Great icosahedron
| Great icosahedron | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Type | Kepler-Poinsot polyhedron |
| Stellation core | icosahedron |
| Elements | F = 20, E = 30 V = 12 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 20{3} |
| Schläfli symbol | {3,5/2} |
| Wythoff symbol | 5/2 | 2 3 |
| Coxeter-Dynkin | |
| Symmetry group | Ih, H3, [5,3], (*532) |
| References | U53, C69, W41 |
| Properties | Regular nonconvex deltahedron |
 (35)/2 (Vertex figure) |
 Great stellated dodecahedron (dual polyhedron) |
In geometry, the great icosahedron is one of four Kepler-Poinsot polyhedra (nonconvex regular polyhedra), with Schläfli symbol {3,5/2} and Coxeter-Dynkin diagram of ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . It is composed of 20 intersecting triangular faces, having five triangles meeting at each vertex in a pentagrammic sequence.
. It is composed of 20 intersecting triangular faces, having five triangles meeting at each vertex in a pentagrammic sequence.
Images
| Transparent model | Density | Stellation diagram | Spherical tiling |
|---|---|---|---|
 A transparent model of the great icosahedron (See also Animation) |
 It has a density of 7, as shown in this cross-section. |
It is a stellation of the icosahedron, counted by Wenninger as model [W41] and the 16th of 17 stellations of the icosahedron and 7th of 59 stellations by Coxeter. |
 This polyhedron represents a spherical tiling with a density of 7. (One spherical triangle face is shown above, outlined in blue, filled in yellow) |
As a snub
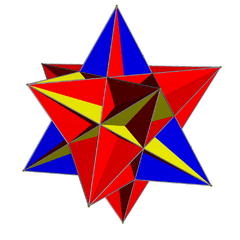
The great icosahedron can be constructed a uniform snub, with different colored faces and only tetrahedral symmetry: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . This construction can be called a retrosnub tetrahedron, similar to the snub tetrahedron symmetry of the icosahedron :
. This construction can be called a retrosnub tetrahedron, similar to the snub tetrahedron symmetry of the icosahedron : ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() . Tetrahedral symmetry icosahedra in general are called pseudo-icosahedra.
. Tetrahedral symmetry icosahedra in general are called pseudo-icosahedra.
Related polyhedra
It shares the same vertex arrangement as the regular convex icosahedron. It also shares the same edge arrangement as the small stellated dodecahedron.
A truncation operation, repeatedly applied to the great icosahedron, produces a sequence of uniform polyhedra. Truncating edges down to points produces the great icosidodecahedron as a rectified great icosahedron. The process completes as a birectification, reducing the original faces down to points, and producing the great stellated dodecahedron.
The truncated great stellated dodecahedron is a degenerate polyhedron, with 20 triangular faces from the truncated vertices, and 12 (hidden) pentagonal faces as truncations of the original pentagram faces, the latter forming a great dodecahedron inscribed within and sharing the edges of the icosahedron.
| Name | Great stellated dodecahedron |
Truncated great stellated dodecahedron | Great icosidodecahedron |
Truncated great icosahedron |
Great icosahedron |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram |
|||||
| Picture |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974). Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-09859-9.
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Du Val, P.; Flather, H. T.; Petrie, J. F. (1999). The fifty-nine icosahedra (3rd ed.). Tarquin. ISBN 978-1-899618-32-3. MR 676126 (1st Edn University of Toronto (1938))
External links
| |||||||||||||||||
| Notable stellations of the icosahedron | |||||||||
| Regular | Uniform duals | Regular compounds | Regular star | Others | |||||
| Icosahedron | Small triambic icosahedron | Medial triambic icosahedron | Great triambic icosahedron | Compound of five octahedra | Compound of five tetrahedra | Compound of ten tetrahedra | Great icosahedron | Excavated dodecahedron | Final stellation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 | ||
| The stellation process on the icosahedron creates a number of related polyhedra and compounds with icosahedral symmetry. | |||||||||