Greater omentum
| Greater omentum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| The greater omentum and corresponding vasculature is visible covering the intestines (dissection image with liver held out of the way). | |
 | |
| Diagrams to illustrate two stages in the development of the digestive tube and its mesentery. The arrow indicates the entrance to the bursa omentalis. | |
| Latin | omentum majus |
| Gray's | subject #246 1157 |
| Precursor | Dorsal mesentery |
| MeSH | Omentum |
The greater omentum (also the great omentum, omentum majus, gastrocolic omentum, epiploon, or, especially in animals, caul) is a large apron-like fold of visceral peritoneum that hangs down from the stomach. It extends from the greater curvature of the stomach, passing in front of the small intestines and reflects on itself to ascend to the transverse colon before reaching to the posterior abdominal wall. The common anatomical term "epiploic" derives from "epiploon" from the Greek "epipleein" meaning to float or sail on, since the greater omentum appears to float on the surface of the intestines. It is the first structure observed when the abdominal cavity is opened anteriorly.[1]
Functions
The functions of the greater omentum are:
- Fat deposition, having varying amounts of adipose tissue[2]
- Immune contribution, having milky spots of macrophage collections[2]
- Infection and wound isolation; It may also physically limit the spread of intraperitoneal infections.[2] The greater omentum can often be found wrapped around areas of infection and trauma.
Structure
The greater omentum is the largest peritoneal fold. It consists of a double sheet of peritoneum, folded on itself so that it is made up of four layers.
The two layers which descend from the greater curvature of the stomach and commencement of the duodenum pass in front of the small intestines, sometimes as low down as the pelvis; they then turn upon themselves, and ascend again as far as the transverse colon, where they separate and enclose that part of the intestine.
These individual layers may be easily demonstrated in the young subject, but in the adult they are more or less inseparably blended.
The left border of the greater omentum is continuous with the gastrolienal ligament; its right border extends as far as the commencement of the duodenum.
The greater omentum is usually thin, presents a cribriform appearance, and always contains some adipose tissue, which in obese people accumulates in considerable quantity.
Subdivisions
The greater omentum is often defined to encompass a variety of structures. Most sources include the following two:[3][4]
- Gastrocolic ligament - to transverse colon (occasionally on its own considered synonymous with "greater omentum"[3])
- Gastrosplenic ligament - to spleen
The splenorenal ligament (from the left kidney to the spleen) is occasionally considered part of the greater omentum.[5][6]
Blood Supply
The right and left gastroepiploic vessels provide the sole blood supply to the greater omentum. Both are branches of the celiac trunk. The right gastroepiploic is a branch of the gastroduodenal artery, which is a branch of the common hepatic artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk. The left gastroepiploic artery is the largest branch of the splenic artery, which is a branch of the celiac trunk. The right and left gastroepiploic vessels anastomose within the two layers of the anterior greater omentum along the greater curvature of the stomach.
Development
The greater omentum develops from the dorsal mesentery that connects the stomach to the posterior abdominal wall. During stomach development, the stomach undergoes its first 90° rotation along the axis of the embryo, so that posterior structures are moved to the left and structures anterior to the stomach are shifted to the right. As a result, the dorsal mesentery folds over on itself, forming a pouch with its blind end on the left side of the embryo. A second approximately 90° rotation of the stomach, this time in the frontal plane, moves structures inferior if they were originally to the left of the stomach, and superior if they were originally to the stomach's right. Consequently, the blind-ended sac (also called the lesser sac) formed by the dorsal mesentery is brought inferiorly, where it assumes its final position as the greater omentum. It grows to the point that it covers the majority of the small and large intestine.
Omentectomy
Omentectomy refers to the surgical removal of the omentum, a relatively simple procedure with no major side effects, that is performed in cases where there may be spread of cancerous tissue into the omentum. Examples for this conditions are ovarian cancer and advanced or aggressive endometrial cancer as well as intestinal cancer. The procedure is generally done as an add-on when the primary lesion is removed.
Additional images
-

Vertical disposition of the peritoneum. Main cavity, red; omental bursa, blue. (Greater omentum labeled at left.)
-

The greater omentum is attached to the lower portion of the stomache (here the attachment is cut and the stomache is lifted up).
-
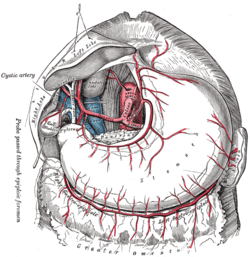
The celiac artery and its branches; the liver has been raised, and the lesser omentum and anterior layer of the greater omentum removed.
-
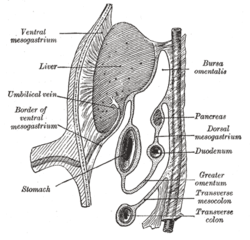
Schematic figure of the bursa omentalis, etc. Human embryo of eight weeks.
-

Diagrams to illustrate the development of the greater omentum and transverse mesocolon.
See also
References
- ↑ Drake, Richard L., et al. Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia, PA: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier, 2010. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 The omentum: A unique organ of exceptional versatility Indian Journal of Surgery, May 1, 2006, Alagumuthu, M; Das, Bhupati; Pattanayak, Siba; Rasananda, Mangual
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Dalley, Arthur F.; Moore, Keith L. (2006). Clinically oriented anatomy. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 237. ISBN 0-7817-3639-0.
- ↑ Anatomy Tables - Stomach & Spleen
- ↑ Kyung Won, PhD. Chung (2005). Gross Anatomy (Board Review). Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 205. ISBN 0-7817-5309-0.
- ↑ "Module - Peritoneal Cavity Development". Retrieved 2007-12-01.
External links
- SUNY Figs 37:03-07
- SUNY Figs 37:05-12
- 37:07-0100 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- Diagram at Tn.edu
- Photo of model at Waynesburg College digirep/greateromentum
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||