Glycol stearate
| Glycol stearate[1] | |
|---|---|
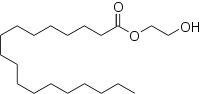 | |
| IUPAC name 2-Hydroxyethyl octadecanoate | |
| Other names Ethylene glycol monostearate; Glycol monostearate; Octadecanoic acid, 2-hydroxyethyl ester; 2-Hydroxyethyl stearate; Stearic acid, 2-hydroxyethyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 111-60-4 |
| ChemSpider | 23148 |
| UNII | 0324G66D0E |
| KEGG | D01542 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C20H40O3 |
| Molar mass | 328.53 g mol−1 |
| Melting point | 55-60 °C |
| Boiling point | >400 °C[2] |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R22 R36/37/38 R60 R63 |
| S-phrases | S24/25 S26 S27 S28 S36/37/39 S45 S53 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Glycol stearate (glycol monostearate or ethylene glycol monostearate) is an organic compound with the molecular formula C20H40O3. It is the ester of stearic acid and ethylene glycol. It is used as an ingredient in many types of personal care products and cosmetics including shampoos, hair conditioners, and skin lotions.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ Ethylene glycol monostearate at ChemicalBook.com
- ↑ Bradley, E. L.; Food Additives & Contaminants, Part A: Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure & Risk Assessment 2009, V26(4), P574-582
- ↑ Glycol stearate, Household Products Database, United States National Library of Medicine