Gnetum
| Gnetum | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Gnetum gnemon | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Gnetophyta |
| Class: | Gnetopsida |
| Order: | Gnetales T.M. Fries |
| Family: | Gnetaceae Lindley |
| Genus: | Gnetum L. |
| Species | |
|
See text. | |
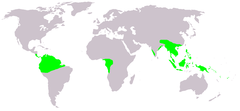 | |
| Distribution | |
Gnetum is a genus of about 30-35 species of gymnosperms, the sole genus in the family Gnetaceae and order Gnetales. They are tropical evergreen trees, shrubs and lianas. Unlike other gymnosperms they possess vessel elements in the xylem. Some species have been proposed to have been the first plants to be insect pollinated as their fossils occur in association with the extinct pollinating scorpionflies.[1] Molecular phylogenies based on nuclear and plastid sequences from most of the species indicate hybridization among some of the Southeast Asian species. Fossil-calibrated molecular-clocks suggest that the Gnetum lineages now found in Africa, South America, and Southeast Asia are the result of ancient long-distance dispersal across seawater.[2] [3]
Species
- Gnetum sect. Gnetum
- Gnetum subsect. Gnetum - 2 species of trees; southeast Asia
- Gnetum gnemon
- Gnetum costatum
- Gnetum subsect. Micrognemones - 2 species of lianas; tropical west Africa
- Gnetum africanum
- Gnetum buchholzianum
- Gnetum subsect. Araeognemones - 9 species of lianas; tropical South America and Central America - Ituá
- Gnetum amazonicum
- Gnetum camporum
- Gnetum leyboldii
- Gnetum nodiflorum
- Gnetum paniculatum
- Gnetum schwackeanum
- Gnetum urens
- Gnetum venosum
- Gnetum subsect. Gnetum - 2 species of trees; southeast Asia
- Gnetum sect. Scandentia - about 20 species of lianas; southern Asia
- Gnetum subsect. Stipitati
- Gnetum arboreum
- Gnetum contractum
- Gnetum gracilipes
- Gnetum latifolium
- Gnetum montanum
- Gnetum oblongum
- Gnetum pendulum
- Gnetum tenuifolium
- Gnetum ula
- Gnetum subsect. Sessiles
- Gnetum acutum
- Gnetum bosavicum
- Gnetum cleistostachyum
- Gnetum cuspidatum
- Gnetum diminutum
- Gnetum globosum
- Gnetum gnemonoides
- Gnetum hainanense
- Gnetum klossii
- Gnetum leptostachyum
- Gnetum loerzingii
- Gnetum luofuense
- Gnetum macrostachyum
- Gnetum microcarpum
- Gnetum neglectum
- Gnetum oxycarpum
- Gnetum parvifolium
- Gnetum raya
- Gnetum ridleyi
- Gnetum subsect. Stipitati
Uses
Many Gnetum species are edible, with the seeds being roasted, and the foliage used as a leaf vegetable. Some are also valued in herbal medicine.
References
- ↑ Ren D, Labandeira CC, Santiago-Blay JA, Rasnitsyn A, Shih CK, Bashkuev A, Logan MA, Hotton CL, Dilcher D. (2009). Probable Pollination Mode Before Angiosperms: Eurasian, Long-Proboscid Scorpionflies. Science, 326 (5954), 840-847. doi:10.1126/science.1178338
- ↑ Won H, Renner SS: The internal transcribed spacer of nuclear ribosomal DNA in the gymnosperm Gnetum. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 2005, 36:581-597. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2005.03.011
- ↑ Won, H., and S. S. Renner. 2006. Dating dispersal and radiation in the gymnosperm Gnetum (Gnetales) – clock calibration when outgroup relationships are uncertain. Systematic Biology 55(4): 610-622. doi:10.1080/10635150600812619
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gnetum. |