HD 100546
| Observation data Epoch J2000.0[2] Equinox J2000.0[2] | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Musca |
| Right ascension | 11h 33m 25.441s[3] |
| Declination | −70° 11′ 41.24″[3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 6.698[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | B9Vne[2] |
| Details | |
| Age | >106[4] years |
| Astrometry | |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −38.93 ± 0.36[3] mas/yr Dec.: 0.29 ± 0.38[3] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 10.32 ± 0.43[3] mas |
| Distance | 320 ± 10 ly (97 ± 4 pc) |
| Other designations | |
| Extrasolar planet | List of extrasolar planets| | |
|---|---|---|
| Parent star | ||
| Star | HD 100546 | |
| Right ascension | (α) | 11h 33m 25.441s[3] |
| Declination | (δ) | −70° 11′ 41.24″[3] |
| Spectral type | B9Vne[2] | |
| Physical characteristics | ||
| Mass | (m) | ~20[5] MJ |
| Orbital elements | ||
| Semimajor axis | (a) | 6.5[5] AU |

HD 100546 is a star 320 LY from Earth.[3] It is orbited by an approximately 20 Mj planet at 6.5 AU,[5] although further examination of the disk profile indicate it might be a more massive object such as a brown dwarf or more than one planet.[6] The star is surrounded by a circumstellar disk from a distance of 0.2 to 4 AU, and again from 13 AU out to a few hundred AU, with evidence for a protoplanet forming at a distance of around 47 AU.[7]
Estimated to be around 10 million years old, it is at the upper age limit of the class of stars it belongs to—Herbig Ae/Be stars, and also the nearest example to our Solar System.[4]
Possible birth of new planet
In 2013, researchers reported that they had found what seems to be a planet in the process of being formed, embedded in the star's large disc of gas and dust. If confirmed, it would represent the first opportunity to study the early stages of planet formation observationally.[8]
HD 100546 b
Evidence for a planetary companion to HD 100546 was gathered using the UVES echelle spectrograph at the VLT in Chile.[5] This confirms other data indicating a planetary companion. The planet's size puts it near the border between a giant planet and a brown dwarf.[5]
Protoplanetary material
Spectroscopic analysis of mid-IR data taken from OSCIR on the 4 m Blanco Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory indicates the presence of a small particles (10 - 18 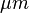 ) containing silicates.[4] The material is found at distances out to 17 AU away from the star and has a temperature of approximately 227 K.[4]
) containing silicates.[4] The material is found at distances out to 17 AU away from the star and has a temperature of approximately 227 K.[4]
References
- ↑ "The Birth of a Giant Planet?". ESO. Retrieved 3 April 2013.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "SIMBAD Object query: HD 100546".
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357.Vizier catalog entry
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 Grady, C. A. et al. "The Disk and Environment of the Herbig Be Star HD 100546". The Astronomical Journal 122 (6): 3396–3406. Bibcode:2001AJ....122.3396G. doi:10.1086/324447.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Acke, B.; van der Ancker; M. (November 2005). "Resolving the disk rotation of HD 97048 and HD 100546 in the [O I] 6300A line: evidence for a giant planet orbiting HD 100546". Astronomy and Astrophysics 449 (267): 267. arXiv:astro-ph/0512562. Bibcode:2006A&A...449..267A. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054330.
- ↑ Mulders, Gijs D.; Paardekooper, Sijme-Jan; Pani´c, Olja; Dominik, Carsten; van Boekel, Roy; Ratzka, Thorsten (2013). "Planet or Brown Dwarf? Inferring the Companion Mass in HD 100546 from the Wall Shape using Mid-Infrared Interferometry". Astronomy & Astrophysics 557A (A68): 10. arXiv:1306.4264. Bibcode:2013A&A...557A..68M.
- ↑ Quanz, Sasch P.; Amara, Adam; Meyer, Michael P.; Kenworthy, Matthew P.; Kasper, Markus; Girard, Julien H. (2013). "A young protoplanet candidate embedded in the circumstellar disk of HD 100546". Astrophysics Journal 766: L1–L6.
- ↑ "Is HD 100546 showing us the birth of a giant planet?". Science Codex. 2013-02-28. Retrieved 2013-03-01.
Further reading
- Butler, R. P. et al. (2006). "Catalog of Nearby Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal 646 (1): 505–522. arXiv:astro-ph/0607493. Bibcode:2006ApJ...646..505B. doi:10.1086/504701.
- Ecuvillon, A.; Israelian, G.; Pont, F.; Santos, N.; Mayor, M. (August 2006). "Kinematics of planet-host stars and their relation to dynamical streams in the solar neighbourhood". Astronomy and Astrophysics 461 (171): 171–182. arXiv:astro-ph/0608669. Bibcode:2007A&A...461..171E. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20065872.
- Jones, B.; Sleep, P.; Underwood, D. (June 2006). "Habitability of known exoplanetary systems based on measured stellar properties". The Astrophysical Journal 649 (1010): 1010–1019. arXiv:astro-ph/0603200. Bibcode:2006ApJ...649.1010J. doi:10.1086/506557.
- Mandell, A.; Raymond, S.; Sigurdsson, S, Avi M.; Raymond, Sean N.; Sigurdsson, Steinn. "Formation of Earth-like Planets During and After Giant Planet Migration". The Astrophysical Journal 660: 823–844. arXiv:astro-ph/0701048. Bibcode:2007ApJ...660..823M. doi:10.1086/512759.
- Marchi, S. (May 2007). "Extrasolar planet taxonomy: a new statistical approach". The Astrophysical Journal 666: 475–485. arXiv:0705.0910. Bibcode:2007ApJ...666..475M. doi:10.1086/519760.
- Hedrick, C. H.; Doering, R.; Lee, K.-G.; Sosey, M.; Meixner, M.; Ardila, D. (January 2006). "The Circumstellar Dust Disk of HD 100546". American Astronomical Society 37 (4).
External links
- Astronomy picture of the day - May 2, 2001
Coordinates: ![]() 11h 33m 25.4408s, −70° 11′ 41.239″
11h 33m 25.4408s, −70° 11′ 41.239″
| ||||||||||||||||||||