Halogen lamp




A halogen lamp, also known as a tungsten halogen, quartz-halogen or quartz iodine lamp, is an incandescent lamp that has a small amount of a halogen such as iodine or bromine added. The combination of the halogen gas and the tungsten filament produces a halogen cycle chemical reaction which redeposits evaporated tungsten back onto the filament, increasing its life and maintaining the clarity of the envelope. Because of this, a halogen lamp can be operated at a higher temperature than a standard gas-filled lamp of similar power and operating life, producing light of a higher luminous efficacy and color temperature. The small size of halogen lamps permits their use in compact optical systems for projectors and illumination.
History
A carbon filament lamp using chlorine to prevent darkening of the envelope was patented[1] in 1882, and chlorine-filled "NoVak" lamps were marketed in 1892.[2] The use of iodine was proposed in a 1933 patent,[3] which also described the cyclic redeposition of tungsten back onto the filament. In 1959, General Electric patented[3] a practical lamp using iodine.[4]
Halogen cycle
In ordinary incandescent lamps, evaporated tungsten mostly deposits onto the inner surface of the bulb. The halogen sets up a reversible chemical reaction cycle with the tungsten evaporated from the filament. The halogen cycle keeps the bulb clean and the light output remains almost constant throughout life. At moderate temperatures the halogen reacts with the evaporating tungsten, the halide formed being moved around in the inert gas filling. At some time it will reach higher temperature regions, where it dissociates, releasing tungsten and freeing the halogen to repeat the process. The overall bulb envelope temperature must be higher than in conventional incandescent lamps for the reaction to work.
The bulb must be made of fused silica (quartz) or a high-melting-point glass (such as aluminosilicate glass). Since quartz is very strong, the gas pressure can be higher,[5] which reduces the rate of evaporation of the filament, permitting it to run a higher temperature (and so luminous efficacy) for the same average life. The tungsten released in hotter regions does not generally redeposit where it came from, so the hotter parts of the filament eventually thin out and fail.
Quartz iodine lamps, using elemental iodine, were the first commercial halogen lamps launched by GE in 1959.[6][7] Quite soon, bromine was found to have advantages, but was not used in elemental form. Certain hydrocarbon bromine compounds gave good results.[8][9] Regeneration of the filament is also possible with fluorine, but its chemical reactivity is so great that other parts of the lamp are attacked.[8][10] The halogen is normally mixed with a noble gas, often krypton or xenon.[11] The first lamps used only tungsten for filament supports, but some designs use molybdenum — an example being the molybdenum shield in the H4 twin filament headlight for the European Asymmetric Passing Beam.
High temperature filaments emit some energy in the UV region. Small amounts of other elements can be mixed into the quartz, so that the doped quartz (or selective optical coating) blocks harmful UV radiation. Hard glass blocks UV and has been used extensively for the bulbs of car headlights.[12] Alternatively, the halogen lamp can be mounted inside an outer bulb, similar to an ordinary incandescent lamp, which also reduces the risks from the high bulb temperature. Undoped quartz halogen lamps are used in some scientific, medical and dental instruments as a UV-B source.
For a fixed power and life, the luminous efficacy of all incandescent lamps is greatest at a particular design voltage. Halogen lamps made for 12 to 24 volt operation have good light outputs, and the very compact filaments are particularly beneficial for optical control (see picture). The range of MR-16 (50 mm diameter) reflector lamps of 20 W to 50 W were originally conceived for the projection of 8 mm film, but are now widely used for display lighting and in the home. More recently, wider beam versions are available designed for direct use on supply voltages of 120 or 230 V.
Effect of voltage on performance
Tungsten halogen lamps behave in a similar manner to other incandescent lamps when run on a different voltage. However the light output is reported as proportional to  , and the luminous efficacy proportional to
, and the luminous efficacy proportional to  .[13] The normal relationship regarding the lifetime is that it is proportional to
.[13] The normal relationship regarding the lifetime is that it is proportional to 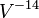 . For example, a bulb operated at 5% higher than its design voltage would produce about 15% more light, and the luminous efficacy would be about 6.5% higher, but would be expected to have only half the rated life.
. For example, a bulb operated at 5% higher than its design voltage would produce about 15% more light, and the luminous efficacy would be about 6.5% higher, but would be expected to have only half the rated life.
Halogen lamps are manufactured with enough halogen to match the rate of tungsten evaporation at their design voltage. Increasing the applied voltage increases the rate of evaporation, so at some point there may be insufficient halogen and the lamp goes black. Over-voltage operation is not generally recommended. With a reduced voltage the evaporation is lower and there may be too much halogen, which can lead to abnormal failure. At much lower voltages, the bulb temperature may be too low to support the halogen cycle, but by this time the evaporation rate is too low for the bulb to blacken significantly. There are many situations where halogen lamps are dimmed successfully. However, lamp life may not be extended as much as predicted. The life span on dimming depends on lamp construction, the halogen additive used and whether dimming is normally expected for this type.
Spectrum
Like all incandescent light bulbs, a halogen lamp produces a continuous spectrum of light, from near ultraviolet to deep into the infrared.[14] Since the lamp filament can operate at a higher temperature than a non-halogen lamp, the spectrum is shifted toward blue, producing light with a higher effective color temperature.
Safety
Halogen lamps get hotter than regular incandescent lamps because the heat is concentrated on a smaller envelope surface, and because the surface is closer to the filament. This high temperature is essential to their operation. Because the halogen lamp operates at very high temperatures, it can pose fire and burn hazards. In Australia, numerous house fires each year are attributed to ceiling-mounted halogen downlights.[15][16] The Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services recommends that home owners consider instead using compact fluorescent lamps or light emitting diode lamps because they produce less heat.[17] Some safety codes now require halogen bulbs to be protected by a grid or grille, especially for high power (1–2 kW) bulbs used in theatre, or by the glass and metal housing of the fixture to prevent ignition of draperies or flammable objects in contact with the lamp.
To reduce unintentional ultraviolet (UV) exposure, and to contain hot bulb fragments in the event of explosive bulb failure, general-purpose lamps usually have a UV-absorbing glass filter over or around the bulb. Alternatively, lamp bulbs may be doped or coated to filter out the UV radiation. With adequate filtering, a halogen lamp exposes users to less UV than a standard incandescent lamp producing the same effective level of illumination without filtering.
Handling precautions

Any surface contamination, notably the oil from human fingertips, can damage the quartz envelope when it is heated. Contaminants will create a hot spot on the bulb surface when the lamp is turned on. This extreme, localized heat causes the quartz to change from its vitreous form into a weaker, crystalline form that leaks gas. This weakening may also cause the bulb to form a bubble, weakening it and leading to its explosion.[18] Consequently, manufacturers recommend that quartz lamps should be handled without touching the clear quartz, either by using a clean paper towel or carefully holding the porcelain base. If the quartz is contaminated in any way, it must be thoroughly cleaned with alcohol and dried before use.
Applications

Halogen headlamps are used in many automobiles. Halogen floodlights for outdoor lighting systems as well as for watercraft are also manufactured for commercial and recreational use. They are now also used in desktop lamps.
Tungsten-halogen lamps are frequently used as a near-infrared light source in Infrared spectroscopy.
Halogen lamps were used on the Times Square Ball from 1999 to 2006. However, from 2007 onwards, the halogen lamps were replaced with LED lights. The year numerals that light up when the ball reaches the bottom used halogen lighting for the last time for the 2009 ball drop. It was announced on the Times Square website that the year numerals for the 2010 ball drop would use LED lights.[19]
Automotive

Tungsten-halogen lamps have commonly used as the light sources in automobile headlamps, but are increasing being replaced by Xenon and LED lights.
Architectural
- Linear in various sizes and power
- R7S: linear halogen lamp measuring 118mm or 78mm. Also known as a double ended halogen lamp.
- Dichroic and plain reflector spots. Higher efficiency versions using infrared reflective coating (IRC) technology are 40% more efficient than standard low voltage halogen lamps
Cooking
Halogen lamps are used as the heating element in a halogen oven.
Home use
Halogen multifaceted reflector bulbs are widely available. The most common format is MR16, which is available in 10–50 W power ratings (150–800 lumens).[20] Low voltage lamps use the MR16 and similar bi-pin bases, whereas mains voltage lamps use the same caps as normal mains tungsten filament lamps, or a special GU10/GZ10 base. The GU10/GZ10 bases are shaped to prevent dichroic reflector lamps being used in luminaires intended for aluminised reflector lamps, which could cause overheating of the fitting. Higher efficiency LED versions of all of these lamps are now available, but these have widely varying light output and quality.
With the help of some companies such as Philips and Osram Sylvania, halogen bulbs have been made for standard household fittings, and can replace banned incandescent light bulbs of low luminous efficacy.[21][22][23]
Tubular lamps with electrical contacts at each end are now being used in standalone lamps and household fixtures. These come in various lengths and wattages (50–300 W).
Stage lighting
Tungsten halogen lamps are used in the majority of theatrical and studio (film and television) fixtures, including Ellipsoidal Reflector Spotlights and Fresnels. PAR Cans are also predominately tungsten halogen.
Specialized
Projection lamps are used in motion-picture and slide projectors for homes and small office or school use. The compact size of the halogen lamp permits a reasonable size for portable projectors, although heat-absorbing filters must be placed between the lamp and the film to prevent melting. Halogen lamps are sometimes used for inspection lights and microscope stage illuminators. Halogen lamps were used for early flat-screen LCD backlighting, but other types of lamps are now used.
Disposal
Halogen lamps do not contain any mercury. General Electric claims that none of the materials making up their halogen lamps would cause the lamps to be classified as hazardous waste.[24]
See also
- Bi-pin connector for base designations GY6.35, G8, etc.
- FEL lamp
- Lamp base for other bases
- List of light sources
References
- ↑ US 254780
- ↑ Harold Wallace A Different Kind of Chemistry: A History of Tungsten Halogen Lamps, IEEE Industry Applications Magazine Nov/Dec 2001, p. 11
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 US 2883571
- ↑ Raymond Kane, Heinz Sell Revolution in lamps: a chronicle of 50 years of progress (2nd ed.), The Fairmont Press, Inc. 2001 ISBN 0-88173-378-4 page 75
- ↑ Some lamps have as much as 15 times atmospheric pressure when cold, and some lamps increase pressure five-fold at operating temperature. Kane and Sell 2001, page 76–77
- ↑ Zubler and Mosby Illuminating Engineering 1959 54.734
- ↑ http://home.frognet/~ejcov/newhalogen.html
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Burgin and Edwards Lighting Research and Technology 1970 2.2. 95–108
- ↑ T'Jampens and van der Weijer Philips Technical Review 1966 27.173
- ↑ Schroder Philips Technical Review 1965 26.116
- ↑ Häussinger, Peter; Glatthaar, Reinhard; Rhode, Wilhelm; Kick, Helmut; Benkmann, Christian; Weber, Josef; Wunschel, Hans-Jörg; Stenke, Viktor; Leicht, Edith; Stenger, Hermann (2002). "Noble gases". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Wiley. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_485.
- ↑ Burgin Lighting Research and Technology 1984 16. 2 71
- ↑ Neumann Lichtechnik 1969 21 6 63A
- ↑ Tungsten-halogen lamp information at Karl Zeiss Online Campus site (accessed Nov. 2 2010)
- ↑ Thousands at risk from halogen-light death traps at The Sunday Age site (accessed 22 Dec. 2012)
- ↑ Halogen down light fire safety at Fire and Rescue NSW site (accessed 22 Dec. 2012)
- ↑ Downlights at Western Australia Department of Fire and Emergency Services site (accessed 22 Dec. 2012)
- ↑ Kremer, Jonathan Z."Types of Light Bulbs and Their Uses" Megavolt, section "Halogen", Accessed May 26, 2011.
- ↑ "Times Square Alliance - New Year's Eve - 2010 Widgets".
- ↑ "Replace Inefficient MR16 Halogen Lamps with LEDs". Maxim. September 25, 2007.
- ↑ http://www.consumersearch.com/light-bulbs/philips-halogena-energy-saver
- ↑ http://www.lighting.philips.com/us_en/products/halogena/index.php?main=us_en_consumer_lighting&parent=7593748565&id=us_en_products&lang=en
- ↑ http://www.sylvania.com/en-us/products/halogen/Pages/default.aspx
- ↑ http://www.geconsumerandindustrial.com/environmentalinfo/documents/msds/msds_quartzline_lamps.pdf General Electricl Lamp Material Information Sheet
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Halogen light bulbs. |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||