Goyder crater
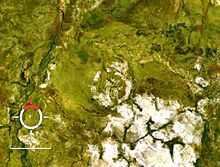
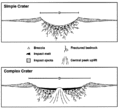
Goyder is an impact structure (or astrobleme), the eroded remnant of a former impact crater. It is situated in Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory, Australia, and was named after the nearby Goyder River. The impact occurred into Mesoproterozoic sedimentary rocks of the McArthur Basin. The deformed area is exposed at the surface and marked by a 3 km diameter ring of fractured and faulted sandstone, which is interpreted as the eroded relic of a central uplift (material that rebounded within the crater to once form a central peak); the original crater rim, long since removed by erosion, being estimated at approximately 9–12 km diameter.[1] Evidence for an impact origin includes the presence of shatter cones and shocked quartz in outcrops of deformed sandstone at the center of the site.[2][3]
The time of impact cannot be accurately constrained, however, it probably happened more recently than 1325 Ma (middle Mesoproterozoic), which is the age of igneous rocks that are inferred to have been uplifted by the impact based on aeromagnetic evidence, and significantly older than Cretaceous.[1] The site is very remote and difficult to access.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Haines PW (2005). "Impact cratering and distal ejecta: the Australian record". Australian Journal of Earth Sciences 52 (4-5): 481–507. Bibcode:2005AuJES..52..481H. doi:10.1080/08120090500170351. Abstract
- ↑ Haines PW (1996). "Goyder impact structure, Arnhem Land, Northern Territory". AGSO Journal of Australian Geology & Geophysics 16: 561–66.
- ↑ "Goyder". Earth Impact Database. University of New Brunswick. Retrieved 2009-08-13.
Coordinates: 13°28′34″S 135°02′35″E / 13.476°S 135.043°E