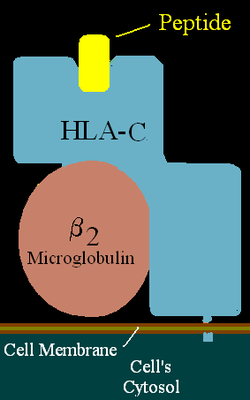
HLA-C
HLA-C belongs to the MHC (human = HLA) class I heavy chain receptors. The C receptor is a heterodimer consisting of a HLA-C mature gene product and β2-microglobulin. The mature C chain is anchored in the membrane. MHC Class I molecules, like HLA-C, are expressed in nearly all cells, and present small peptides to the immune system which surveys for non-self peptides.
HLA-C is a locus on chromosome 6, which encodes for a large number of HLA-C alleles that are Class-I MHC receptors. HLA-C, localized proximal to the HLA-B locus, is located on the distal end of the HLA region. Most HLA Cw:B haplotypes are in strong linkage disequilibrium and many are as ancient as the human species itself.
Disease Associations
By Serotype
Cw1: Multinodular goiters[1]
By Allele
Cw*16: B chronic lymphocytic leukemia[2]
Nomenclature
Cw*01
- Cw1 Serotype: Cw*0102 and Cw*0109
- Cw11 ?
- Cw*0104 to *0108
Cw*02
- Cw2 Serotype: Cw*0202 and *0208
- Cw*0203 to *0207, and 0209
Cw*03
- Cw9 Serotype: Cw*0303
- Cw10 Serotype: Cw*0302, *0304, and *0306
- Cw3 Serotype: Cw*0307
- Cw*0305 and 0308
Cw*04
- Cw4 Serotype: Cw*0401, *0407, and *0410
Cw*05
- Cw5 Serotype: Cw*0501 and *0502
- Cw*0503 to *506 and *0508 to *0510
Cw*06
- Cw6 Serotype: Cw*0602 and *0605
- Cw6*0603, *0604 and *0606 to *0611
- Cw7 Serotype: Cw*0701 to *0706, *0712, *0714, *0716
- Cw*0707 to *0711, *0713, *0715, and *0717 to *0729
Cw*08
- Cw8 Serotype: Cw*0801, *0802 and *0803
- Cw*805 to *0812
Cw*1202 to *1215
Cw*1402 to *1405
Cw*1501 to *1511
Cw*1601 to *1606
Cw*1701 to *1703
Cw*1801 and *1802
Common Haplotype
Cw4-B35 (Western Africa to Native Americans) Cw7-B7 (Western Eurasia, South Africa) Cw7-B8 (Western Eurasia) Cw1-B46 (China, Indochina) Cw5-B44 (Western Eurasia)
Interactions
HLA-C has been shown to interact with KIR2DL1.[3][4][5][6] and with various members of the Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor family, particularly the activating receptors LILRA1 and LILRA3 [7]
References
- ↑ Ríos A, Rodríguez J, Moya M, Galindo P, Canteras M, Alvarez M, Parrilla P (2006). "Associations of HLA-C alleles with multinodular goiters: study in a population from southeastern Spain.". Arch Surg 141 (2): 123–8. doi:10.1001/archsurg.141.2.123. PMID 16490887.
- ↑ Montes-Ares O, Moya-Quiles M, Montes-Casado M, Guerra-Pérez N, Campillo J, González C, López-Bermejo A, Tamayo M, Majado M, Parrado A, Muro M, Marín L, Alvarez-López M (2006). "Human leucocyte antigen-C in B chronic lymphocytic leukaemia.". Br J Haematol 135 (4): 517–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2006.06334.x. PMID 17054674.
- ↑ Boyson, Jonathan E; Erskine Robert, Whitman Mary C, Chiu Michael, Lau Julie M, Koopman Louise A, Valter Markus M, Angelisova Pavla, Horejsi Vaclav, Strominger Jack L (December 2002). "Disulfide bond-mediated dimerization of HLA-G on the cell surface". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (United States) 99 (25): 16180–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.212643199. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 138585. PMID 12454284.
- ↑ Baba, E; Erskine R, Boyson J E, Cohen G B, Davis D M, Malik P, Mandelboim O, Reyburn H T, Strominger J L (December 2000). "N-linked carbohydrate on human leukocyte antigen-C and recognition by natural killer cell inhibitory receptors". Hum. Immunol. (United States) 61 (12): 1202–18. doi:10.1016/S0198-8859(00)00184-1. ISSN 0198-8859. PMID 11163076.
- ↑ Valés-Gómez, M; Reyburn H T, Mandelboim M, Strominger J L (September 1998). "Kinetics of interaction of HLA-C ligands with natural killer cell inhibitory receptors". Immunity (UNITED STATES) 9 (3): 337–44. doi:10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80616-0. ISSN 1074-7613. PMID 9768753.
- ↑ Fan, Q R; Long E O, Wiley D C (May 2001). "Crystal structure of the human natural killer cell inhibitory receptor KIR2DL1-HLA-Cw4 complex". Nat. Immunol. (United States) 2 (5): 452–60. doi:10.1038/87766. ISSN 1529-2908. PMID 11323700.
- ↑ Jones DC, Kosmoliaptsis V, Apps R, Lapaque N, Smith I, Kono A, Chang C, Boyle LH, Taylor CJ, Trowsdale J, Allen RL (March 2011). "HLA class I allelic sequence and conformation regulate leukocyte Ig-like receptor binding". J Immunol 186 (5): 2990–7. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1003078. PMID 21270408.
Further reading
- Geyer M, Fackler OT, Peterlin BM (2001). "Structure--function relationships in HIV-1 Nef.". EMBO Rep. 2 (7): 580–5. doi:10.1093/embo-reports/kve141. PMC 1083955. PMID 11463741.
- Greenway AL, Holloway G, McPhee DA, et al. (2004). "HIV-1 Nef control of cell signalling molecules: multiple strategies to promote virus replication.". J. Biosci. 28 (3): 323–35. doi:10.1007/BF02970151. PMID 12734410.
- Bénichou S, Benmerah A (2003). "[The HIV nef and the Kaposi-sarcoma-associated virus K3/K5 proteins: "parasites"of the endocytosis pathway]". Med Sci (Paris) 19 (1): 100–6. doi:10.1051/medsci/2003191100. PMID 12836198.
- Leavitt SA, SchOn A, Klein JC, et al. (2004). "Interactions of HIV-1 proteins gp120 and Nef with cellular partners define a novel allosteric paradigm.". Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 5 (1): 1–8. doi:10.2174/1389203043486955. PMID 14965316.
- Tolstrup M, Ostergaard L, Laursen AL, et al. (2004). "HIV/SIV escape from immune surveillance: focus on Nef.". Curr. HIV Res. 2 (2): 141–51. doi:10.2174/1570162043484924. PMID 15078178.
- Joseph AM, Kumar M, Mitra D (2005). "Nef: "necessary and enforcing factor" in HIV infection.". Curr. HIV Res. 3 (1): 87–94. doi:10.2174/1570162052773013. PMID 15638726.
- Anderson JL, Hope TJ (2005). "HIV accessory proteins and surviving the host cell.". Current HIV/AIDS reports 1 (1): 47–53. doi:10.1007/s11904-004-0007-x. PMID 16091223.
| ||||||||||||
External links
| ||||||||||||||||||||||