Gravitational plane wave
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In general relativity, a gravitational plane wave is a special class of a vacuum pp-wave spacetime, and may be defined in terms of Brinkmann coordinates by
![ds^{2}=[a(u)(x^{2}-y^{2})+2b(u)xy]du^{2}+2dudv+dx^{2}+dy^{2}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/0/2/1/4/0214d891c5c44fa514f768b37d515c0c.png)
Here, 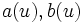 can be any smooth functions; they control the waveform of the two possible polarization modes of gravitational radiation. In this context, these two modes are usually called the plus mode and cross mode, respectively.
can be any smooth functions; they control the waveform of the two possible polarization modes of gravitational radiation. In this context, these two modes are usually called the plus mode and cross mode, respectively.
See also
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.