Greater fairy armadillo
| Greater fairy armadillo[1] | |
|---|---|
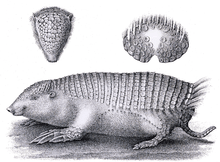 | |
| Holotype published by Hermann Burmeister | |
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Cingulata |
| Family: | Dasypodidae |
| Subfamily: | Euphractinae |
| Genus: | Calyptophractus Fitzinger, 1871 |
| Species: | C. retusus |
| Binomial name | |
| Calyptophractus retusus (Burmeister, 1863) | |
 | |
| Greater fairy armadillo range | |
The greater fairy armadillo (Calyptophractus retusus), also known as Burmeister's armadillo or the Chacoan fairy armadillo, is a species of armadillo in the family Dasypodidae. It is found in Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical dry shrubland and subtropical or tropical dry lowland grassland. It is threatened by habitat loss.[2] It is the only species in the genus Calyptophractus.[1]
Description
The greater fairy armadillo is a small species, growing to a length of from 140 to 175 millimetres (5.5 to 6.9 in) with a tail about 35 millimetres (1.4 in) long and weighing up to a kilogram (2.2 lb). Like other armadillos it has bands of armour on its dorsal (upper) surface but, in common with the pink fairy armadillo Chlamyphorus truncatus but unlike most other armadillos, these bands are fused to its pelvis and spine. They are soft in texture and are linked together with skin which gives flexibility to the body. They come to an abrupt end at the rear of the body. The ventral surface is clad in dense, woolly hair and there are some sparse hairs on the dorsal surface as well. The forefeet are scoop-shaped and have curved claws, and the hind feet have sharp claws for burrowing.[3]
Distribution and habitat
The greater fairy armadillo is native to the Gran Chaco region of northern Argentina, central and south-eastern Bolivia and western Paraguay. It inhabits dry grassy areas and is found only in places with light sandy soils in which it can burrow.[2]
Behaviour
The behaviour of the greater fairy armadillo has been little studied. It is an expert tunneller and spends most of its time in the shallow burrows that it excavates and is seldom seen above ground during the day. If disturbed, it can bury itself rapidly, and may block the entrance to its burrow with its hindermost plates. It has an omnivorous diet and feeds on worms, insect larvae, insects, snails, roots and seeds.[3]
The breeding habits of this species are largely unknown. After mating has taken place, the fertilised egg may remain in the uterus for several months before implantation takes place. The egg may then divide and up to four embryos may develop from a single fertilised egg. The gestation period is probably about four months as in other species of armadillo. The young are precocial and can move about within a few hours of birth. Their body armour does not harden until they are a few weeks old and they are weaned about the same time. They become sexually mature at between six months and one year.[3]
Status
At one time the greater fairy armadillo was listed by the IUCN as "Near Threatened" because of the loss of its habitat but in 2010, its status was changed to "Data Deficient" on the grounds that the animal was insufficiently known for it to be properly evaluated. Its distribution is quite patchy and in some areas it is persecuted due to a traditional belief that it is an animal of ill omen.[2] However, it is present in some nature reserves and national parks where it should be undisturbed by humans.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gardner, A. L. (2005). "Order Cingulata". In Wilson, D. E.; Reeder, D. M. Mammal Species of the World (3rd ed.). Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 95. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. OCLC 62265494.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Abba, A.M. & Superina, M. (2009). "Chlamyphorus retusus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2010.3. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 18 Sept. 2010.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Gonsiorowski, Elizabeth (2002). "Calyptophractus retusus: greater fairy armadillo". Animal Diversity Web. University of Michigan Museum of Zoology. Retrieved 2013-10-12.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
