Grubel–Lloyd index
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
The Grubel–Lloyd index measures intra-industry trade of a particular product. It was introduced by Herb Grubel and Peter Lloyd in 1971.
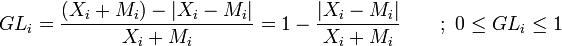
where Xi denotes the export, Mi the import of good i.
If GLi = 1, there is only intra-industry trade, no inter-industry trade. This means for example the Country in consideration Exports as same quantity of good i as much at it Imports. Conversely, if GLi = 0, there is no intra-industry trade, only inter-industry trade. This would mean that the Country in consideration only either Exports or only Imports good i.
References
- Grubel, Herbert G.; Lloyd, Peter J. (1971). "The Empirical Measurement of Intra-Industry Trade". Economic Record 47 (4): 494–517. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4932.1971.tb00772.x.
- Grubel, Herbert G.; Lloyd, Peter J. (1975). Intra-industry trade: the theory and measurement of international trade in differentiated products. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-470-33000-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.