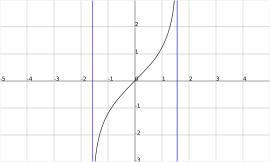
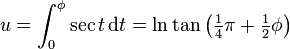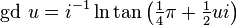Gudermannian function

The Gudermannian function, named after Christoph Gudermann (1798–1852), relates the circular functions and hyperbolic functions without using complex numbers.
It is defined by
Some related formulas don't quite work as definitions. For example, for real x,  . (See inverse trigonometric functions.)
. (See inverse trigonometric functions.)
The following identities hold:
The inverse Gudermannian function, which is defined on the interval −π/2 < x < π/2, is given by
(See inverse hyperbolic functions.)
The derivatives of the Gudermannian and its inverse are
The expression
defines the angle of parallelism function in hyperbolic geometry.
History
The function was introduced by Johann Heinrich Lambert in the 1760s at the same time as the hyperbolic functions. He called it the "transcendent angle," and it went by various names until 1862 when Arthur Cayley suggested it be given its current name as a tribute to Gudermann's work in the 1830s on the theory of special functions.[1] Gudermann had published articles in Crelle's Journal that were collected in Theorie der potenzial- oder cyklisch-hyperbolischen functionen (1833), a book which expounded sinh and cosh to a wide audience (under the guises of  and
and  ).
).
The notation gd first appears on page 19 of the Philosophical Magazine, vol. XXIV, where Cayley starts by calling gd. u the inverse of the integral of the secant function:
and then derives "the definition" of the transcendent:
observing immediately that it is a real function of u.
Applications
The Gudermannian of the latitudinal (due North/South) distance from the equator on a Mercator projection is the meridian arc length, i.e. actual latitude on the globe.
The Gudermannian appears in a non-periodic solution of the inverted pendulum.[2]
See also
- Hyperbolic secant distribution
- Mercator projection
- Tangent half-angle formula
- Tractrix
- Trigonometric identity
Notes
References
- CRC Handbook of Mathematical Sciences 5th ed. pp. 323–325.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Gudermannian", MathWorld.
![{\begin{aligned}{{\rm {{gd}}}}\,x&=\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {{\mathrm {d}}t}{\cosh t}}\\[8pt]&=\arcsin \left(\tanh x\right)={\mathrm {arctan}}\left(\sinh x\right)\\[8pt]&=2\arctan \left[\tanh \left({\tfrac 12}x\right)\right]=2\arctan(e^{x})-{\tfrac 12}\pi .\end{aligned}}\,\!](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/5/8/a/e/58ae130895fe967c5e6e89fe84774c35.png)

![{\begin{aligned}\operatorname {gd}^{{-1}}\,x&=\int _{0}^{x}{\frac {{\mathrm {d}}t}{\cos t}}\\[8pt]&=\ln \left|{\frac {1+\sin x}{\cos x}}\right|={\tfrac 12}\ln \left|{\frac {1+\sin x}{1-\sin x}}\right|\\[8pt]&=\ln \left|\tan x+\sec x\right|=\ln \left|\tan \left({\tfrac 14}\pi +{\tfrac 12}x\right)\right|\\[8pt]&={\mathrm {artanh}}\,(\sin x)={\mathrm {arsinh}}\,(\tan x).\end{aligned}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/a/7/f/ea7f0570c60a90fdc4718dbd1dedc903.png)