Gymnopilus luteofolius
| Gymnopilus luteofolius | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Gymnopilus luteofolius | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Basidiomycota |
| Class: | Agaricomycetes |
| Order: | Agaricales |
| Family: | Cortinariaceae |
| Genus: | Gymnopilus |
| Species: | G. luteofolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Gymnopilus luteofolius (Peck) Singer | |
| Gymnopilus luteofolius | |
|---|---|
|
| |
| gills on hymenium | |
| cap is convex | |
| hymenium is adnate | |
| stipe has a ring | |
| spore print is reddish-brown | |
| ecology is saprotrophic | |
| edibility: psychoactive | |
Gymnopilus luteofolius, also known as Yellow-Gilled Gymnopilus is a large and widely distributed mushroom which grows in dense clusters on dead hardwoods and conifers. It has a rusty orange spore print and a bitter taste. It contains the hallucinogen psilocybin.[1]
Systematics
Gymnopilus luteofolius was first described as Agaricus luteofolius by Charles Horton Peck in 1875. It was renamed Pholiota luteofolius by Pier Andrea Saccardo in 1887, and was given its current name by mycologist Rolf Singer in 1951.[2]
Description
The fruit bodies of Gymnopilus luteofolius have reddish to purplish to yellow caps 2 to 8 cm (0.8 to 3.1 in) in diameter, which often develop green stains. This cap surface is covered with fasciculate scales which start out purplish, soon fade to brick red, and finally fades to yellow as the mushroom matures. The context is reddish to light lavender, fading to yellowish as the mushroom matures. The gills have adnate attachment and start off yellow, turning rusty brown as the spores mature. The stipe is the same color as the cap, often dusted with rusty brown spores, fibrillose, measuring 3 - 9 by 3 - 10 mm thick, equal to enlarged near the base. The stipe often has greenish stains near the base. The taste is bitter.[3]
The spores are bright rusty brown in deposit, measuring (5.5) 6 - 8.5 x (3.5) 4 - 4.5 μm, ellipsoid to subellipsoid, inequilateral, roughened and dextrinoid, with no germ pore. The basidia measure 24 - 28 x 6 - 7 μm and are 4-spored. The basidioles are often brown. The pleurocystidia (cystidia on the gill face) measures 30 - 38 x 5 - 10 μm, hyaline, fusoid to subventricose. The cystidia on the gill edge (cheilocystidia) measures 23 - 28 x 4 - 7 μm, ventricose to flash shaped, often capitate. The lamellar trama is made up of parallel hyphae 5 - 18 μm across, frequently septate, with yellowish pigment which is dissolved by KOH. The pileus trama is interwoven, and the pileus cuticle has brown tufts of brown incrusted hyphae. The pileocystidia measures 44 - 53 (100) μm, and are clavate, cylindrical or ventricose terminal elements on the hyphae that forms the scales on the cap. Cystidia on the stem (caulocystidia) are 20 - 63 x 3 - 15 μm, clavate, ventricose or flask shaped. The gill trama and pileus trama are pale yellowish-brown in KOH and reddish brown in Melzer's_reagent. Clamp connections are present.[3]

-

Gymnopilus luteofolius
-

Gymnopilus luteofolius
-

Gymnopilus luteofolius
-
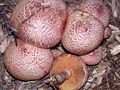
Gymnopilus luteofolius
-

Gymnopilus luteofolius
-

Gymnopilus luteofolius
See also
References
External links
- Gymnopilus luteofolius in Index Fungorum.
- Gymnopilus luteofolius at mushroomobserver.org
- Gymnopilus luteofolius occurrence map
- Guzmán-Dávalos, Laura; Mueller, Gregory M.; Cifuentes, Joaquín; Miller, Andrew N.; Santerre, Anne (Nov–Dec 2003). "Traditional infrageneric classification of Gymnopilus is not supported by ribosomal DNA sequence data". Mycologia 95 (6): 1204–1214. doi:10.2307/3761920. JSTOR 3761920. PMID 21149021.