiece as compared to the Double Wasp radial engines in the American P-61 purpose-built night fighter. The He 219B's wing was also to have had an increased wing span of 22.06 m (72.38 ft) for better high altitude performance. The Jumo 222s did not reach production status however, with just under 300 examples built in at least two differing displacement sizes, and only a test machine or two were ever fitted for the engines; some additional airframes with the enlarged wing were slated to fly with high-altitude versions of the DB 603. But again, only one or two test machines ever flew in that configuration.
A further adaptation would have been the He 219C, also intended to use the big wing and Jumo 222 powerplants as well as an all-new fuselage of 17.15 m (56.27 ft), with a complete three-man Ju 388J cockpit section forward, converted to accept the He 219A's standard nose gear layout (the Ju 388 itself used the Ju 88's conventional gear) and a manned power tail turret aft, possibly the Hecklafette "quadmount" four-gun turret intended for later He 177A versions. Day bomber and night fighter versions were proposed and metal was cut for the project but, without the >1,500-kW output Jumo 222 engines getting out of their strictly experimental status, they never flew.
Paper projects include the very-high-altitude He 219E with a vastly increased wingspan of 28.5 m (93.5 ft) and DB 614 engines, which were apparently an uprated DB 603G capable of 1,491 kW (2,000 hp).
A more reasonable project was the Hütter Hü 211, a design by Wolfgang Hütter that took a standard He 219 fuselage and tail and added a long-span, high aspect ratio wing of 24.55 m (80.54 ft) to create a fast, high altitude interceptor. Since this design was also meant to be powered by the ill-fated Jumo 222 it never flew, although work continued on two sets of wings until they were destroyed by Allied bombing.
The He 219 was the only piston-engined night fighter capable of facing the British Mosquito on equal terms, given its speed, manoeuvrability and firepower,[12] but it never played a significant role in the war because the industry failed to make it available in sufficient numbers.[10]
Variants
- He 219 A-0
- Initially used for pre-production aircraft but became first major production version with 1,750 PS DB 603A engines, 104 built as of 30 November 1944,[13]
- He 219 A-1
- Proposed reconnaissance-bomber aircraft; project abandoned
- He 219 A-2
- Similar to A-0 but extended engine nacelles with additional fuel tanks, 1,670 PS DB 603AA engines, 85 built as of 30 November 1944 [13]
- He 219 A-5
- Planned three-seat night fighter, only some prototypes known to have been built from A-2 airframes
- He 219 A-6
- Planned Mosquito-hunter, stripped-down version of the He 219 A-2, armed with four 20 mm MG 151/20s
- He 219 A-7
- Improved night fighter version, powered by two 1,800 PS DB 603E engines, 210 ordered as of 30 November 1944 [13]
- He 219 D-1
- He 219 A-7 airframes adapted for Jumo 213E engines, five known to be delivered in 1945
- He 319
- An unbuilt multi-role aircraft project entirely unrelated to the He 219; only having the number sequence in common
- He 419
- Various derived projects culminating in He 419 B-1/R1, six of which were flown; use of the He 319 tail, very long-span wing of 59 square metres (635 sq ft), two 20 mm MG 151/20 in the wings and four 30 mm MK 108 in ventral housing. Speed of 422 mph (679 km/h) to 44,619 ft (13,600 m).
- Letov LB-79
- Two He219s built from recovered components in Czechoslovakia during 1950, with one being used as a jet engine test-bed.
Survivors


When the war had ended in Europe, the U.S. Army Air Forces Intelligence Service, as part of "Operation Lusty" (LUftwaffe Secret TechnologY), took control of three He 219s at the Grove base of the 1st Night Fighter Wing (Nachtjagdgeschwader 1) in Jutland, Denmark starting on 16 June 1945. These aircraft were made flight-worthy by "Watson's Whizzers" and flown to Cherbourg, France. He 219 A-2 Werknummer 290202 was shipped to the United States with 21 other captured German aircraft on board the British escort carrier HMS Reaper, and was reassembled at Ford Field, Newark, New Jersey.
Werknummer 290202 was given the foreign equipment number FE-614, and later T2-614. The aircraft was flown to Freeman Field, Indiana for flight testing along with a second of the three He 219s: a He 219 A-5 prototype, Werknummer 290060 and given the foreign equipment number FE-612. The fate of Werknummer 290060 is unknown. Following testing, He 219 A-2 Werknummer 290202 was then moved to Orchard Place Airport in Park Ridge, Illinois in 1946. It was stored in a vacant aircraft factory and then transferred to the Smithsonian's National Air Museum on 3 January 1949. Finally, the He 219 was crated and shipped to the Smithsonian's Silver Hill, Maryland storage facility in early 1955.
He 219 A-2 Werknummer 290202 is undergoing restoration in the collection of the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum in Washington, D.C., USA. Recently the fuselage has been put on display at the Steven F. Udvar-Hazy Center by Dulles Airport, however, the wings are still being restored at the Paul Garber Facility in Silver Hill, Maryland. As of 2012, the completely restored fuselage and tail surfaces, along with the aircraft's partially restored DB 603 engines and nacelles (possibly as Kraftei unitized powerplant installations) displayed nearby, can be seen displayed near the museum's Dornier Do 335 and Arado Ar 234, aircraft that accompanied it across the Atlantic over 60 years ago.[14]
In April 2012, a previously unknown He 219 was salvaged from the sea bed, 100 meters from the beach, north of Hirtshals, Denmark. The remains are in several pieces, but will undergo restoration and eventually be displayed at Aalborg, Denmark. As of late April 2012, no information was available as to the sub-model or Werknummer of the aircraft.[15]
Operators
- Czechoslovakian Air Force (Postwar)
Specifications (He 219 A-7)
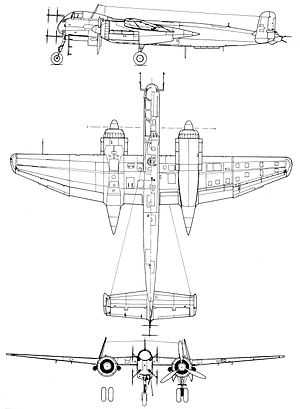
Data from Jane's Fighting Aircraft of World War II[16]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 15.5 m (51 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 18.5 m (60 ft 8 in)
- Height: 4.4 m (14 ft 5 in)
- Wing area: 44.4 m² (478 ft²)
- Max. takeoff weight: 13,580 kg (29,900 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Daimler-Benz DB 603E liquid-cooled inverted V12 engine, 1,800 PS (1,324 kW) each
- Propellers: VDM three blade constant speed airscrew
Performance
- Maximum speed: 616 km/h (333 kn, 385 mph)
- Range: 1,540 km (831 nmi, 960 mi)
- Ferry range: 2,148 km(1,160 nmi, 1,335 mi)
- Service ceiling: 9,300 m (30,500 ft)
- Guns:
- up to 4 × 20 mm MG 151 cannons in a detachable fairing under the fuselage, 300 rpg
- 2 × 20 mm MG 151s in wing roots, 300 rpg
- 2 × 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 108 cannons, Schräge Musik (oriented 65° above horizontal), 100 rpg
See also
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Bristol Beaufighter NF
- de Havilland Mosquito NF
- Focke-Wulf Ta 154
- Messerschmitt Bf 110
- Nakajima J1N Gekko
- Northrop P-61 Black Widow
- Related lists
References
Notes
- ↑ Boyne 1997, p. 330.
- ↑ Green and Swanborough 1989, p. 12.
- ↑ Chef für Ausz. und Dizsiplin Luftwaffen-Personalamt L.P. [A] V Films, Film C. 2027/I", Bundesarchiv/Militaerarchiv, Freiburg.
- ↑ Smith and Kay 1972, p. 298.
- ↑ "Air International Magazine", Volume 9, No. 1, July 1975, p. 24, see also Wings of the Luftwaffe, Airlife, 1987.
- ↑ Chorley 1997
- ↑ Chorley 2004
- ↑ Franks 2000
- ↑ Abschüsse auf He 219. Mitteilung 1/44 TAD/Se, dated 25.7.44, detailing all claims made on the He 219 to 17.7.44 List is reproduced with additions to November 1944 in Joachim Dressel and Manfred Griehl, "Heinkel He-219 Uhu"
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Greenhous 1994, p. 705. I
- ↑ He 219 A-0 aircraft manual, section 8A Beiheft 1 Schrägbewaffnung, October 1944.
- ↑ Kay and Smith 2002, p. 154.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 "BA/MA RL 3/1024 Flugzeug-Programm 227 Ausgabe 1, 9." Military archive Freiburg, January 1945.
- ↑ "Heinkel He 219 A-2/R4 Uhu (Eagle Owl)." Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. Retrieved: 25 April 2012.
- ↑ Christensen, Abildgaard. "Sjældent fly til Aalborg" (in Danish). tv2nord, 24 April 2012.
- ↑ Bridgeman 1946
Bibliography
- Boyne, Walter J. Clash of Wings. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1994. ISBN 0-684-83915-6.
- Bridgeman, Leonard (editor). “Heinkel He 219.” Jane’s Fighting Aircraft of World War II. London: Studio, 1946. ISBN 1-85170-493-0.
- Chorley, W.R. Royal Air Force Bomber Command Losses of the Second World War, Volume 5, 1944: Amendments and Additions. London: Ian Allan Publishing, 1997. ISBN 978-0-904597-91-2.
- Chorley, W.R. Royal Air Force Bomber Command Losses of the Second World War, Volume 6, 1945: Amendments and additions. London: Ian Allan Publishing, 2004. ISBN 978-0-904597-92-9.
- Franks, Norman L.R. Royal Air Force Fighter Command Losses of the Second World War: Volume 3. Operational Losses: Aircraft and Crews 1944-1945 (Incorporating Air Defence Great Britain and 2nd TAF): 1944-1945. Hersham, Surrey, UK: Midland Publishing, 2000. ISBN 978-1-85780-093-7.
- Green, William. Warplanes of the Third Reich. London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Ltd., Fourth edition 1979, First edition 1970. ISBN 0-356-02382-6.
- Green, William and Gordon Swanborough. "Heinkel's Nocturnal Predator... The He 219". Air Enthusiast, Issue Forty, September–December 1989, pp. 8–19, 70–72. Bromley, Kent: Tri-Service Press.
- Greenhous, Brereton. The Crucible of War: 1939-1945. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 1994. ISBN 0-8020-0574-8.
- Kay, Anthony and John Richard Smith. German Aircraft of the Second World War: Including Helicopters and Missiles (Putnam's History of Aircraft). London: Putnam, 2002. ISBN 0-85177-920-4.
- Nowarra, Heinz J. Heinkel He 219 "Uhu". Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Inc., 1989. ISBN 0-88740-188-0.
- Remp, Roland. Heinkel He 219: An Illustrated History Of Germany's Premier Nightfighter. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing Inc., 2007. ISBN 0-7643-1229-4.
- Smith, J.R. and Antony L. Kay. German Aircraft of the Second World War. London: Putnam, 1972. ISBN 978-0-370-00024-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Heinkel He 219. |
- "Tour the Last Remaining Heinkel He 219": Heinkel 219 A-0, FE 614, before its completed fuselage restoration to display condition-article's date is 1997
- He 219A-0 Pilot's Manual - in German
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||